MORAES, Franklin Marcelo de [1], FONTÃO, Henio [2], LOPES, Eloisa de Moura [3]
MORAES, Franklin Marcelo de; FONTÃO, Henio; LOPES, Eloisa de Moura. The variables representing the degree of Attractiveness of the Posts of a Fanpage. Multidisciplinary Core scientific journal of knowledge. 03 year, Ed. 05, vol. 01, pp. 89-106, may 2018. ISSN:2448-0959
Summary
Globalization and the advent of social networks of relationships are phenomena that are transforming the consumer profile. Social networks change the way people interact with each other, communicate and the way they perceive the reality to your surroundings. These consequences of this new scenario, in itself, represent a problem, by means of which justified the need to understand how social networks design new features to consumers, changing their expectations regarding their relations with the companies. The general objective of this research was to identify the variables that make up the degree of attractiveness of corporate social media postings on a not-for-profit company, in the Paraíba Valley. The inferential statistical method, by means of techniques of design of experiments. The object searched was a corporate fanpage used to disclosure of events and competitions of recreational games. The independent variables were socio-economic factors relating to the company's customers that are users of fanpage. The dependent variable corresponded to the level of attractiveness of the posts made up of parameters proposed by Furlan and marine (2014). The sample was limited to twenty one respondents and structured questionnaires used for data collection. The data were treated quantitatively, through statistical procedures inferenciais. It was used, within the Group of parametric statistical tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA) to observe whether there were, in the normal distribution of the variables, significant differences between the averages. The sample data processing was done through the MINITAB software, version 14. To ensure a degree of confidence of at least 95% the quality of responses, data analysis and interpretation of the results was made about the factors that showed significance levels less than or equal to 5%. The results showed that, overall, the variables were significant for four major responses linked to the degree of attractiveness of the posts. In other words, it shows that in the opinion of the respondents, regardless of their socioeconomic profiles, are perceived as added value to the fanpage, in particular, the following parameters: the quality of image resolution; the size of the images; the length of the videos and the frequency of posts. It is concluded that companies, especially small and micro, may use the method applied in this research, with low operating costs, to identify, on the basis of the profiles of its users, the best parameters of attractiveness of your media, targeting occasionally your Marketing projects.
Keywords: Fanpage, degree of Attractiveness, Customer Profile, design of experiments, Marketing.
1. Introduction
Since the emergence of the modern concept of Marketing in 1950, by Neil Borden, your function within the market structure has been transforming and changing the focus of activity, as well as the positioning of the companies within the market. These changes were (and are) due to the change in the profile of consumers and several are the factors that contribute to this, such as: the improvement in expectation and quality of life, the new offers of products and services, changes in economic, cultural and technological etc.
One of the factors that have influenced consumer behavior was the advent of computers and the emergence and availability of the internet on a large scale. New ways to connect and have access to information affect how people perceive and act in the world. It also influences the interaction with society and raises expectations as to how organizations should behave.
The popularity of social networks is a current and relevant factor that exerts influence in changing human behavior. Social networks are introducing new ways to communicate and keep in touch, new ways to mobilize information and select which are the most relevant information for each person.
On account of these changes, it is necessary for companies to pay attention to these new media, on how to exert influence on people's behavior and what are the new ways to relate so they can track and address the concerns of customers.
To this end, it is necessary that companies and institutions are inserted in the digital world, in particular in social networks. In these, not only are a vehicle for the dissemination of the brand, as well as a relationship tool and feedback. In this sense, the corporate fanpages can be more than vehicles of brand exposure, but also tools for promoting the values that the company has and interaction with other companies and individuals, however, there needs to be a plan for the creation and maintenance of this.
They need to be checked against the interests of customers, which values the company wants to relay, which wishes to have digital partners, frequency of posts etc. From these constituencies, it is proposed in this research, the application of design of experiments as a support for the decision-making process to identify the parameters that make up the degree of attractiveness of social media posts in a not-for-profit company, in the Paraíba Valley.
As the use of social networking as a Marketing strategy is recent, this study sought to validate the application of experiment Planning tool as a mechanism to assist in decision-making regarding the creation and maintenance of a social network, with the collection the crucial points that guided the construction of more relevant and attractive content to your users and followers. To this end, the tool along with a fanpage belonging to a non-profit located in the Paraíba Valley, which uses social networking to promote your services and events it promotes.
2. Theoretical Foundation
2.1. The evolution of Marketing
Kotler, Kartajaya and Setiawan (2010, p. 3) point out that Marketing has so far three stages: 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 Marketing.
1.0 marketing is just a function of support for the production, by developing a product (Product), determine your price (Price), carry out the promotion (Promotion) and set the distribution point (Place) in other words, only the sale of products for anyone who wants to buy them. At this stage, the products are relatively basic, designed to serve a mass market. The goal is to just standardize the product and manufactures it in large scale. Is product-focused marketing (KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 3 and 30).
The Marketing 2.0 realizes the value of the product is determined by the client and, therefore, the attention turns to this. As consumer tastes are varied, market segmentation and product development is directed to a target market. Kotler, Kartajaya and Setiawan (2010, p. 4) state that the objective is to achieve/meet the minds and hearts of consumers, but businesses assume that their customers are passive viewers of their marketing campaigns.
As well as the 2.0, 3.0 Marketing is oriented to the consumer. However, companies who practice it are more concerned with the contribution which they will give to the world through your Mission, vision and values. This stage believes that due to the conception of man is complete and complex consumer and their respective needs and hopes should never be neglected companies should not worry about the quality and your product and differential with the customer satisfaction, but also with the image and values that all (stakeholders) have her own. The company is concerned about your position in the world and the issues related to the environment, social and cultural issues and changes that occur when your around, especially those concerning consumer attitude and behavior (KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 4 and 5).
This new stage is born from the need of companies to cultivate their inner values and exteriorizá them. Increasingly, consumers are concerned about (in search of) solutions to satisfy your yearning to transform the world. They seek companies that match your wishes, both globally, as cultural and local.
In this scenario in which emerges the Marketing 3.0, the company sees himself exposed to the world, and can reach any individual and as belonging to a locality and responsible for this. Consumers are not satisfied anymore, only, only with the products they consume.
Scott McNealy (apud KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 7) States that since the beginning of the years 2000, the society is immersed in a new wave of technology that enables connectivity and interactivity between individuals and groups. According to him, is the era of participation, where people create and consume news, ideas and entertainment. All this provided by the emergence of social media.
Through these media consumers can influence each other through their opinions and experiences. The decisions that they take are not more unconscious, but, based on information obtained from their peers. Today there is more confidence among consumers than between these and the companies. Fact justified by thinking about how far the development of your marketing 2.0 stage.
As Kotler, Kartajaya and Setiawan (2010, p. 37), we must regain consumer confidence and it means rethinking the way companies are and are constituted.
To (re) gain customers and treat them as full human beings, companies need to understand and work three points considered crucial to Kotler: Co-creation, "Communization" (sic!) and personality development.
Co-creation, a term coined by Prahalad Krishnan (2008, p. 4) would make the consumer agent active in the participation and development of the product (and the company). The experience that each individual has on the use of a product/service is unique and should not be neglected. Are these singular experiences that give symbolic value for the right offered by the companies. Kotler, Kartajaya and Setiawan (2010, p. 37 and 38) state that companies must have a platform or environment where your clients can expose their experiences with the products/services, their feedback and thus able to develop them, in order to meet your their wishes.
"Communization" concerns the yearning of people to connect to each other. In Tribes, Seth Godin (apud KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 38) States that consumers want connect to each other and not to the companies and that, therefore, companies need to make room for this need and help your customers connect to each others.
Finally, the development of personality comes to the companies develop authentic DNA that differentiate from the others. Pine and Gilmore (apud KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 39), Authenticity, remember that every time you turn around immediately, but in the long run. However, when a consumer sees a brand, assesses immediately, if it is false or true (about their values).
Work these three points is move in the marketers, reaching your third stage. Is trying to understand the anxieties and desires of consumers, do what Stephen Covey (apud KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 40) calls "crack the code of the soul", or what Kotler calls address the spirit of the consumer.
Roberts (2004, p. 36), Lovemarks, indicates that the consumer profile has changed and reached to a level of production of goods and services that only make them well and with quality does not guarantee any company competitive advantage on the market. In other words, it is necessary to attract the consumer's attention, creating an emotional bond and establish a relationship that is long lasting. So this attention and relationship are perceived by the customer, companies to connect customers, from what is important to them (ROBERTS, 2004, p. 35 and 36).
Of this, realizes the importance of companies and brands are present in the virtual world and in particular in social media (social networks), since not only are they the cause of changes in people's behavior, as the buying decision, as also to interact among themselves and with their own companies. Every company, be it small, medium or large is present on the internet, either because it has channels of communication and interaction in this environment or because someone makes any reference to it, whether for or against.
For that to be effective the creation of a corporate profile in any social network it needs to be developed:
- Collaborative Marketing, allowing and encouraging everyone to opine about the brand, products and collaborate for the growth of the same and, in addition, to feel this fellow-agents;
- Cultural Marketing, that is, understand the community, social problems related to their business and do something to solve them;
- Spiritual Marketing, which is the value of the non-material aspects of life demonstrating the possibility of a better and lasting reality, i.e. provide meanings, directions to what people do and the company does (KOTLER, Kartajaya, Setiawan, 2010, p. 5-23).
But before you structure a corporate profile in any social network, it must be planned. It is necessary that any company that will create a corporate profile or a fanpage worry with content that will expose to its potential followers.
As advocated by Marketing 3.0, the posts need to contemplate the collaboration, culture and Spirit. Make use of emotions, search companies and profiles that meet the "DNA" of the company, with their values and responsibilities. Just as people do in their profiles, the contents need to be diverse. "Great ideas, like humor, come from the limits of the mind, of the extreme point. That's why the humor can break impasses in personal relationships as business us "(ROBERTS, 2004, p. 18).
Just like people, companies need to leave your mark on social networks and as a result, the people who come into contact with her. But, for such there needs to be a deployment planning, because unlike most eager customer profile, whatever is done needs to be thought out carefully. "Currently, a company with a significant number of followers or tanners on social networks is viewed positively by society in General, and particularly within business, enhance your market positioning" (marine, 2014, p. 3).
The main reason for a plan for the creation of a profile on a social network is to avoid making mistakes, is about that post, when posting and what public wants to achieve with the content. How each social media has its own characteristics and also a specific audience, it is necessary that companies meet these particularities so that you can then think about the content that will be used.
Once defined the social media they need to be defined the content that will be available. To this end it is necessary to create strategies that will be adopted, define the methodology and, finally, deploy what was thought.
As for the strategy, the company needs to answer clearly the following questions:
- What the company wants to communicate on the internet?
- Want to advertise only products, services or brand?
- You want to attract and acquire new customers?
- Want to transform the image and gain strength in the market?
- Has specific goals other than the above?
- What is the profile of the target audience?
- In that time they access the social network?
- What kind of content he likes best and usually share?
- Who will be responsible for fanpage, as for content creation, maintenance and interaction with the followers?
For the creation of the corporate profile and maintenance company must choose and define which tools will be used to check the effectiveness of fanpage. Here the proposal of Experiment planning techniques in order to identify with at least 95% confidence, the variables that make up the degree of attractiveness of the object of research posts.
2.2. Design of experiments
Ribeiro, Alves and Silva (2007, p. 37) claim that the tool design of experiments is an excellent option at orientation solutions for solving problems involving several variables or factors. George (2004) States that it was originally broadcast in the fields of medicine and engineering, especially in Lean Six Sigma projects, where the data collected will assist in decision-making on the part of managers. "The designs of experiments are tests conducted in a planned, in that the inputs (or factors or variables controlled) are changed so planned to assess your impact on an output (or reply)" (RAMOS, 2006, p. 234). This technique fits within the DMAIC cycle (Define, measure, analyze, Improve and Control), specifically, the Better; or in the DMEDI cycle (Define, Measure, Explore, Develop and Implement) the item Develop or PDCA cycle, in the parameters to "Check" the development process that has been or will be introduced.
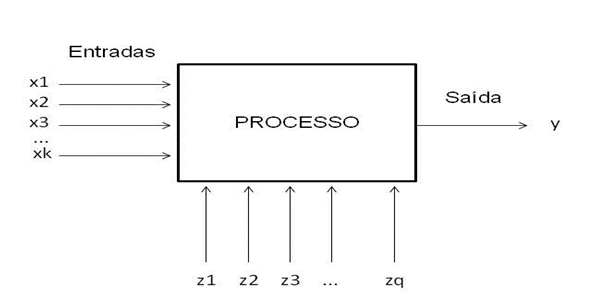
The design of experiments is a statistical survey which associates every variable you want to watch and their interactions and how they affect the process. Basically she is divided into three items that are singled out by Branches (2006, p. 235):
- Factors-are independent variables or process inputs (X's) that can be modified (controlled) in experiments and whose effect can be tested.
- Levels – is each of the possible values that a factor can assume in the experiment.
- Reply-is the dependent variable of the experiment or process output (Y), which will be used to evaluate the influence of the factors.
In other words, this is an equation of Y function, where are observed and analyzed which factors that will influence positively or negatively a given result you want to achieve.
Still, according to Branches (2006, p. 235-236), regardless of which is the application of the tool, it always aims to one or more of the following objectives:
- Determine what factors (X's) have greater influence on the answer (Y);
- Determine how to adjust the factors (X's) so the answer (Y) have the desired value (to verify the performance of a process);
- Determine how to adjust the factors (X's), so that the variance of the response (Y) is the smallest possible (for example, to increase the capacity of a process);
- Determine how to adjust the factors (X's) so that the effects of the uncontrolled variables (Z) on the answer (Y) are minimal (since the whole process is subject to several factors which do not have a control or which are not justified economically).
In Figure 1, you can see how, in short, the design of experiments.
For the realization of experiments, there are some basic steps that are crucial in order to avoid invalidating the results (RAMOS, 2006, p. 236-237). They are:
- Recognition and definition (outline) of the problem – the problem to be solved is very clear so that you can define which factors influence.
- The choice of factors and levels – factors are those "X's" that exert a major influence on the outcome and that in which levels of control they will be divided to be observed.
- Selection of the response variable.
- Choose the type of experiment – what resources will be used to collect and collate the data.
- Running the experiment (data acquisition).
- Data analysis – consists in determining which factors influence on response studied.
- Conclusions and recommendations – consists in the preparation of a report that demonstrates the results achieved.
In the case of construction of a corporate profile and on maintenance, it applies to associate profile of followers with the posted content, time of posting and the largest number of shares. Using the observed data, you can decide which content is most important, when they should be used and what degree of breadth of them. She is part of the standards improvement models used by the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC cycle: (Define, measure, analyze, Improve and Control) and the DMEDI cycle (Define, Measure, Explore, Develop and Implement) (FONTÃO; LEE, 2010, p. 149).
3. Methodological Procedures
For the realization of this work it was decided to use an exploratory research inductive in nature, because it provides a greater familiarity with the problem observed, making it more explicit (GERHARDT; SILVEIRA, (2009, p. 35) and allowing, by means of an analysis in particular, indicate the applicability of a tool for use by other companies, namely "walking for more comprehensive plans, going private findings to general laws and theories, in ascending connection "(LAKATOS; MARCONI, 1991).
For experimental research, have chosen a non-profit located in the Vale do Paraíba region that has a profile on a social network. The company was selected due to the fact the fanpage to promote events and competitions of recreational games which takes place within the establishment. In this case, an online questionnaire posted inside the fanpage, indicating that it was a collection of data with respect to the belief that his followers have the same, in order to improve it, thus serving better the expectations of users and providing content and formats that most coddle them.
The choice by the questionnaire format occurred due to your ability to provide data that allowed raise opinions, feelings of orderly and controlled by the browser, too, allowing a structured treatment of the data and meet the research objectives (GERHARDT; SILVEIRA, 2009, p. 69). The online format is justified by the need to collect data only from the people who have direct contact with the parsed object, ensuring assertiveness to information.
For the application of the tool, data collection and analysis, we used the experimental, statistical and inferential method. This part of the conceptual logic built into the method of design of experiments cited and reproduced in Figure 2-design of Methodological research Structure, where follow the following steps: choosing the object of research; selection and categorization of input variables and their respective levels of observation; selection of the dependent variable; selection of experimental (observational) array; definition of the universe and population; data collection: instruments and profile of informers; sampling and observation arrangement structured and quantitative data analysis and interpretation of results.
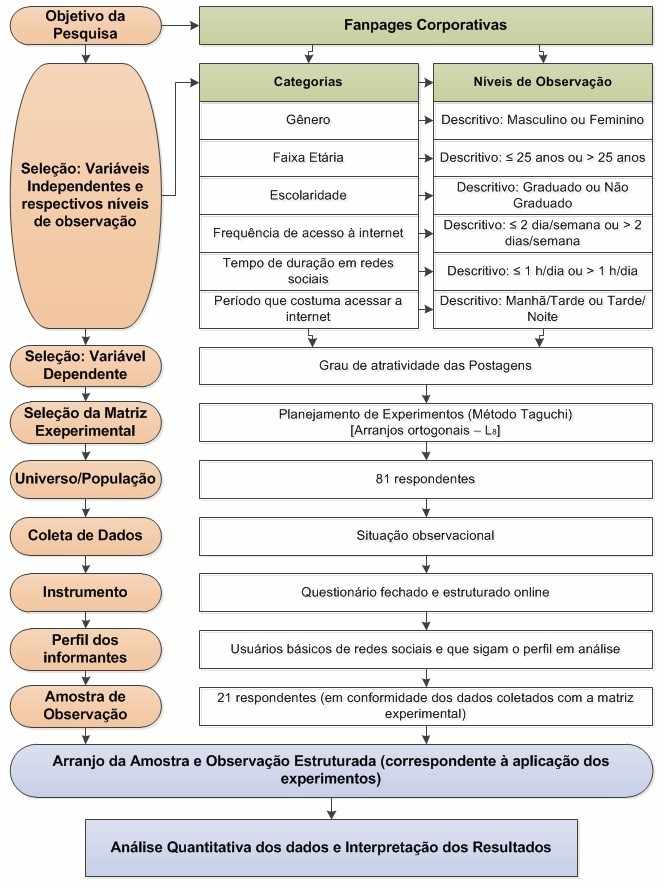
After determining the company settled the independent variables that characterize the profile of the followers of fanpage. These are economic oriented and take into account customers ' profile, and factors that influence the way the same understand social media. In this sense, took into consideration the elements observed by Furlan and marine (2014) on the alignment of the contents with the followers.
This analysis originated to the Table 1 contains seven variables. For seventh variable chose to be a ghost seen to make the calculation of the estimated experimental error to contrasts without previous variables were excluded from the analysis. In all the calculations the average of this variable will be deleted to perform the analysis of variance for medium.
Table 1: independent variables and levels of control (socio-economic).
| Independent Variables (Socio-Economic) | |||
| Low (1) | High (2) | ||
| The | Genus | Male | Female |
| (B) | Age Group | Up to 25 years | With more than 26 years |
| (C) | Schooling | Graduate | Don't graduate |
| (D) | Frequency of internet access | Up to two days/week | Three or more days/week |
| And | Time spent on social networks | Up to 1 hour/day | More than 1 hour/day |
| (F) | Period usually access | Morning/Afternoon | Afternoon/Evening |
| G | Ghost variable | – | – |
Each variable was divided into two levels of control to check how people with different profiles are realizing the fanpage and if the change between levels affect the dependent variable. The determination of low and high level was completely arbitrary as suggested by Ramos (2006, p. 238). The establishment of the levels is to assess the existence of factors that influence the answers and understand better the public. For the definition of the parameters observed and that defined the levels were based on the profile of the audience who frequents the place and of those who follow the company on social network analysis. Such analysis was made with the aid of a table of contrasts several factors as proposed by Ramos (2006, p. 242).
As the dependent variable was the analysis of the degree of Attractiveness of the posts. To measure this, established some parameters that are consistent with the possibility that Facebook allows you to do inside it. Took into consideration the exposed by Furlan and marine (2014, p. 54-55) as noted in table 2.
Table 2: dependent variables.
| Degree of Attractiveness of the posts. | ||
| Dimensions. | Response code (Rn). | Dependent Variables. |
| Texts. | R1. | Simplicity in the language used. |
| R2. | Size (length) of the texts. | |
| Images. | R3. | Quality (resolution) of the images. |
| R4. | Size of the images. | |
| R5. | List of texts with the images. | |
| Videos. | R6. | Quality (resolution) of the videos. |
| R7. | Size (length) of the videos. | |
| R8. | List of texts with the videos. | |
| Timetables. | R9. | The time at which the posts that they facilitate found. |
| R10. | Frequency of posts. | |
| Subjects. | R11. | Range of topics covered in the posts. |
The dependent variables were measured by means of the values assigned by informants to each of the listed indicators. The performance of the posts is represented by the answers to the questions of quality measured on a scale of one to ten, that is: (1 = Bad); (2 = very bad); (3 = bad); (4 = Bad); (5 = Partly reasonable); (6 = reasonable); (7 = Good); (8 = good); (9 = very good) and (10 = Great).
To justify the maximization of the process, according to the techniques of Taguchi, i.e. "greater value is synonymous with best result" (signal-to-noise ratio: S/N = -10 log (Σ1/y2)/n), the criteria for measuring the responses left the premise that companies have more attractive profiles feature positive responses to what is expected of fanpage that is the expansion of range and fixing of the brand. The statement of Pepper et al. (2012, p. 99), using the Taguchi method, since this allows you to analyze variables and their interaction from a small number of experiments.
For composition of the experimental array was selected the Taguchi method through its orthogonal arrays for matrix L8 (represented in table 3) which features eight experiments to seven factors or levels of control. The use of this array is justified by the applicability in find between the data observed a part probabilistic sampling.
Table 3: array of Taguchi L8.
| Array of Taguchi L8. | |||||||
| Observations. | The | (B) | (C) | (D) | And | (F) | G |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 8 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Source: adapted from Castro (2014).
For the sampling data analysis, the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The ANOVA is a statistical method used to interpret the experimental data in decision making and to test statistically the average of the results, in its different policies. That way, you can compare three or more factors and their interactions, and can be used in addition to Taguchi method, making use of the F-test, to check what are the really significant factors in the process (CORREIA; CARDOZA, 2011, p. 61).
The data were treated quantitatively, through statistical procedures inferenciais. Using, within the Group of parametric statistical tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA) to see if there are any, on normal distribution of variables, significant differences between the averages and, also, if the input variables exert significance on the output variables. The sample data processing was done by means of software MINITAB 14 version. To ensure a level of confidence of 95% of assertiveness to the quality of the responses, data analysis and interpretation of the results was made about the factors that have a significance level less than or equal to 5%.
4. Results
Twenty-one were selected respondents of the questionnaire according to the parameters established by the array of Taguchi L8. This selection corresponds to the socioeconomic profile is already predetermined. The Table 4 shows the average responses R1 to R11, which represent the arithmetic means between the replicatas in each observational situation.
The averages of the responses are the values measured response variables. Were they used for the calculations and quantitative analyses that generated the results that are the basis for the discussion and interpretation of the interactions between variables. It is through this analysis that those responsible for the maintenance of the fanpage shall take their decisions on what needs to be done and which factors influence, according to the opinion of the followers, the quality and attractiveness of fanpage.
Table 4: average responses (selected data for analysis).
| Dependent variables (measured). | |||||||||||
| Note (replicatas). | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 |
| 1 (3) | 8 | 7 | 7.3 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 7.3 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 6.7 |
| 2 (2) | 7 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6 |
| 3 (4) | 8.5 | 8 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 7.2 | 8.2 | 9.5 | 7.2 | 9 | 9 | 6.8 |
| 4 (3) | 7.3 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 9 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 7.3 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 6 |
| 5 (3) | 8.7 | 8.7 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 8.7 | 8 | 8.7 | 8.7 | 6.7 |
| 6 (1) | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 6 |
| 7 (2) | 8 | 8.5 | 8 | 8.5 | 8 | 8.5 | 9 | 8 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7 |
| 8 (3) | 8.7 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 8.7 | 8 | 7.7 | 8 | 7.7 | 6 |
First, we analyzed the influence and the significance of the eight independent variables (A to G) on the eleven variables of answers (R1 to R11). The collected data were analyzed quantitatively by following the concepts of design of experiments/Taguchi method.
The results are presented in the following sequence: logic
- Analysis of the effects of factors on averages of answers: to identify/quantify the size of the influence of factors on the responses;
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) on the average of the responses/significance test to identify what are the factors that maximize the answers: to analyze the influence of factors on the response and to identify/quantify what are the factors significant for the maximization of the studied responses.
- Proposal for better adjustment of the levels of observation of the significant factors for maximizing the replies: to propose a combination among the significant factors and their respective levels of observation, which with statistical confidence equal to or greater than the 95%. This has to lead to the maximization of results expected/desired by using a social network as a Marketing promotion tool.
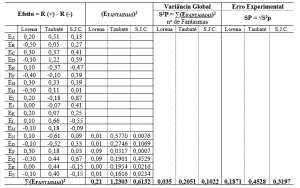
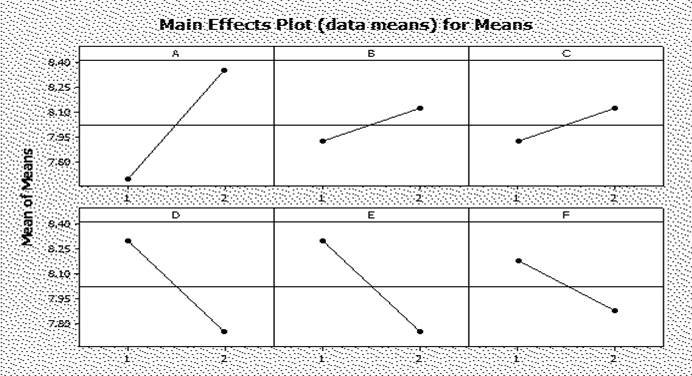
The 5 Frame shows the calculations of the main effects of factors on averages of R1. Has:
- in the second line, the effects of the factors about the averages of the response to low levels (-) Note:
- in the third line, the effects of the factors about the averages of the response to the high (+) Note:
- in the fourth line, the effects of the factors about the average:
- the "Rank", in the fifth and final line, which corresponds to the classification in descending numeric scale, the size of the influence of main factors on the R1.
Table 5: Calculation of the effects of factors on averages of R1.
| Level. | The | (B) | (C) | (D) | And | (F) | G |
| 1. | 7.700 | 7.925 | 7.925 | 8.300 | 8.300 | 8.175 | 7.825 |
| 2. | 8.350 | 8.125 | 8.125 | 7.750 | 7.750 | 7.875 | 8.225 |
| Delta. | 0.650 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.550 | 0.550 | 0.300 | 0.400 |
| Traffic rank. | 1 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 5 | 4 |
The variable G was dropped for the subsequent analysis because it is a ghost variable. Graph 1 shows the main effects of factors on averages of R1, abstracted the G factor.
The exclusion of the variable G also served to make the estimate of the residual error, which can be observed in table 1.
For the sake of standardization of which variables should be excluded, was adopted the pattern of dropping the last inside the "rank" determined by the tool. If there are two or more with the same, all seeding will be discarded.
To ensure the evaluation of the quality of the fit of any model, the examination of waste is essential. The waste must be small, otherwise the template will be bad (BARROS NETO; SCARMÍNIO; BRUNS, 2007).
Table 1 shows the analysis of variance (ANOVA) on the medium of R1, where:
- GL (degrees of freedom) = # of note – 1 levels;
- SQ Seq. (sum of squares of the factors) = 2 (Mx1-Y) 2 + 2 (Mx2) 2;
- SQ (A.j.) = Seq SQ. /DF;
- QM (a.j.) = SQ (a.j.)/residual error;
- F = SQ (A.J.)/QM (A.J.);
- P = significance level of the factors about the answer.
In this research, the statistical confidence level of 95% was. In practice, this implies that all the factors that presented values of P (seventh column of the table 1) equal to or less than 0.05 were considered significant to the maximization of the R1. In the case of R1, no variable showed some influence over what is expected of fanpage that is the optimization of the interaction of users, causing them to replicate the content.
Table 1: analysis of variance (ANOVA) on the medium of R1
| Source | GL | SQ Seq | SQ (A.J.) | QM (A.J.) | (F) | P |
| The | 1 | 0845 | 0845 | 0845 | 2,640 | 0351 |
| (B) | 1 | 0080 | 0080 | 0080 | 0250 | 0705 |
| (C) | 1 | 0080 | 0080 | 0080 | 0250 | 0705 |
| (D) | 1 | 0605 | 0605 | 0605 | 1,890 | 0400 |
| And | 1 | 0605 | 0605 | 0605 | 1,890 | 0400 |
| (F) | 1 | 0180 | 0180 | 0180 | 0560 | 0590 |
| Waste error | 1 | 0320 | 0320 | 0320 | ||
| Total | 7 | 271,500 |
The same statistical procedures used to note the inferences of the factors on the R1, were also applied to the analysis of selected factors on other answers studied (R2 up to R11). However, in order to synthesize this article, the other answers were deleted text. So, are the 6 Framework to direct the interpretation and discussion of the results obtained, short way, but.
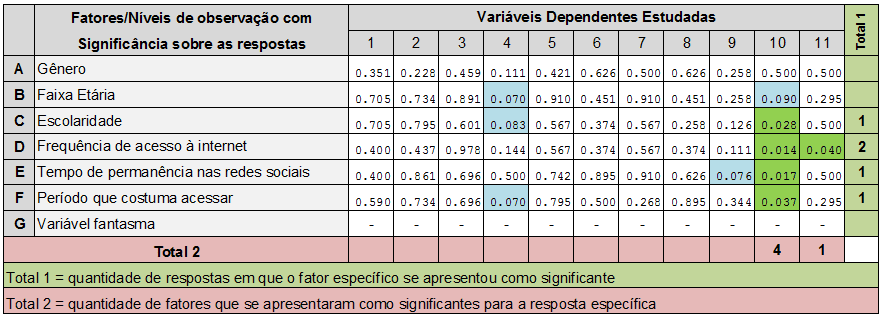
As can be seen in the fields highlighted in green in the table 6, among the six factors studied (since the ghost was excluded in all calculations), we have:
- the dependent variable "frequency of posts" (R10) significantly influenced by four factors: education; frequency of internet access; time spent on social networks; period usually access (C, D, E and F, respectively).
- the dependent variable "variety of topics covered in the posts" (R11) significantly influenced by factor: frequency of internet access (D).
- Can highlight three more variables influenced (as it approached the 0.05 value) by four factors: age group; schooling; time spent on social networks; period usually access (fields highlighted in blue).
When you think of a content that go attract the attention and interaction of followers of the profiles studied, administrators must pay attention especially as regards the frequency of posts (the frequency) and as to the variation in subject. The R10 is influenced by factors that are related to time (frequency of access, length of stay and time of access), which underscores the importance of this variable in degree of attractiveness of the posts.
In this case, the company should seek to act in a more incisive on schedule to have more interaction with the followers, not forgetting to take into consideration that the issues should be separated, because one of the important variables (R11) is linked precisely the frequency with which the followers access. To find out what the best time, in the case of Facebook, the company may verify this information in the administrator mode of fanpage.
When you think of plurality of issues that can be addressed and your relationship with the frequency factor is justified because if the person cannot access the social network at any time, in doing so, she hopes to have contact with a variable number of subjects (topics) differentiate of posted generally by their peers. It should be remembered that the 3.0 Marketing recommends that the company present to customers to your identity that is beyond their products, she is shown as realizing the reality to your back and as an active agent in society.
A study conducted by the Pew Research Center in 2013 (SMITH, 2014) found that the world average of contacts that a Facebook user has is of 200 friends. When the universe of young people between 18 and 29 years, 27% of those with more than 500 people added. According to the September report of the Socialbakers (2014), the active users in October enjoyed about of 39 month fanpages. These figures indicate that for a fanpage can increase your level of interaction with the followers, whereas in a timeline appears several other content, that this needs to pay attention, in addition to time and frequency (R10), also the age group and education, what we see in most variables showed significant in interaction with the factors (B) and (C).
Final Considerations
This article aimed to demonstrate that Marketing is constantly evolving and that companies need to adopt a new strategy and posture to attract and keep customers. When you think about it and your trajectory since the emergence and your next role playing within companies, it was found that the element that most mold is the behavior of customers.
By detailing done by Kotler of the evolution of Marketing stages, elucidated that the element that more has shaped the behavior of human beings in this beginning of century is access to new technological tools and their derivatives. In particular, social media, because of your popularity and ease of use, have given new trends when it comes to how people communicate and seek or provide new information.
These behavioural changes are causing consumers to realize the reality of a new point of view of overall and looking to identify with companies who share your beliefs and expectations.
For companies to be able to meet these expectations and to transmit its values to customers, they can make use of social media. However, so your posts can reach your audience, it is necessary that certain features are perceived and what is important for followers is not neglected. This was the application of Experiment planning tool in support of verification of the characteristics that require attention on the part of the administrators of a business's Facebook fanpage.
When applying the tool along to the public of a fanpage belonging to a company of the Paraíba Valley, it was observed that she provided data that indicate which content are better accepted, well regarded, by followers of the same and in what conditions they are more significant. We also observed some singularities of profiles of followers that help focus on what characteristics need to be taken into consideration when thinking about the content that will be worked on and that will meet with the identity of the company.
The tool was demonstrated as a valuable tool, as it allows to observe in detail each variable that has been selected for observation and interaction levels pre-set. Using the data generated, it becomes easier to define what are the points that need to be thought of later.
The design of experiments is not an end in itself, but an instrument that makes up the constant observation and planning cycle that should be employed when you think to create a corporate profile within a social network.
It is suggested that after the standardisation of data and subsequent analysis, surveys are made that indicate what are the characteristics of content already indicated by the tool please that audience in question so that the same the replicate. Roberts (2004) remember clearly in your work that a lovemark is the one that wins the "heart" of the customer and causes others to meet. One of the goals of having a profile within a social network is the possibility that this media helps to make the company, identity and your products/services known increasingly for other people. However, if people do not replicate the contents, the scope of the mark is restricted to those who already know.
Finally, it is concluded that companies, especially small and micro, may use the method applied in this research, with low operating costs, to identify, on the basis of the profiles of its users, the best parameters of attractiveness of your media, targeting your Marketing projects on time.
REFERENCES
BARROS NETO, B.; SCARMÍNIO, I. S.; BRUNS, r. e. How do experiments: research and development in science and industry. Campinas: Universidade Estadual de Campinas, 2007.
CORREIA, E. A. S.; CARDOZA, j. a. s. design of experiments in the productive process using Taguchi method. GEPROS magazine-production management, operations and systems, Bauru, Year 6, no. 1, p. 55-66, jan-mar 2011.
FONTAO, H.; LEE, e. m. application of tool design of experiments in relationship marketing: a study in retail. Remark-Brazilian Marketing Magazine, São Paulo, v. 9, n. 3, p. 144-169, Sept./dez. 2010. Available in: <http: www.spell.org.br/documentos/download/5403="">.</http:> Access in: 29 jul. 2013.
FONTAO, H.; LEE, E. M.; RAO, l. c. the Taguchi method to measure the significance of the risks involved in the process of Technological Access in the context of open innovation. XXXVII Meeting ANPAD, Rio de Janeiro, 7 to 11 September 2013. Available in: <http: www.anpad.org.br/diversos/trabalhos/enanpad/enanpad_2013/08%20-%20gct/pdf%20gct%20-%20tema%206/2013_enanpad_gct1455.pdf="">.</http:> Access in: 7 mar. 2014.
FURLAN, B.; Marinho, B. Corporate Social Networks. São Paulo: Instituto Develops t. I, 2014.
GEORGE, m. l. Lean Six sigma for services: how to use Lean speed and six sigma quality to improve services and transactions. Rio de Janeiro: Thorsons, 2004.
GERHARDT, T. E.; SILVEIRA, D. T. (. ). Research methods. Coordinated by the Open University of Brazil-UAB/UFRGS and the Technology degree course: planning and management for Rural development of SEAD/UFRGS. Porto Alegre: Editora da UFRGS, 2009. Available in: <http: www.ufrgs.br/cursopgdr/downloadsserie/derad005.pdf="">.</http:> Access in: 11 Apr. 2014.
KOTLER, P.; KARTAJAYA, H.; SETIAWAN, i. Marketing 3.0: the forces that are defining the new human-centered marketing. 9. reprint. Ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2010.
LAKATOS, E. M.; MARCONI, m. a. methodology of scientific work. São Paulo: Atlas, 1991.
Marinho, b. l. Social Media Media Planning. São Paulo: Instituto Develops T.I., 2014.
PEPPER, C. D.; SILVA, M. B.; RAJA, R. B.; Of COURSE, f. a. e. Taguchi Method applied in the identification of the causative factors of decarburization of steel wire SAE 51B35, during heat treatment of esferoidização. GEPROS magazine-production management, operations and systems, Bauru, year 7, n. 2, p. 97-108, Apr-jun 2012. Available in: <http: revista.feb.unesp.br/index.php/gepros/article/viewfile/800/445="">.</http:> Accessed: March 25, 2014.
PRAHALAD, C. K.; KRISHNAN, M. S. The new age of innovation: innovation focused on the relationship with the client. Rio de Janeiro: Campus/Elsevier, 2008.
RAMOS, a. w. Improving the process: design of experiments. In: ROTONDARO, R. G. (. ). Six Sigma: Management Strategy for improvement of processes, products and services. 1. Ed. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2006. p. 234-263.
RIBEIRO, L. G. M.; ALVES, L. H. D.; SILVA, m. b. improved quality in the production of large parts of cast steel using design of experiments. Technology in Metallurgy and materials, São Paulo, v. 4, no. 1, p. 36-41, Jul.-set. 2007. Available in: <http: www.tecnologiammm.com.br/files/v4n1/v4n1a07.pdf="">.</http:> Access in: 15 Oct. 2013.
ROBERTS, k. Lovemarks: the future beyond brands. São Paulo: m. Books Brazil's Editora Ltda., 2004.
SMITH, a. 6 new facts about Facebook. Pew Research Center. Factank-News in the numbers. 3 February 2014. Available in: <http: www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2014/02/03/6-new-facts-about-facebook/="">.</http:> Access in: 2 Nov. 2014.
SOCIALBAKERS. Social Marketing regional Report-Brazil, October 2014. Available in: <http: d3kjz34bnewkku.cloudfront.net/october-2014-social-marketing-report-brazil-regional.html?policy="eyJTdGF0ZW1lbnQiOlt7IlJlc291cmNlIjoiaHR0cDpcL1wvZDNranozNGJuZXdra3UuY2xvdWRmcm9udC5uZXRcL29jdG9iZXItMjAxNC1zb2NpYWwtbWFya2V0aW5nLXJlcG9ydC1icmF6aWwtcmVnaW9uYWwuaHRtbCIsIkNvbmRpdGlvbiI6eyJEYXRlTGVzc1RoYW4iOnsiQVdTOkVwb2NoVGltZSI6MTQxNzUzOTcwNH19fV19&Signature=dV3wvgS4XnFc-UJKocVe-EEA4GOrolqXkxoCqN/C-sZ-P6N3pkbvDXGetAqZMseZGpUikOzFYLXvvVFC3VW64YVLDxJp8J1KaHCguVJhj/GNYJwyKnYOccaRLVnvip7xslR1aHmmIEPAnXfwYSHvheSZUezJb3V63Qu/NnAAiIA_&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJCF5RTYWTPDS3AGQ">.</http:> Accessed on: 2 nov. 2014.
[1] College of technology Professor Darin May
[2] Faculty of Technology of Pindamonhangaba; Centre for research in Economic and Sociology of organizations, Lisbon, Portugal
[3] Faculty of Technology of Pindamonhangaba