ORIGINAL ARTICLE
CHAGAS, Edgar Thiago de Oliveira [1]
CHAGAS, Edgar Thiago de Oliveira. Blockchain: the technological revolution and impacts to the economy. Multidisciplinary Core scientific journal of knowledge. 04 year, Ed. 03, vol. 07, pp. 110-144. March 2019. ISSN: 2448-0959.
SUMMARY
Blockchain technology began with the introduction of the Bitcoin to avoid duplicity of transactions. Little time has passed and the technology expanded their horizons can be implemented on several fronts. The Blockchain, as the literal translation, is a chain of blocks, which keep the most diverse types of information in a secure, immutable and privacy, preventing data corruption. In this context, this article sought to elucidate the panorama of Blockchains and your implementation in various fields and, especially, within economic, noting the impacts caused by your application. Through extensive bibliographical analysis, to prepare, so descriptive qualitative, the current context of this technology and how it can assist future transactions.
Keywords: Blockchain, economy, security.
1. INTRODUCTION
The world is increasingly globalized, interconnected and connected via the internet. Currently, it’s rare to find someone that does not have files, photos or other information saved in the cloud, mainly businessmen. In this sense, it is important to stress the importance of safety of this information within the network to prevent disorders.
The issue at hand is a database, a technology for distributed records covering transactions or events that is shared between the parties through their connected devices.
The Blockchain is a record distributed among several connected devices representing a decentralized network that stores various kinds of records with a timestamp, or time stamp and a digital signature.
The term timestamp or timestamp as a string on the hour or the correct date of when the event occurred, while the digital signature refers to a method used to authenticate digital information authentication eliminates the need for paper version of the document
The main purpose of this registry is distributed to provide a more advanced degree of certainty to those information, since there is a need for agreement of all connected devices on the records stored. All transactions are backed by the consensus of the majority of the participants of the Blockchain.
Once the information is entered, cannot be erased. This record has distributed a record certain and verifiable of all transactions at once.
Blockchain technology has worked well in recent years and has been successfully applied in the context of financial investments or not through the world and has been cited as a very important invention.
The digital economy depends on a reliable authority, so that online transactions depend on trust that the transaction was effected, the point is that there is a reliance on third parties to establish the safety and effectiveness of a particular event, in addition to the question of privacy of our digital activities. Analyzing this light, managed by third party information can be manipulated, getting hacked or erased. Hence shows the importance of the Blockchain.
This technology can revolutionize the digital market, allowing each part of a particular online transaction can check it out at any future time and without compromising the information, privacy and other individuals involved. Especially in transactions with digital assets, although the Blockchain can encompass any type of information.
This article aims to clarify the issues involving the Blockchain and how your use has revolutionized the record of information more securely and the impacts on the economy through the use of this technology.
Have aimed to point out the benefits of this technology to the economy and to elucidate how safe is your use listing companies that have joined the Blockchain to safeguard your transaction records. To this end, the methodology applied covers wide bibliographical review about the subject with articles, theses, books and statistics that relate to the theme in order to illustrate the issues on screen.
Blockchain technology is still not disclosed what justifies this article to disseminate information about this distributed record that can address issues involving custody of data securely.
2. DEVELOPMENT
2.1 GENERAL POINTS
In the field of economy, focus this article on Blockchain, it should be noted that e-commerce is a growing reality. And transactions carried out in this virtual environment depend on financial institutions, namely, third party trusted to perform digital payments. Generally, this system works well, but a failure may occur, which entails a breach of faith. Second Nakamoto[2] “there is no mechanism for effecting payments through a communication channel without a relying party”.
The article published by Satoshi Nakamot[3]o was the first to conceptualize Blockchain technology, in 2008, joining the the bitcoin. Currently, your application is not connected to this criptomoeda, but especially in the economic sphere. Conceptualized the electronic currency as a chain of digital signatures, where each owner transfers the currency for the next digitally signing the deal, but still would need a third, a reliable central authority.
Nakamoto considers that the first transaction is the most important and should be announced publicly, so that other parties give your endorsement in the order they receive, providing a solution to avoid receiving double of certain amount: a server timestamp, which will determine at what point given event has occurred.
In fact, the initial idea of Nakamoto, deals with the bitcoins in order to avoid double payments. In the case of encrypted digital currencies, like the bitcoin, the ledge records the sending and receiving of these transactions.
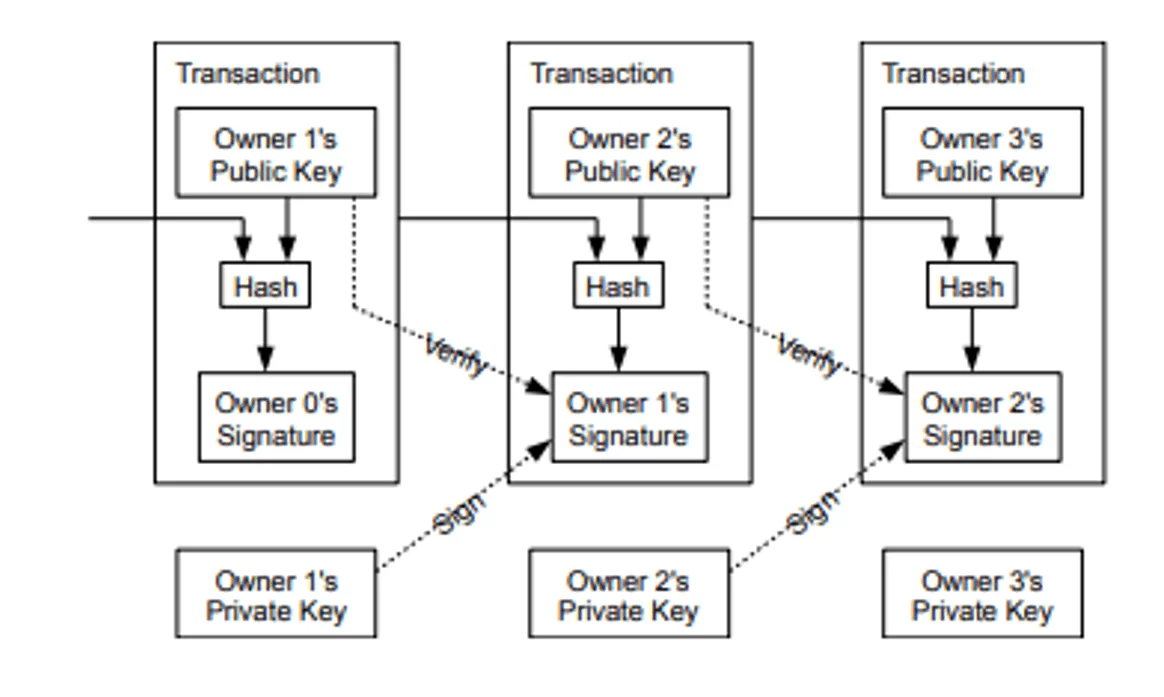
odel: Nakamoto
According to the model of Nakamoto, each transaction must be checked and backed by the outgoing titleholder, through a digital signature. With a rough translation, Blockchain would be “block”, which refers to the initial model of Nakamoto.
Blockchain technology is a network of interlocking blocks, that require a digital validation. Thus, the subsequent block contains the digital signature validation or previous block added to your content or your information.
The Blockchain is especially known as a technology to perform encrypted coins as the bitcoin, which to this day is the most used with this technology. The bitcoin is characterized by maintaining the value of the currency in any governmental administration in control and is the most successful digital currency using the Blockchain.[4]
According to the website I[5]HODL, conceptualizes-if Blockchain how to:
Distributed database, which means that the storage devices of the database are not all linked to a common processor. The same maintains a growing list of sorted records, called “blocks”. Each block has a timestamp and a link to the previous block. Encryption ensures that users can only edit parts of Blockchain that “hold” by having the private keys needed to write to the file. Also ensures that the copy of the distributed Blockchain to which all have access is kept in sync.
It is necessary to clarify the meaning of some technical concepts. Hash is a term that refers to a function that transforms a message or file into a code with letters and numbers representing the information entered. The Hash brings together a lot of information and a reduced amount of data. Is the digital representation of a file. When information is changed, the hash is modified as well.
The hash ensures that the signature of a given block. The creation of a new block that contains the previous hash creates a digital stamp which is verifiable and signals any change. Such information is listed on the ledger as a ledger, a species of ledger. When it stores the hash or fingerprint of an asset, instead of storing the digital asset itself, anonymity is guaranteed, as well as privacy.
It is necessary to point out how the structure of the Blockchain. A block has a header that includes the set of rules for the validation that the block must follow, pointing so your version; the 256-bit hash value that indicates what the previous block, called Parent block hash; the hash value that refers to all transactions of that block, named merkle root hash; the timestamp; a compact hash-nBits; and Nonce a field of 4 bytes and increases for each hash.
The body of the block is formed by a transaction counter and for these transactions. The maximum number of transactions that a block behaves depends on your size and the size of each transaction. Blockchain technology uses asymmetric encryption to validate each transaction in a non-trusted environment.[6]
The structure of the block follows the specifications listed in the site Bitcoin investment:[7]
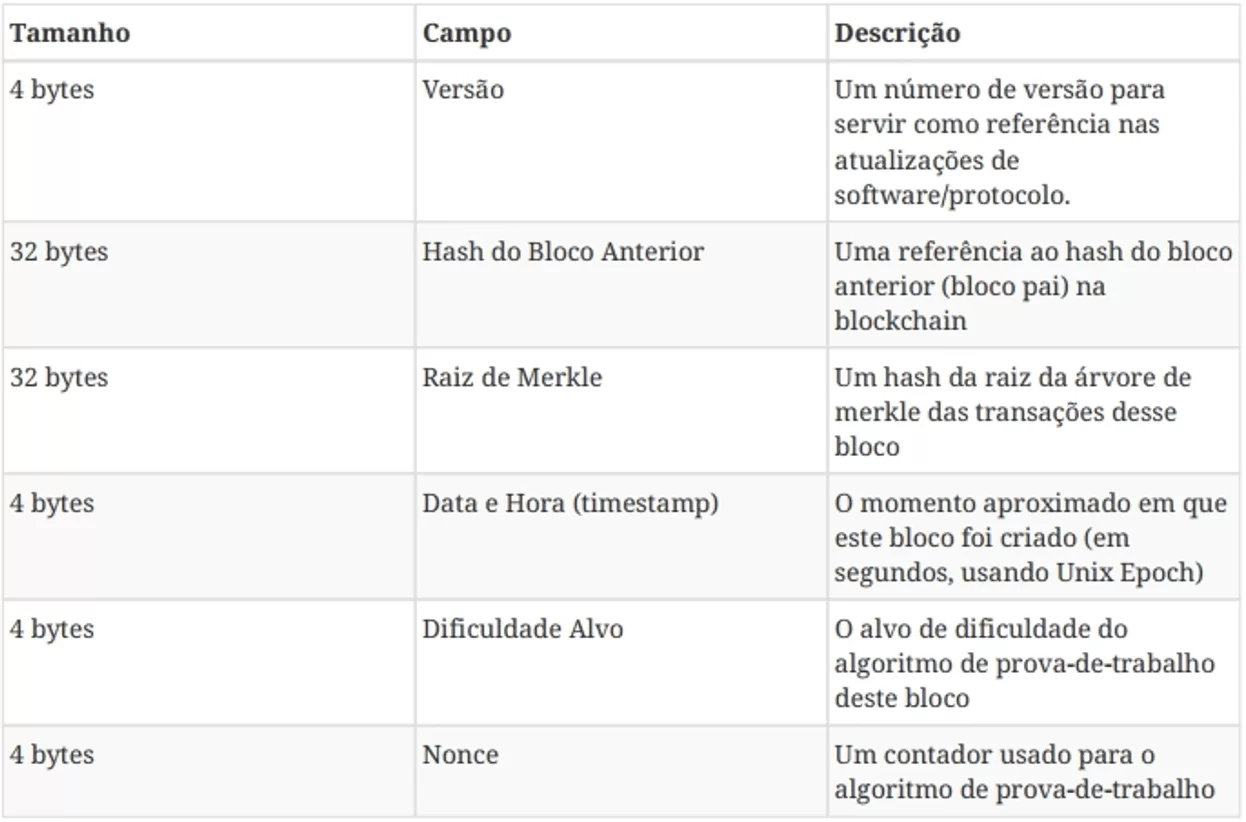
Source: Bitcoin investment
According to Alex Bar[8]ron, CTO of Star Labs in your lecture on Web.br Blockchain technology is very safe, since it uses the processing power to ensure that the hash of each block is valid.
In another lecture, André Sale[9]m, a researcher at the IBM Blockchain, conceptualized the Blockchain how to transfer items and value between the participants, through a common ledger distributed, that everyone has a copy and whose content is constantly synchronized.
ource: IHODL, 2017
Even though the beginning of the Blockchain technology is intrinsically linked to the bitcoin, can be applied to any digital asset transaction online.
In the case of the bitcoin is employed in place of the third encryption for that the parties implement transactions in the digital environment. Each of the transactions is protected by a digital signature that is posted for the public key of the recipient, and validated with the private key of the sender. To spend the criptomoeda the owner must prove ownership of the private key.
Only in peer-to-peer bitcoin transactions are reported in the order in which they are generated, the need for certification of those that are performed to avoid double spending, i.e. in the bitcoin there is no guarantee that the order of transactions is correct.
The peer-to-peer network is structure of computers or networks that share events or files between pairs, called peers, all of which have the same prerogatives and privileges in the Blockchain environment, which does not occur on other platforms. In a peer-to-peer home user is called “node”.
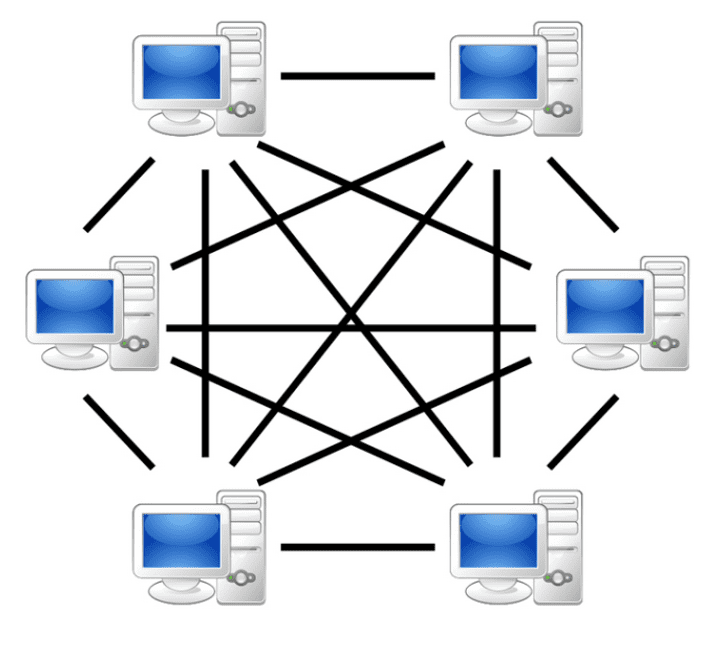
Source: Silva, Alves and Fernandes
Each of these “we” works as a user or server, enabling the sharing of services and information without the need of a central server. Blockchain technology, peer-to-peer network is composed of multiple computers and servers where each one represents a “node” in the network. When new information comes into the network, it is spread among all the nodes in the peer-to-peer network, validated, encrypted and private. You can’t identify who added the info on the net, just validate it.
To avoid the duplication of expenses was born this tool, because the entire network Bitcoin should have enough data to determine the order of transactions and avoid the duplication of events, which was solved by Blockchain.
To ensure a higher degree of security Blockchain technology involves computer programs that run automatically the terms of a contract, called smart contracts. In the event there is a pre-configured clause in this agreement between participating entities Smart is fulfilled, the parties involved can automatically make payments securely and in accordance with the contract.
Another issue that involves the Blockchain is smart that is related to the control of a property or asset through this technology using smart contracts. This property can be physical or virtual.
Blockchain technology is being applied in various financial and non-financial areas. Currently, the application of this technology for financial institutions is a reality and does not represent a threat to the traditional models and the banks that have not yet joined, are looking for opportunities and researching new applications for the Blockchain. As regards non-financial applications of this technology one can conceive your use to prove the veracity of legal documents, health records, among others.
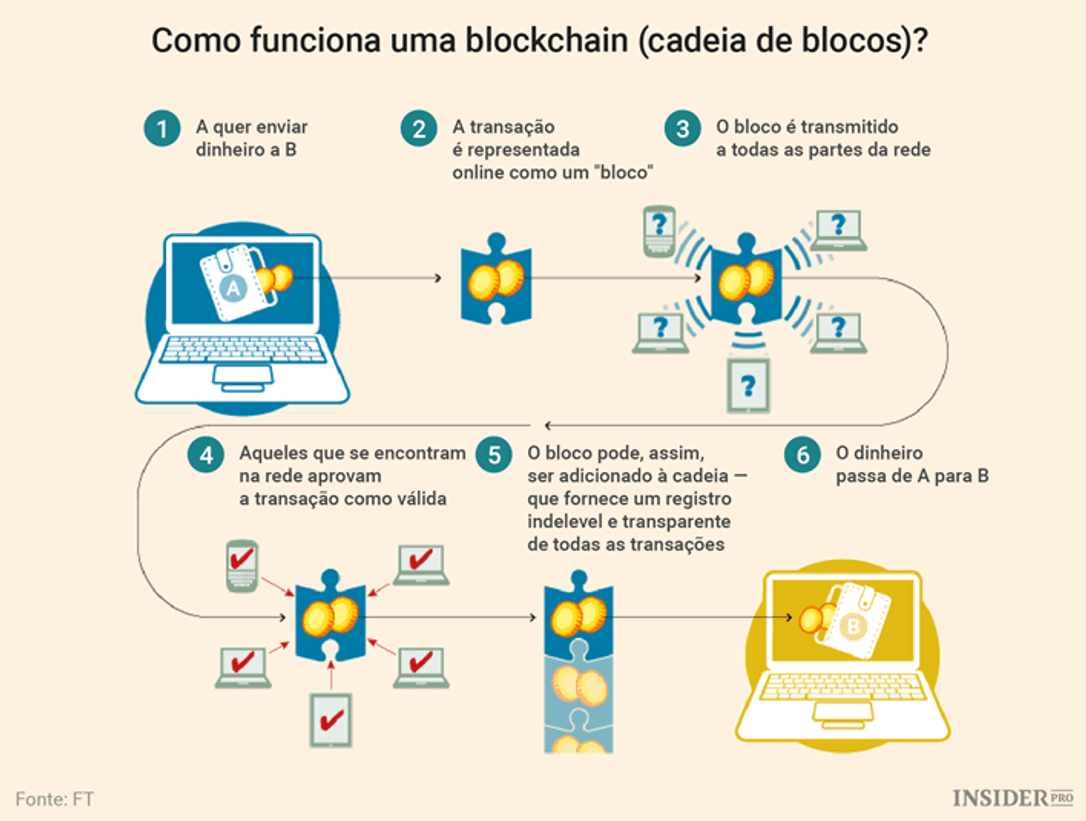
Fit the Blockchain enables the continuous record of all transactions with equity and distributed form, i.e. without a third party certification body, which ensures independence of either party, as shown in the figure below:
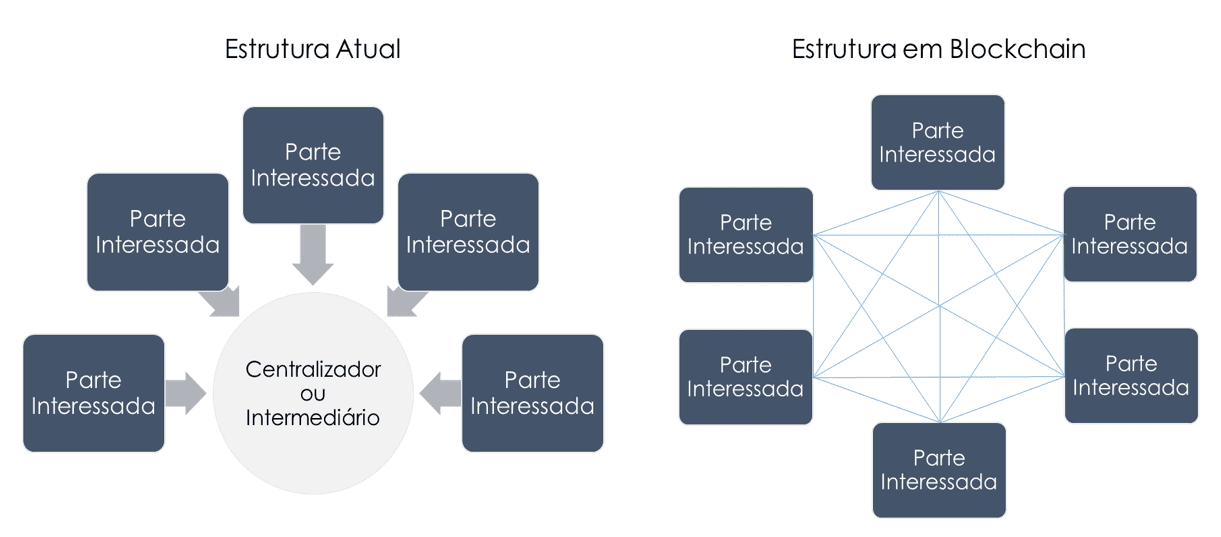
ource: Bridge Consulting
According to Camara,[10] the technology person-to-person (peer-to-peer) enables collaboration between peers in the digital environment, without intermediary or centralized control, while the hash encryption ensures the confidentiality, authenticity of the.
The Blockchain can boost the growth of the digital economy, considering that the use of the internet as a means to make purchases, share personal data and perform transactions shows more and more commonplace.
Any transaction carried out in Blockchain technology is only supported when that “block” of transactions is fully populated. As analyzed, these blocks are sealed by encrypted codes (hash) which makes the possibility of alteration of this information impossible to ensure that, in case the coin reaches the specific purpose; There is no duplication of payments and changes in transactions already carried out. These factors ensure safety in the use of the Blockchain.
An example of the use of Blockchain is known as ether, which is a decentralized encrypted currency, which feeds the Ethereum network. The Ethereum network is a network of Blockchain that gathers data from the execution of programming code in any decentralized application, which may not be manipulated or altered.[11]
The Ethereum has created a platform that allows anyone to develop your own criptomoeda and use it to perform and pay for smart contracts, while the criptomoeda ether paid services, and thus are encouraging governmental areas, banks freelancers and other transactions using smart contracts.
Several banks have shown interest in this technology and intend to deploy it in their processes to optimize international bank transfers within the same bank. Second Largh[12]i, Banco ITA has implemented the margin control derivatives transactions using Blockchain technology and reports about the benefits of your use
The idea of using the tool for those assets, according to bank executives, comes from the fact that the price of derivatives are not accompanied by a regulator and cannot be found in a clearing. Therefore, the value that the parties Transact is decided by means of a negotiation between them. With the tool, this transaction is closed virtual[13]
Banco ITA uses a program where the parties can negotiate through a chat the asset value. At the end of the transaction is generated a digital document with the transaction information is stored in Blockchain.
Another bank that turned out to be interested in this technology is the Banco Santander, which seeks to develop an application to their account holders in another country can conduct transactions between accounts via the network safely and faster. The same technology would be offered to customers located in Brazil that have account in other countries. Other major institutions concerned in the application of Blockchain technology are HSBC and Bradesco.
Bradesco search employ Blockchain technology to enhance procedures and provide solutions to reduce process costs and benefit the end customers. To this end, groups have been formed to evaluate how technology and Blockchain can integrate financial services.
There are few studies on Blockchain to explain the technology and structure that come changing transactions and which platforms can be supported under economic, because there are many Blockchain technology applications. However, this article aims to elucidate the impacts to the economy, pointing to its benefits, as well as the points that require greater attention.
Much of the economic and social information are currently scanned, which requires more security to avoid leakage and illegal use of such data. Blockchain technology came to curb the dissemination of this information, enabling market participants to assess the conditions of the transaction and execute contracts without exposing the hidden data to third parties, which allows the parties to confirm the veracity of the information, without access to previous records.[14]
Blockchain technology provides the certification of characteristics of the transaction so as to preserve privacy. In this sense, the scanning reduced costs of verification of various types of transactions to almost zero.
A Blockchain as the Bitcoin can be used to check the property and exchanges on criptomoeda. The implementation of Blockchain need a computing infrastructure to protect transactions and enlarge your ledger, a small requirement in comparison to the costs of labor and capital involved in transactions with financial infrastructure traditional.
Other intermediate platforms have access to all transaction information and accumulate market power, which does not occur with systems based on Blockchain technology, which ensures a higher level of competition for various types of services.
When there is an economic transaction, this comes with some basic features, namely: the transaction, when it occurred, information about the parties and their credentials, among other information that underlie the implementation of actions thereafter.
However, some events may require an additional check, for example, an audit that may require data from market participants, to perform a process based on the case of exception. Such processes are expensive and may require a third party mediator between buyer and seller.
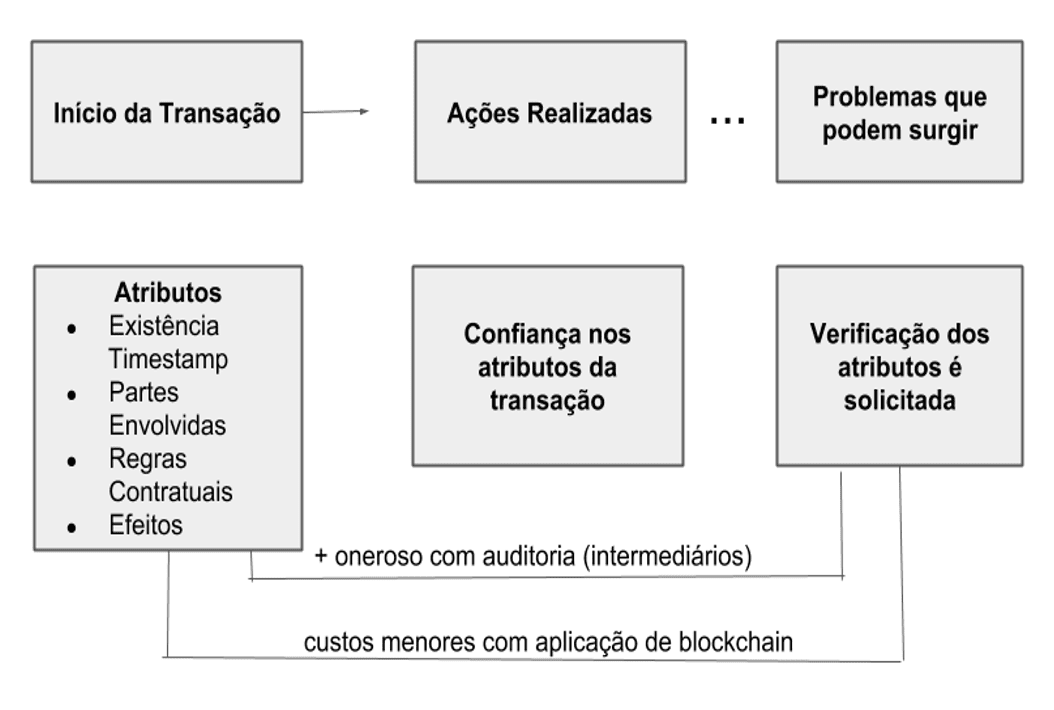
It is understood that the Blockchain changes this flow by facilitating the verification of the problem without major costs. The attributes of the information on the parties involved are stored in a distributed ledger can be accessed in real time by market participants, so that trust is deposited in the underlying code and contractual rules agreed. These rules define how this distributed network can evaluate regularly the State of shared information needs to maintain for the market to operate properly.[15]
These shared information may include past transactions and pending on a cryptographic token. Advanced platforms, such data can also hide the code and the information needed to perform a specific operation, such as a verification of contractual clauses, known as smart contracts[16].
The effects caused by the introduction of Blockchain technology and the consequent reduction of costs in check services were notorious for intensive production and margin for digital assets, where former investors moved existing transactions for Blockchain-based systems to reduce operating costs.
The Ripple, gross settlement system in real time, currency exchange and shipping network, uses this technology to enable payments between countries for way cheaper than in Fiat money between banks.[17]
Assets and digital chains come using the same strategy to deliver more effective business of financial assets, including the Western Union invested in space to reduce costs in the remittance market. Open and Circle using this technology to global payments peer-to-peer in fiduciary currencies, while the NASDAQ has implemented a solution to observe impartiality in closely held companies[18].
The implementation of Blockchain for reducing the cost of checking add value to the existing value chains, reducing the cost of settlement and reconciliation of transactions.
In addition, although many verification steps have their prices reduced by extreme competition, intermediaries still participate to provide a user friendly environment, managing specific cases requesting verification forms intensive offline, which explains the slow diffusion in the application of this technology, since the verification of digital attributes can be applied through a Blockchain, but the initial mapping of off-line institutions and their digital representations are activities guys to start and maintain.
There is, therefore, that verification costs fall, in contrast to Blockchain technology becomes more valuable. The Blockchain can be used to settle business of digital goods scarce and self-reliant within a platform. The compliance with the rules laid down in the code defines how the tokens are obtained and how the network reaches the endorsement on the true state of property of the tokens over time.
The cost of checking the transaction attributes and application of simple contracts to independent tokens is practically null, which allows the value to be transferred through the Bitcoin for a short.
Compliance with the rules Know-Your-Customer and Anti-Farmville Money may require individuals and businesses to keep additional costs to link their credit identities offline with your Bitcoins, but judging individuals wake up the underlying value token, shows itself as a medium of Exchange extremely cheap[19].
Thus, a cryptographic token that can be used to facilitate low-cost transactions of digital resources as in the case of the Ethereum computing, data storage, as in Filecoin or bandwidth or electricity, as in the verification of attributes of transactions.
On the other hand, when the entries in a ledger distribuited are digital representations of identities, products, services and related transactions, check with reduced costs is more difficult.
In this case, the decrease in the cost of checking is secondary in maintaining a reliable link between offline events and your online registration. This link is cheaper to establish when the offline attributes are easy to catch and expensive to change or falsify, tell if, in the case of diamonds, Everledger uses the physical properties of gems like a fingerprint that can be recorded and tracked in a Blockchain, identifying the products and your supply chain location avoiding falsification[20].
Maintaining a robust link between off-line and distributed records is still expensive and may require several trusted intermediaries to various parts to set the rules for entry and secure sharing of data. In the absence of a link with offline records and online events, asymmetric data and the moral hazard will still be a problem.
According to Tapscott, Blockchain technology allows you to transact all, which makes it part of the “internet of value”, allowing the negotiation of various items without intermediaries and without tariffs. Changing the way business has been conducted for centuries exerts impacts on the economy[21].
International transactions grow with the phenomenon of globalization. Through Blockchain you can send values without possibility of fraud, and without exchange rate. Security is cryptography, generating a reliable protocol on the network.
The author reports although several companies are betting that technology around the criptomoedas. Companies such as Kodak want to throw your criptomoeda for the remuneration of professional image. The application of this technology and Smart Contracts inherent to it allow records and transactions more efficient and makes the intellectual property more liquid[22].
In other countries, Blockchain technology has been applied in several fronts. In the Netherlands, some cities have created applications developed in Blockchain to manage real estate contracts, while in the United States, the postal service works with Blockchain developing a tool to track your deliveries.
2.2 LEGAL ASPECTS
Questions about the impact of Blockchain in the development of the country and how would your rules. Valley perform a brief caught on Blockchain technology in the legal environment. According to Mckinse[23]y this technology may cause changes in several economic sectors, making them more democratic, secure, transparent and effective.
In this sense, Vieira, marine and couples, raise the issue on the relevant legal solutions when there is an enforcement in the event of a conflict on the rights and obligations arising from the records in the Blockchain[24]
These authors point out that the Parties shall initially recognise that there is a transaction designed and managed by Blockchain, otherwise the parties would have only “an illusion of rights and duties”. The solution determined through Smart Contracts within the framework of the Blockchain technology, must be recognized by the la[25]w.
The records in Blockchain can serve as proof for businesses that do not depend on public instrument or other formality required by law. However, when they are required for the validity or efficacy solemnities, such records are questionable.
According to the Art. 406 of the code of Civil procedure law request public instrument as evidence of the Act, no other evidence you can supply you lack. Vieira, marine and couples show that the legislation should update itself in favor of new technologie[26]s.
Other legal issues involve the Blockchain in the legal area. The notarized affidavit is an instrument issued by the registry with public faith, noting the facts and proving your existence, where the registry ensures the certification.
It turns out that the Blockchain, not only owned the public faith, but is able to provide a record set in stone with timestamp and with the possibility of verifying the authenticity of the content. Another benefit of such use in the performance of acts by individuals would be the reduction of costs and the possibility of failure and personal motivations.
As the Act produced by the registry in Blockchain, in your recording of public and encrypted way, everyone will be able to access the online form acts. With respect to the contents of the decrypted and transparent form, only the parts will have access, ensuring the privacy of information[27].
As for contracts in Blockchain, your infrastructure allows the establishment of a digital access keys certification and approvals that guarantee the impartiality and the authenticity of manifestations of will. The Blockchain can reduce the steps for the implementation of Smart Contracts, given the connection related to validity of the previous transaction, whether on a contractual analysis or validation for your digital certificate.
In addition, the trading time would be reduced, because the parties would have access to a immutable copy of the agreement and the contract would have immediate execution after agreeing a your acting in the process.
Abr[28]eu also reports the importance of Blockchain as a witness, since this technology can ensure judicial acts. Currently, in the tax sphere, the proof of delivery at the federal, State and municipal departments of Farm System. This technology can prove the regularity of transactions, and compliance with ancillary obligations.
With respect to intellectual property, the registration and validity of the transaction may constitute proof of copyright, which is created by the National Library Foundation and School of fine arts, containing the author’s identification requirements.
On the other hand, the Brazilian Government has been studying the possibility of including the data of the Federal Government under the care of Blockchain technology, as reported by the Court of Auditors, in case # 033,619/2016-6 CT.
Group I – CLASS II-Plenary 033,619/2016-TC 6 Nature: National Congress request Bodies/entities: the Central Bank of Brazil; National Treasury Secretariat Interested: Banco Nacional de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social (33,657,248/0001-89); Ministry of finance; Attorney General of the National Treasury (00394,460/0216-53) legal representation: Bernardo Faustino Clarkson and others representing National Bank for economic and Social development; Miška Raeisi, representing Brazil’s Central Bank; Francisco Eduardo de Holanda Bessa, representing the Treasury Department. SUMMARY: THE NATIONAL CONGRESS REQUEST. APPLICATION FOR SUPERVISION OVER THE INTERNAL FEDERAL GOVERNMENT DEBT. Audit. DETERMINATIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO THE GOVERNMENT DEBT MANAGERS. SCIENCE TO THE NATIONAL CONGRESS. Archiving.
. Reported that studies in Congress, the Central Bank and the Securities and Exchange Commission (CVM) on the regulatory environment for application of Blockchain, considered also stumbling the model in Brazil. The data processing company of the Federal Government (Serpro) recently launched the Blockchain platform according to information disclosed in the company’s Web site. It is known that the need to maintain confidentiality on customer data is one of the biggest challenges for technology Blockchain be adopted by Wall Street financial market[29]
Such applications are emerging in the field of law so that the Blockchain is still a novelty in this area, but in the benefits would be many. In this context, Tapsc[30]ott, believes that Governments can act as regulators of Blockchain bordering your acting and damaging your development as occurred recently in Korea, that has restricted business with Bitcoin.
According to Tap[31]scott, limit this kind of innovation can harm the economy for years, because investors would find other means of trading virtual coins and perform their transactions.
2.3 ECONOMIC ASPECTS
Nationally, the economy is based on agricultural commodities and minerals and the implementation of the Blockchain you can insert it in global supply chains, making measurable production, controllable and traceable and each commodity unit will be identified[32].
According to a report from IBM,[33] disclosed in 2016 the financial market and banking are adopting this technology very quickly and trying to adapt it to the business. It is believed that in 2020, 66% of the banks will use Blockchain on a commercial scale.
Although this technology impact all sectors of the economy, the sector most affected is the market action, but without major changes in the short term. A report prepared by the firm GreySpark Partners in 20[34]16, points out that the disruption will occur over a period of 10 years through the redefinition of all processes.
Reducing the costs of negotiation and security will benefit users and will provide an increase in transactions and in the stock market, the transaction validation processes will be the most impacted. The pós-transação process is still manual and reduces the profitability of organizations. Blockchain technology allows the reduction of pós-transação processes, which will decrease the risks to the parties involved in the transactions.
The question of centralization shows up as a principle of Organization for the economy, as well as for society, that works effectively when transaction costs are high. In this way, the Blockchain has the ability to democratize the economic sector, reducing costs to create and manage an online platform.
The transactions undergo smart contracts or can be performed at a lower cost for small suppliers, which facilitates the emergence of new models for decentralized organizations. No directors or hierarchy, with collective administration by the parties cooperating with Blockchain technology.
Without intermediary, the value produced on these platforms can be distributed in a more righteous among those who cooperated to your creation. An example to be cited shared savings is the La zooz[35], a Blockchain-based application, managed by code deployed and designed to manage interactions between drivers and users, rewarding drivers who collaborate with the platform through tokens.
In this sense, the brazilian capitalist economy requires a cash flow approach, with active and passive positions. This economy needs a system of balance sheets related to each other, with the Fiat currency, as well as with the Bank currency constituting the core of contemporary payment system[36].
In the modern monetary system, the Brazilian coins are coins fiduciary, which has your state value guaranteed by the issuing State and accepted by citizens and businesses compulsorily in the national territory.
Furthermore, are the only form of payment accepted by the State tax and by the Central Bank for the context of the positions of the banks. The modern capitalism requires a global currency, the US dollar.[37]
It turns out that the national currencies are becoming fiduciary, used basically due to your trust acceptability by the Government for the payment of fees, which ensures your demand. Wonders, then, what can occur when the Population Fund trust in digital Blockchain system allowing for cost reduction and freedom of transaction online.
The banking system, led by large international banks, demonstrates the impacts caused by the implementation of the Blockchain technology, so that such institutions have been working actively in this sphere[38].
According to[39] Morgan, the impacts of Blockchain are due to shared and protected from a common pattern, low failure rate and continuous transfer of digital assets, showing quite functional for the modern financial system, which is centered.
In addition to the positive effects and imminent on the back office and the internal process of these entities, the Blockchain features to enable the transfer of data at high speed, providing flexibility in settling contracts, enabling the pricing and supply of innovative services.
The concept of Blockchain, initially, affected financial services, with venture capital and investment and reaching for technology startups. However, it is believed that your application in systems and processes of financial and banking services today becomes increasingly huge and real, contrary opinions about your vulnerability.
Investments in startups that use Blockchain technology have increased, especially in the Fintechs (startups working to innovate and optimize financial system services).[40]
The big international banks are noting the association between peer-to-peer, asymmetric cryptography and cryptographic hashing from the bitcoin. However, these entities, this technology has been developed and implemented within the State rules, because allows the decentralization of the confidence of the parties and an information processing system able to provide millions of transaction at the same time[41].
The Blockchain has the ability to enable the reduction of the risk, assign actual calculation of asset risk and ensure a more accurate pricing of assets, in addition to providing a better positioning of financial products and services, as well as promote a system more effective asset management.
It is understood that the use of Blockchain may allow a more effective use of resources, with greater speed in transactions and reduced costs of financial products and services offered by banks and the financial system.
Morgan[42] States that the impact of the Blockchain can rearrange the market structure, the customer experience and the capacity of the product, in addition to influencing the world economic system in a sustainable way, which shows that such technology is in addition to the criptomoedas, being implemented in various institutions of the current monetary order.
Several international banks joined the Investment Bank UBS to generate a virtual currency for leveling and settle financial transactions, seeking to overcome the issues involving the Blockchain, promoting dialogue between central banks and agencies regulators about the matter[43].
This initiative aims to make financial markets more effective, as well as reduce risk, speed up the settlement of BackOffice systems, freeing capital for international financial operations.
This settlement currency aims to enable communities to carry out financial payments between themselves or acquire financial instruments more quickly with digital currency, convertible into money in central banks reducing the time pós-transação.
Digital currencies convertible in different countries, would be assembled using the Blockchain, an accounting system of distributed ledge, enabling rapid exchange for financial instruments traded.
According to Morg[44]an, Blockchain technology can provide a restructuring of the financial system, making less expensive and simpler transactions, ensuring also, greater privacy and control over financial transactions to users.
Likewise, can motivate the development of better tools for monitoring and protection to regulators. It should be noted that there are technical difficulties, legal and regulatory Blockchain technology, and your speed, scale and questionable, especially Security.
Finally, it is pointed out that the digital currency based on Blockchain technology should be used by financial institutions to Transact directly with each other, to circumvent the traditional process of settlements and reduce the time and cost of liquidation and trading post.
2.4 advantages and DISADVANTAGES of BLOCKCHAIN
Note that there are many applications and advantages in the use of Blockchain technology, among which we can highlight:
- The Elimination of the third intermediary in transactions, with the Blockchain, the parties involved can perform the Exchange without intermediaries who oversee the event, reducing the risk of default of the parties.
- Quality of data and information, because the authenticity of transactions is checked when there is the closing of each block. In the event the transaction is not achieved, it will not be added to the given block. It is concluded that the information contained in each block and along the Blockchain are consistent, dated and believable, which ensures high degree of data quality.
Another relevant point deals with the durability and reliability of this technology, since the network is decentralized, peer-to-peer design, so that the Blockchain does not have a central point. When there is a failure in the system, or even if this is hacked, the decentralization helps in protecting the system, due to the talk from a central point. Each “peer” has a copy of the data which prevents them getting lost.
The integrity of the process is another advantage of the Blockchain system. Users have to guarantee that the transactions will be made in accordance with the terms proposed, otherwise the event will not be validated. Transparency, immutability and advertising related mainly to public Blockchain is pointed to as another relevant factor for the transparency of transactions.
The process of compressing all the information demonstrates the simplicity of assembling in a single public all ledger transactions, as well as reducing the cost per transaction. Without the intervention of third parties, related expenses and exchange goods diminishes.
The use of Blockchain technology also features beneficial to the environment because it reduces the number of prints of documents and spaces for files. Every document or can be hidden or reduced in the form of code and referenced in the ledger, demonstrating that Blockchain technology has broad applications.
Other advantageous applications with the implementation of the Blockchain are:
- Creating marketplaces distributed and autonomous: according to Z, I, it’s [45]like a virtual shopping marketplace, bringing together various brands and stores all in one place. Thus, the Blockchain guarantees the transfer of assets in a secure, private, autorregulada and swiftly, allowing flexibility to the cashier, and asset management.
Reiterates that the technology does not need third-party intermediaries Blockchain and, therefore, if a company provide items of value to potential buyers, with the guarantee of authenticity, the relationship is positive through the open competition and best deals.[46]
- Business transactions made easy: With the application of this technology, the expense management becomes easier, since it provides that organizations to create a network of suppliers and partners, automating and monitoring contracts the entire supply chain.[47] Moreover, with the reduction of human interactions, the Blockchain reduces transaction errors or lack of information, implementing agility among the parties.
- Administer and ensure private decentralized records: each record is encrypted and requires a custom access key, which guarantees total safety data, including in educational institutions and companies in the sector of Human resources, without concern for the possibility of forgery.[48]
- Monitor the origin of products and materials: the Blockchain can ensure the quality and safety of a given product and the trace of their inputs.[49]
According to[50] Garcia, watching under a social vision, using Blockchain technology allows one of the advantages already described the auto-soberania, which allows users to identify, at the same time, and control the storage and management of your data personal.
Another inherent advantage Blockchain technology is the speed in the transmission of values, given that some financial institutions take days to perform a wire transfer and does not work on weekends. In the case of international transactions, timezone interferes. With the implementation of Blockchain, transactions can be carried out 24 hours a day, every day, to any location and with immediate shipping confirmation. The question is what else ails those interested in Blockchain technology and your business application. According to Wood [51]is no difference between public networks, called private networks permisionless, permissioned calls.
In the case of private networks, where the parties know, security is determined by the structure of nodes in the peer-to-peer network. The ledger transaction authorized under the joint validation of the members. Each node has an exact copy of the ledger, which is updated constantly, and Blockchain private operators control who can perform what in each peer and the connections between them. To validate an active node, it must keep a certain number of active connections.
Thus, a node that shows flawed in the transmission of information, should be identified and limited itself to maintain the integrity of the system. Not to lock the system policies are applied to consensual operation high availability. The proof-of-work is a validation prior to permission to create a new block, which increases security and reliability of the processes.
In the case of public networks, validation of members, known as consensus, occurring in 10 minutes lapses average time for choosing a leader node validator to perform the update from the ledger, practice known as mining. After a few hours the transactions are considered safe in this environment. In the meantime, the transaction can be invalidated after new update, known as operation fork. For older transactions from the ledger, perform a fork I would like high cost of equipment and would duality of transactions.
Due to need for mining on public networks, it is considered that the percentage of security does not reach the 100%, but the application of different strategies of consensus algorithms could determine who invests as many goods in Blockchain, as the the proportional miner invested.[52]
It is also to highlight the challenges that the implementation of Blockchain technology may face, namely:
- The speed of the miners, which seek to verify with agility to transactions and the information that you enter in Blockchain, which requires costly equipment and income.
- Regulation by States: it is understood that there is a certain fear about the regulation of this technology, especially regarding the criptomoedas that are in the Blockchain as the bitcoin. Financial institutions and of the State itself has lost market share, causing an economic and political instability.
- Power consumption: The miners of the Blockchain spend time and many computer resources to validate transactions.
- Control, security and privacy: Without State regulation, there is no control or security in data sharing, even with smart contracts, for contracts may be violated and, as noted, justice is starting on the path of this technology.
- Integration: Blockchain technology is still new and little used and the creation of a network depends on the acceptance of undertakings to develop internal strategies for, anyway, apply this technology on a large scale. In this context, your scope must be more extensive to consider Blockchain as a network effectively decentralized.
- Cost: the price and the timing of transactions is reduced. On the other hand the cost of initial capital for your application are very high.
- Complex application: your application lacks the meeting of diverse projects which can be a difficult task.
According to Lamonier[53], in 2018, 23% of companies had intended to implement the technology Blockchain in your business. Among them, financial institutions had higher percentage, while 43% of companies were interested, but no study on the subject. The implementation of Blockchain requires more research, but it has the potential to operate large industries and transform the economy.
The steps shown in the following figure on the implementation of a Blockchain, it is worth clarifying the concept of POC-Proof of Concept which is a term used when the Blockchain is in test. Lamonie[54]r explains that many companies are willing to invest in proof of concept for this technology and clarifies that a recent survey, 66% of the experts pointed at you, and the CEOs believe that the Blockchain will be the next digital revolution.
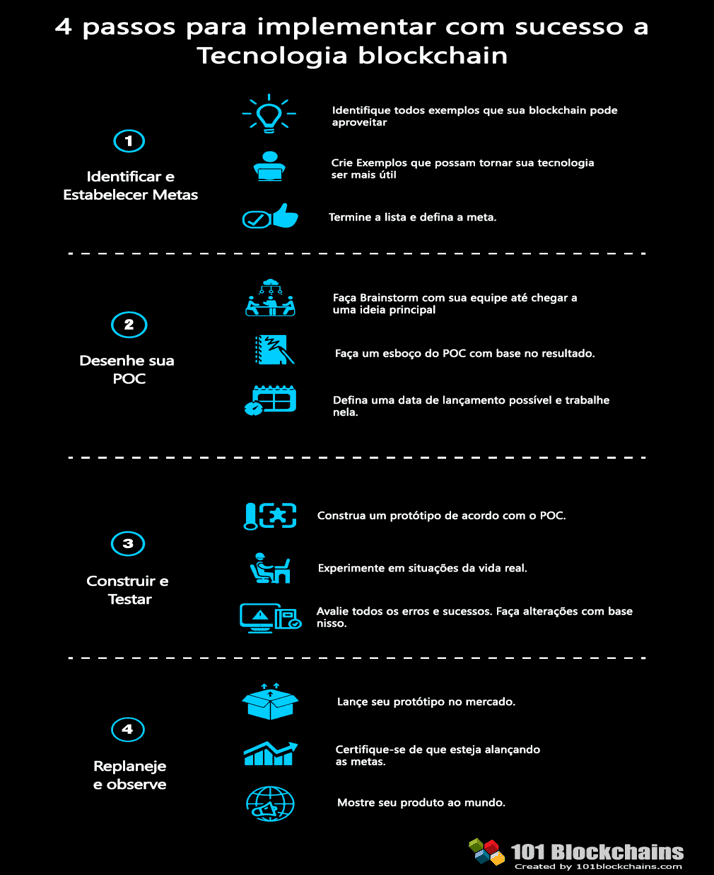
Source: Veronica, 2018
In this context, the banking system is the sector with the largest number of implementations of technology Blockchain successfully, so that the new companies that use Blockchain security can attract investment from traditional banks, of which some have already are adapting to this technology.
Its application in this field enables financial services have greater accuracy and safety in their financial transactions, which ensures a better service to its customers inside and outside the country with great agility.
Within the scope of banking services can be mentioned as benefits reduced costs, shorter settlement time; better data quality; easy and transparent audit, in addition to greater safety.
3. FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
Blockchain technology is best known for supporting the Bitcoin, however features many applications nowadays. This technology represents a permanent record distributed among parties which demonstrates a security measure based on decentralisation of information, mainly focused on the financial market. Its scope has expanded to the custody of any document type.
One of the great advantages of using Blockchain is globalization, because there is no interference from external factors such as data, capital or even the Government. Its technology lies in the custody of the records of transactions, especially economic transactions, stored in a block with an identification number, known as a hash. When the block is full, it is sealed with the hash, determining that block transactions are valid and imodificáveis, starting a new block.
This technology allows the parties, companies or individuals, create contracts, make transactions and move values without relying on intermediaries to ensure the event and establish business in accordance with commercial standards.
It turns out that the banks have studied the implementation of Blockchain in your transactions aiming at reducing costs and speeding up the process of liquidity. Cash, stocks, bonds, securities, shares, contracts and all kinds of assets can be moved and stored securely, and peer to peer, this technology.
Cost reduction and flaws show up as the main points that have led financial institutions, auditing firms and banks to invest in solutions with Blockchains, given that financial intermediaries cost too much for their own operations.
The studies carried out by innovative companies in the area of Blockchain, with sure can reduce the risks of the process of application of Blockchain in the financial environment. The decrease in costs between all the actors in the economy would allow through peer-to-peer network a mass collaboration that would influence our existing arrangements.
The increase in online transactions require greater security for data that can be provided by this technology. Although your innovative nature, the Blockchain offers reasonable assurance to safeguard data, documents and records of financial transactions primarily with security.
The impacts of Blockchain on the consumer’s relationship with financial institutions can be observed through changing focus of the institutions, because the disruptive potential is greater than expected under economic, financial and social. The regulation of Blockchains is necessary to ensure legal relations established in your interior, but can also allow the Government to limit the powers of this technology.
It is understood that Blockchain technology still need to grow and earn credibility in the face of this new virtual market. In this context, new research must be performed to add value to Blockchain and ensure your credibility, enhancing the network and impacting so beneficial in the economy of the country.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES
ABREU, Miguel Tadeu stands at of. Law and Blockchain, what an attorney needs to know about it? Very much! 2018. Available at: https://migueltbertanha.jusbrasil.com.br/artigos/601450372/direito-e-Blockchain-o-que-um-advogado-precisa-saber-sobre-isso-muito
AMARO, Roberto. What is Blockchain: going beyond the bitcoin. 2017. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/blogs/robertoa/2017/11/o-que-e-Blockchain-indo-alem-do-bitcoin/
BISSESSAR, Shiva. Opportunities and risks associated with the advent of digital currency in the Caribbean. 2016. Available at: https://www.cepal.org/en/publications/39860-opportunities and risks-associated-advent-digital-currency-caribbean.
BITCOIN INVESTMENT. What is Blockchain and how it works. Available at: https://bitcoinvestimento.blogspot.com/2017/12/o-que-e-Blockchain-e-como-funciona.html
BRAKEVILLE, Sloane; Bhargav PEREPA, «Blockchain basics: Introduction to distributed ledgers» (in English). IBM.
BRIDGE. Blockchain and your power of disruption. Available at: https://bridgeconsulting.com.br/insights/Blockchain-e-seu-poder-de-disruptura/
BUNTINK, j. p. Using the Blockchain for sharing a ride with decentralised La’Zooz. 2018. Available at: https://www.newsbtc.com/2016/03/22/using-Blockchain-decentralized-ride-sharing-lazooz/
Camara, Michele Pacheco. The Bitcoin is the alternative to traditional means of payment. 2014. 76f.
Chauhan, Vivek. Blockchain applications on the capital markets. 2018. Available at: https://medium.com/pennBlockchain/Blockchain-applications-in-capital-markets-37432d7caa0
COINMARKETCAP, market Capitalizations of cryptographic currency, 2016. Available at: https://coinmarketcap.com/
DESYATOV, Ivan. Bitcoin Blockchain Technology. Return to Criptomoedas. 2018. Available at: http://trocacriptomoedas.blogspot.com/2018/05/tecnologia-bitcoin-Blockchain.html
ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. As the Blockchain can revolutionize the banks. 2018. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Tecnologia/noticia/2018/02/como-o-Blockchain-pode-revolucionar-os-bancos.html
ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. The big banks of the world want to create a digital currency. 2017. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Mercado/noticia/2017/09/os-grandes-bancos-do-mundo-querem-criar-uma-moeda-digital.html
ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. Four advantages of Blockchain for companies. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Empresa/noticia/2017/12/quatro-vantagens-do-Blockchain-para-empresas.html
I AM AN ENTREPRENEUR. What is fintech, the revolution in the financial market. 2018. Available at: https://eusouempreendedor.com/fintech-mercado-financeiro/
Fernandes, Jose Luiz Nunes. Reduction of transaction cost: the Blockchain Technology and the underlying confidence to organizational processes. Available at: https://periodicos.ufpe.br/revistas/SUCC/article/download/236670/30184
FILIPPOZZI, Luigi. Blockchain: a new approach to supply chain 2018. Available at: https://www.ecommercebrasil.com.br/artigos/Blockchain-uma-nova-abordagem-da-cadeia-de-suprimentos/
GOMES, Helton Sen; LAPORTA, Latika. Understand what is Blockchain, the technology behind the bitcoin. G1. 2016. Available at: https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/entenda-o-que-e-Blockchain-a-tecnologia-por-tras-do-bitcoin.ghtml
IBM. Leading the pack in Blockchain banking Trailblazers set the pace. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=GBP03467USEN
IHODL. Blockchain Guide for beginners. 2017. Available at: https://pt-br.ihodl.com/tutorials/2017-06-29/guia-de-Blockchain-para-principiantes/
LARGHI, Nathalia. Banks start using Blockchain in Brazil. 2018. Available in
https://www.valor.com.br/financas/5294143/bancos-iniciam-uso-de-Blockchain-no-brasil.
KIRKLAND, Rik; TAPSCOTT, Don. Taking seriously the Blockchain. 2018. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/getting-serious-about-Blockchain
KOSBA, Ahmed et al. Hawk: the Blockchain model of encryption and smart contracts that preserve privacy. In: IEEE Symposium on security and privacy (SP). IEEE, 2016. p. 839-858.
LACIA, Lucas. Implementation guide to create your business on Blockchain. 101 Blockchains. Available at: https://101Blockchains.com/pt/Blockchain-implementacao/
Wood, Bernard. Blockchain is safe. 2018. Available at: https://portaldobitcoin.com/o-Blockchain-e-seguro/
MAGUIRE, Eamonn. KYC Blockchain utility. Available at: https://home.kpmg/xx/en/home/insights/2018/02/Blockchain-kyc-utility-fs.html
MORGAN, J. P.; WYMAN, Oliver. Uncovering the economic advantage with Blockchain: a guide for asset managers. New York, 2017. Available at: https://www.oliverwyman.com/content/dam/oliver-wyman/global/en/2016/july/joint-report-by-jp-morgan-and-oliver-wyman-unlocking-economic-advantage-with-Blockchain-A-Guide-for-Asset-Managers.pdf
MOURA, Marcelo. Blockchain is the greatest invention in the history of computing, “says Don Tapscott. Época Negócios online. 2018 available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Tecnologia/noticia/2018/05/Blockchain-e-maior-invencao-da-historia-da-computacao-diz-don-tapscott.html
NAKAMOTO, Satoshi. Bitcoin: Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available at: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
NOMURA RESEARCH INTITUTE. Blockchain Technologies and Related Services, Technical Report. Omohundro, s. 2015. Available at: http://www.meti.go.jp/english/press/2016/pdf/0531_01f.pdf
LEARNING PORTAL. Ethereum for beginners. Available at: https://www.Blockchain.com/pt/learning-portal/ether-basics
PRADO, Jean. What is Blockchain? (going beyond the bitcoin). Tecnoblog. 2018. Available at: https://tecnoblog.net/227293/como-funciona-Blockchain-bitcoin/
PRATES, Daniela Magellan. The asymmetries of the international monetary and financial system. Journal of Contemporary Economy, Rio de Janeiro-RJ may/Aug, v. 9, no. 2, p. 263-288, 2005.
PUBLIEDITORIAL. Blockchain: the most disruptive innovation since the invention of the Web. 2017. Available at: https://www.administradores.com.br/noticias/negocios/Blockchain-a-inovacao-mais-disruptiva-desde-a-invencao-da-web/122355/
SILVA, Valsamis Cay; Alves, Gabriel oak Floors; Fernandes, Lucas Schlee. Pair Networks. 2016. Available at: https://www.gta.ufrj.br/ensino/eel878/redes1-2016-1/16_1/p2p/intro.html
SHIN, Laura. How technology bitcoin if integrate? An analysis of strategies 5. Forbes Magazine. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurashin/2016/01/26/how-will-bitcoin-technology-go-mainstream-an-analysis-of-5-strategies/#4ff34ebd4a32
SWAN, Melanie. Blockchain: Blueprint for a new economy. “O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2015
TCU. 033,619 National Congress request/2016-6. Rapporteur Aroldo Cedraz. Johncthayer. 2018. Available at: https://tcu.jusbrasil.com.br/jurisprudencia/582975197/solicitacao-do-congresso-nacional-scn-3361920166/relatorio-582975475
UK GOVERNMENT. Chief Scientific Adviser. Distributed Ledger Technology: beyond block chain. Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/492972/gs-16-1-distributed-ledger-technology.pdf
VIEIRA, Rodrigo; Marinho, Hugo; COUPLES, Vitor Yeung. Blockchain applications in our legal system. Available at: http://tozzinifreire.com.br/assets/conteudo/uploads/startupfinal-595d32735ed50.pdf
YLI-HUUMO, J, Ko D, CHOI, S; PARK, S; SMOLANDER, k. where’s current research on Blockchain Technology? -A Systematic Review. PLoS One 11 (10): 2016. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163477
Z, I, Richard. What is Marketplace? – see the advantages and disadvantages can be found at: https://www.ecommercebrasil.com.br/artigos/marketplace-vantagens-e-desvantagens/
2. NAKAMOTO, Satoshi. Bitcoin: Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available at: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
3. Idem
4. COINMARKETCAP, market Capitalizations of cryptographic currency; 2016. Available at: https://coinmarketcap.com/
5. IHODL. Blockchain Guide for beginners. 2017. Available at: https://pt-br.ihodl.com/tutorials/2017-06-29/guia-de-Blockchain-para-principiantes/
6. NOMURA RESEARCH INTITUTE. Blockchain Technologies and Related Services, Technical Report. Omohundro, s. 2015. Available at: http://www.meti.go.jp/english/press/2016/pdf/0531_01f.pdf
7. Bitcoin investment. What is Blockchain and how it works. Available at: https://bitcoinvestimento.blogspot.com/2017/12/o-que-e-Blockchain-e-como-funciona.html
8. AMARO, Roberto. What is Blockchain: going beyond the bitcoin. 2017. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/blogs/robertoa/2017/11/o-que-e-Blockchain-indo-alem-do-bitcoin/
9. Idem
10. Camara, Michele Pacheco. The Bitcoin is the alternative to traditional means of payment. 2014. 76f. Monograph (Administration)-Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre.
11. Learning Portal. Ethereum for beginners. Available at: https://www.Blockchain.com/pt/learning-portal/ether-basics
12. Larghi, Nathalia. Banks start using Blockchain in Brazil. 2018. Available at: https://www.valor.com.br/financas/5294143/bancos-iniciam-uso-de-Blockchain-no-brasil
13. Idem
14. Fernandes, Jose Luiz Nunes. Reduction of transaction cost: the Blockchain Technology and the underlying confidence to organizational processes. Available at: https://periodicos.ufpe.br/revistas/SUCC/article/download/236670/30184
15. Idem
16. OSBA, Ahmed et al. Hawk: the Blockchain model of encryption and smart contracts that preserve privacy. In: 2016 IEEE Symposium on security and privacy (SP). IEEE, 2016. p. 839-858.
17. ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. As the Blockchain can revolutionize the banks. 2018. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Tecnologia/noticia/2018/02/como-o-Blockchain-pode-revolucionar-os-bancos.html
18. SHIN, Laura. How technology bitcoin if integrate? An analysis of strategies 5. Forbes Magazine. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurashin/2016/01/26/how-will-bitcoin-technology-go-mainstream-an-analysis-of-5-strategies/#4ff34ebd4a32
19. MAGUIRE, Eamonn. KYC Blockchain utility. Available at: https://home.kpmg/xx/en/home/insights/2018/02/Blockchain-kyc-utility-fs.html
20. DESYATOV, Ivan. Bitcoin Blockchain Technology. Return to Criptomoedas. 2018. Available at: http://trocacriptomoedas.blogspot.com/2018/05/tecnologia-bitcoin-Blockchain.html
21. MOURA, Marcelo. Blockchain is the greatest invention in the history of computing, “says Don Tapscott. Época Negócios online. 2018 available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Tecnologia/noticia/2018/05/Blockchain-e-maior-invencao-da-historia-da-computacao-diz-don-tapscott.html
22. Idem
23. KIRKLAND, Rik; TAPSCOTT, Don. Taking seriously the Blockchain. 2018. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/getting-serious-about-Blockchain
24. VIEIRA, Rodrigo; Marinho, Hugo; COUPLES, Vitor Yeung. Blockchain applications in our legal system. Available at: http://tozzinifreire.com.br/assets/conteudo/uploads/startupfinal-595d32735ed50.pdf
25. Idem
26. Idem
27. ABREU, Miguel Tadeu stands at of. Law and Blockchain, what an attorney needs to know about it? Very much! 2018. Available at: https://migueltbertanha.jusbrasil.com.br/artigos/601450372/direito-e-Blockchain-o-que-um-advogado-precisa-saber-sobre-isso-muito
28. Idem
29. TCU. 033,619 National Congress request/2016-6. Rapporteur Aroldo Cedraz. Johncthayer. 2018. Available at: https://tcu.jusbrasil.com.br/jurisprudencia/582975197/solicitacao-do-congresso-nacional-scn-3361920166/relatorio-582975475
30. MOURA, Marcelo. op. cit.
31. Idem
32. FILIPPOZZI, Luigi. Blockchain: a new approach to supply chain 2018. Available at: https://www.ecommercebrasil.com.br/artigos/Blockchain-uma-nova-abordagem-da-cadeia-de-suprimentos/
33. IBM. Leading the pack in Blockchain banking Trailblazers set the pace. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=GBP03467USEN
34. Chauhan, Vivek. Blockchain applications on the capital markets. 2018. Available at: https://medium.com/pennBlockchain/Blockchain-applications-in-capital-markets-37432d7caa0
35. BUNTINK, j. p. Using the Blockchain for sharing a ride with decentralised La’Zooz. 2018. Available at: https://www.newsbtc.com/2016/03/22/using-Blockchain-decentralized-ride-sharing-lazooz/
36. Chauhan, Vivek. op. cit.
37. PRATES, Daniela Magellan. The asymmetries of the international monetary and financial system. Journal of Contemporary Economy, Rio de Janeiro-RJ may/Aug, v. 9, no. 2, p. 263-288, 2005.
38. BISSESSAR, Shiva. Opportunities and risks associated with the advent of digital currency in the Caribbean. 2016. Available at: https://www.cepal.org/en/publications/39860-
opportunities-and risks-associated-advent-digital-currency-caribbean >.
39. MORGAN, J. P.; WYMAN, Oliver. Uncovering the economic advantage with Blockchain: a guide for asset managers. New York, 2017. Available at: https://www.oliverwyman.com/content/dam/oliver-wyman/global/en/2016/july/joint-report-by-jp-morgan-and-oliver-wyman-unlocking-economic-advantage-with-Blockchain-A-Guide-for-Asset-Managers.pdf
40. I AM AN ENTREPRENEUR. What is fintech, the revolution in the financial market. 2018. Available at: https://eusouempreendedor.com/fintech-mercado-financeiro/
41. GOMES, Helton Sen; LAPORTA, Latika. Understand what is Blockchain, the technology behind the bitcoin. G1. 2016. Available at: https://g1.globo.com/economia/noticia/entenda-o-que-e-Blockchain-a-tecnologia-por-tras-do-bitcoin.ghtml
42. MORGAN, J. P.; WYMAN, Oliver. op. cit.
43. ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. The big banks of the world want to create a digital currency. 2017. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Mercado/noticia/2017/09/os-grandes-bancos-do-mundo-querem-criar-uma-moeda-digital.html
44. MORGAN, J. P.; WYMAN, Oliver. op. cit.
45. Z, I, Richard. What is Marketplace? – see the advantages and disadvantages can be found at: https://www.ecommercebrasil.com.br/artigos/marketplace-vantagens-e-desvantagens/
46. ÉPOCA NEGÓCIOS ONLINE. Four advantages of Blockchain for companies. Available at: https://epocanegocios.globo.com/Empresa/noticia/2017/12/quatro-vantagens-do-Blockchain-para-empresas.html
47. Idem
48. Idem
49. Idem
50. GARCIA, Ezekiel. The main advantages of the Blockchain technology. Bitcoin’s Guide. Available at: https://guiadobitcoin.com.br/as-principais-vantagens-da-tecnologia-Blockchain/
11th Wood, Bernard. Blockchain is safe. 2018. Available at: https://portaldobitcoin.com/o-Blockchain-e-seguro/
52. Idem
53. LACIA, Lucas. Implementation guide to create your business on Blockchain. 101 Blockchains. Available at: https://101Blockchains.com/pt/Blockchain-implementacao/
54. Idem
[1] Bachelor of Business Administration, Professional Trader.
Posted: March, 2019.
Approved: March, 2019.