ORIGINAL ARTICLE
POROCA, Felipe Boueri [1]
POROCA, Felipe Boueri. The SAP S/4HANA system and digital transformation in organizations. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento. Year. 08, Ed. 01, Vol. 01, pp. 54-77. January 2023. ISSN: 2448-0959, Access link: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/technology-en/digital-transformation, DOI: 10.32749/nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/technology-en/digital-transformation
ABSTRACT
In the midst of technological advances and recurrent cyber attacks that affect the data systems of different organizations, the search for automation and acceleration in a structured way are the triggers for the beginning of the modernization of processes in Information Technology (IT). The SAP system, of German origin, is considered a strong system and has been used by medium and large companies, national and multinational. It has specific characteristics, such as automation and agility for internal processes, use of robots and Artificial Intelligence (AI), all of which is stored in the cloud. A SAP system promotes improvements in customer service, inventory control and purchasing needs, avoids or minimizes product losses, streamlining sales processes, asset management and allowing greater ease in consolidating information, including for administrative, accounting and financial sectors. In this context, SAP S/4HANA, or “SAP Business Suite 4 SAP HANA”, is the newest generation of the set of business solutions; is the most advanced version, created to simplify all transactions between organizations, as well as in their internal processes. As a research methodology, bibliographical research was adopted to answer the following question: how to secure data, optimize internal processes and ensure greater agility and savings for organizations? The objective of the article is to present the concepts inherent to each of the mentioned aspects, and to demonstrate the effectiveness of using the SAP S/4HANA system.
Keywords: Digital Transformation, Process Automation, Artificial Intelligence, S/4HANA System.
1. INTRODUCTION
The modernization of operational and data systems of large companies requires constant updating, in order to maintain their competitive advantage, in addition to data security and their organizational processes. Among the issues inherent to this modernization are cyber attacks, causing blocking and/or theft of data, the slowness of separately operated business processes and the consequent need for maintenance, generating delay and higher costs.
The SAP system is an ERP-type Business Management software – Enterprise Resource Planning, created by the German company called SAP AG. Its original name is Systeme, Anwendungen und Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung. According to Capelli et al. (2014, p. 1), has been widely used in recent years, allowing for greater business development, as it promotes “the integration of all data and processes into a single database”.
In a study carried out by Deloitte (n.d.), it was shown that, although the market, at the macro level, still does not have a real understanding of “the potential of Cyber, there is an understanding of most companies that, in an environment of greater cybersecurity, there are opportunities to transform and drive business strategy through the adoption of new technologies.”
In this perspective, having intelligence in this new universe means introducing the digitization of processes within data analysis and in a cheaper way, which is the conception of this author, based on his experiences as a systems analyst and SAP System specialist in a company Brazilian specialist in Information Technology (IT).
There are numerous advantages of using SAP, including the integration of data and information coming from all departments of an organization, protected according to the best technological practices and even preventing duplicate data from being imputed. In addition, there is managerial access to information updated daily, fed by the different sectors of the company, optimizing decision-making.
It is in this context that this bibliographic review article proposes the following question: how to secure data, optimize internal processes and ensure greater agility and savings for organizations? As an objective, it intends to present the concepts inherent to each of the mentioned aspects and demonstrate the effectiveness of using the SAP S/4HANA system.
2. DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
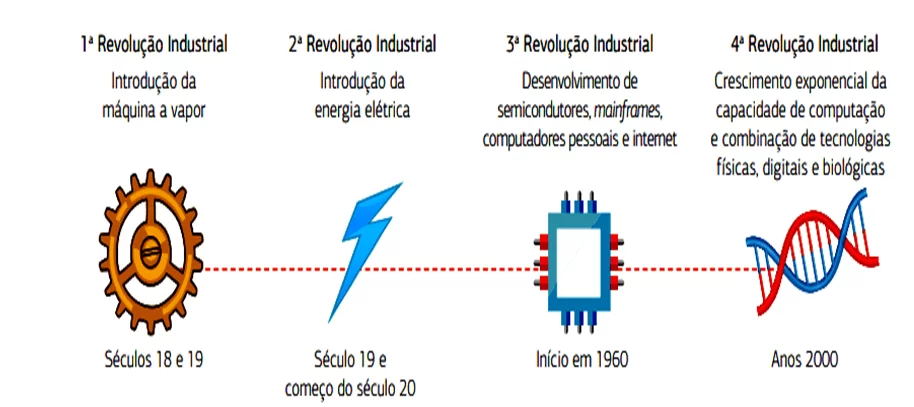
The digital transformation represents evolution, adaptation, perception of new opportunities and greater attention to new customer needs. According to SAP (s.d.a), over time, four were the Industrial Revolutions that humanity went through, among them: the invention of steam engines, the Ford system and its assembly line of mass automobiles, the invention of computers , and now, the age of digitization, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. The four industrial revolutions
However, there are some aspects that need to be clarified in order to dilute some ideas that may permeate the collective imagination about what exactly digital transformation means.
In this regard, Furr; Ozcan and Eisenhardt (2022, p. 2-3) refer to the emergence of several companies born in the digital world and known to be globally active, including: “Google, Booking.com, Alibaba and Amazon, as well as billion-dollar unicorns such as Uber, Pinduoduo, Airbnb and TikTok have come to dominate the collective imagination.”
At first, the idea was that the digital transformation “changes everything”, that is, it appears as a rupture with the forms and models of business that we have known so far, a rupture that, theoretically, extinguishes the business format known until then, face “as more data, connectivity and digital intelligence will eradicate global borders and overthrow the old industrial order” (FURR; OZCAN and EISENHARDT, 2022, p. 3).
However, digital transformation does not “change everything”, which is confirmed by some examples given by Furr; Ozcan and Eisenhardt (2022, p. 2), among them:
-
-
- a transportadora dinamarquesa Maersk usa o blockchain para fazer o que fazia antes do blockchain, ou seja, enviar com mais eficiência ao redor do mundo;
- a empresa holandesa de bebidas Heineken está usando a transformação digital para interagir melhor com os clientes, criar produtos e competir, mas ainda faz cerveja e a envia em caminhões;
- mesmo em indústrias pioneiras digitais – como mídia e viagens – onde os players digitais têm criado uma disrupção significativa, muitas empresas familiares coexistem e até prosperam: o New York Times e o Huffington Post coexistem, enquanto o Airbnb de forma alguma eliminou o Marriott.
-
With these examples, Furr; Ozcan and Eisenhardt (2022) warn of the fact that, despite significant changes in their businesses, most organizations that were willing to accept and adopt digital transformation strategies remain strengthened in their segments. Therefore, it is essential that managers of different organizations are alert and open to market changes, including technological advances and how these impact the life of society as a whole.
For the Fia Business School (2021), digital transformation consists of changing the mindset of companies, many of which have modernized their marketing performance processes to keep up with the technological advances that have impacted the lives of people and organizations since their inception, that is, since “… the industrial revolution and arriving at artificial intelligence and the internet of things…”.
Digital transformation comprises more than “the creation of new tools, mechanisms, devices and services that make our lives easier in some way” (FIA BUSINESS SCHOOL, 2021). In this sense, the existence of some pillars of digital transformation stands out (FIA BUSINESS SCHOOL, 2021):
- Focus on the consumer: understanding and meeting the preferences of its target audience is an aspect of guiding a company’s actions;
- Constant feedbacks: through the failures themselves, the product or service offered can be improved;
- More agile deliveries: from offering a product/service, to correcting flaws in its processes, meeting the needs of its customers must be carried out efficiently and effectively;
- Adaptation to changes: an organization must have agile deliveries, be flexible with regard to constant changes and resilient in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
The fact is that digital transformation consists of adapting to the new global context of the market and society, based on the use of all technology at the service of companies and society as a whole. Among the possible contributions with digital transformation, described by Fia Business School (2021), are:
- Optimize communication quickly and assertively;
- Integration of different sectors, making teams and sectors more collaborative;
- Access to complete information;
- Automation of internal processes and reduction of bureaucracy;
- Favoring decision-making based on system data;
- Offer more instantaneous channels to customers, optimizing their relationship with the company;
- Facilitate management through performance analysis of sectors and people.
3. PREVENTIVE INVESTMENTS FOR CYBER ATTACKS IN THE UNITED STATES
Among the factors that lead organizations to invest in data security and improvements in their systems, cyber attacks stand out the most. At the same time that technologies evolve, their vulnerabilities also grow, causing malicious people to specialize in the invasion and theft/blocking of data, whether on devices of individuals or operating systems within companies.
Chart 1 demonstrates the emergence of viruses and malware, and their evolution to the present day.
Table 1. Emergence of Viruses and Malware between 1980 and 2012
| Date | Type of Virus/Malware | History/Creator | Source of query |
| 1982 | Elk Cloner
|
It was the first massively used virus. It hit computers with the Apple II system. | Pimentel (2021) |
| 1984 | Core Wars | It was created at Bell Computers Laboratories. Stronger than previous viruses, it compromised the machines’ RAM memory. | Pimentel (2021)
|
| 1985 | Brain and Bouncing | Considered the first virus capable of infecting personal computers. | Pimentel (2021)
|
| 1989-1990 | Trojan or Cavalo de Troia.
Considered the first ransomware. |
It was developed by Joseph Frank Popp.
Its purpose was to infect computers. At first, it only affected the Windows platform. As it evolved, it began to reach the Apple, Android and Linux platforms, and at present, even smartwatches. |
Pimentel (2021, p. 3-4); Formasier (2020); Lema and Freitas (2021) |
| 1992 | Virus Michelangelo | Created to be inactive and undetectable until March 6th, the artist’s birthday, and from that date, it corrupted the files, randomly overwriting characters. | Pimentel (2021, p. 3-4)
|
| 1999 | Virus Melissa | Created by David L. Smith, it is considered the first to employ social engineering to be spread, which occurs via email, starting from one of the victim’s contacts. | Pimentel (2021, p. 3-4)
|
| 2000 | Virus I love you | It infected millions of Windows users, including the Pentagon and the CIA. It spread via email, containing an attachment called Love-letter-for-you, which, when executed, relayed the message to all the user’s contacts. | Pimentel (2021, p. 3-4) |
| 2005-2006 | The company Trend Micro, in Russia, discovered malware that compresses and overwrites some types of files, causing data hijacking.
The goal was to ask for data rescue. |
Brito (2016) | |
| 2012 | Spread of cases across Europe and North America. | Brito (2016) |
Source: Teodoro (2022, p. 223).
In turn, the biggest cyber attacks suffered by large US companies in recent years are represented in Table 2.
Table 2. Major Cyber Attacks on US Businesses 2010 – 2021
| Attack date | Target organization | Reach | Losses | Origin of attacks |
| 2013 | Hackers hack into US government data
|
US government systems | Between US$ 24 to US$ 120 billion dollars (R$ 57.9 to R$ 289.5 billion reais). | Invasion attributed to the Chinese army, both by the US government and by the world media. |
| 2017 | Microsoft Windows System | Affected 200,000 computers in over 150 countries | $25 million dollars to Windows system users/victims. | |
| 2021 | Colonial Pipeline, the largest North American gas pipeline, which distributes more than 2.5 million barrels of oil per year (diesel, gasoline and jet fuel) | The company’s data network was shut down and 100GB of pipeline information was stolen | $5 million paid in ransom, for returning data | It was assigned to the Dark Side group. |
| 2021 | JBS, food industry giant | Data hacking and leakage | $11 million paid in ransom for returning data | Invasion attributed to Russian group REvil (known as Sodinokibi |
Source: Prepared by the author based on Santos (2022).
Faced with this reality, research carried out by Deloitte (n.d.) on the consequences arising from cyber attacks suffered by organizations over time demonstrate that managers, in general, awaken to the need and urgency regarding the necessary investments and reformulations in Information Technology (IT), in order to guarantee security, privacy, agility in processes and optimization of financial resources.
The aforementioned survey talked to 122 companies, pointing out that, among the areas to invest, the following responses/indices were obtained (DELOITTE, n.d.):
- 62% intend to improve their Customer marketing area;
- 59% will invest in the automation of operational processes;
- 58% bet on remote work;
- 58% will invest in real-time indicators;
- 57% aim to optimize their paperless routines;
- 56% consider security with public/hybrid cloud;
- 52% aim to expand its digital communication and relationship channels;
- 49% intend to improve their risk monitoring and prevention;
- 43% will invest in research and development ecosystem;
- 41% intend to invest in integrated management of their supply chain.
It is based on these results that the resources and tools that can enable the necessary improvements to the information systems of different organizations, involving the SAP S/4HANA System, will be addressed.
4. CYBER SECURITY AND DATA STORAGE
Data security is something that “has always been at the top of the experts’ agenda” (IBM, 2022, apud TEODORO, 2022, p. 205).
According to Longo (2022), the development of “robust mechanisms” that guarantee digital protection has always been and still is, a great challenge for organizations, since the evolution of new technologies is closely followed by the emergence and evolution of digital crimes, as is the case with viruses in different versions and, above all, with ransomware attacks.
They are malware developed by increasingly daring hackers, who work on software vulnerabilities, being one of the reasons for the constant search for full data and information security (LONGO, 2022).
Based on the vast literature available on the subject, this is a legitimate concern, regarding the advancement of versions and technologies available for devices and software that we have access to today, as well as with regard to the different malicious activities that invade and compromise internal networks, steal user data, affect organizations’ digital assets and even paralyze their systems, many of which cause huge losses.
Among the changes in the vision of companies’ assets, human capital has grown to a level of great relevance, as well as the data and information contained in their systems. For the Federal Court of Accounts – TCU (2012, p. 10),
Informações adulteradas, não disponíveis, sob conhecimento de pessoas de má-fé ou de concorrentes podem comprometer significativamente, não apenas a imagem da instituição perante terceiros, como também o andamento dos próprios processos institucionais. É possível inviabilizar a continuidade de uma instituição se não for dada a devida atenção à segurança de suas informações.
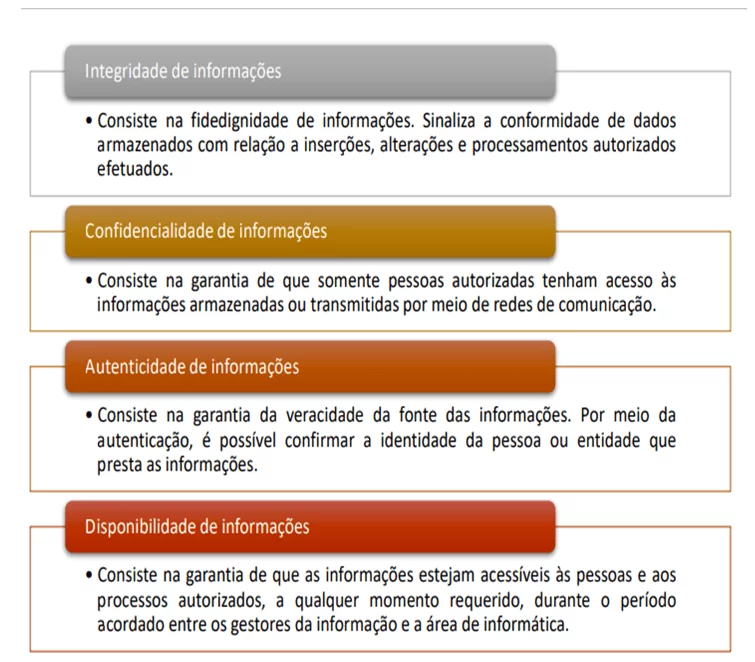
According to the information security concepts described by TCU (2012), integrity, confidentiality, authenticity and availability of information can be mentioned, as explained in table 3.
Table 3. Information Security Concepts
In order for all these needs to be met, it is necessary to pay attention to the main technologies of Digital Transformation, among which we can mention: cloud computing, business management, social media, mobility, Big Data (SOUZA, 2020).
According to Microsoft (2021, apud BARROS, 2021, p. 30),
a computação em nuvem é definida como um conjunto de serviços de computação, incluindo servidores, armazenamento, bases de dados, networking, software, analíticas e inteligência através da Internet (a nuvem) para oferecer inovação mais rápida, recursos flexíveis e economias de escala, onde se paga apenas pelos serviços que se utiliza na nuvem, reduzindo os seus custos nas operações, gerir a infraestrutura de forma mais eficiente, e escalar, à medida que o negócio precisa de mudança.
Since digital security strategies are part of the digitization process, it is worth highlighting the “steps, actions and techniques that promote the protection of systems, programs, networks and equipment” (LONGO, 2022).
Figure 2. Structure of cloud computing
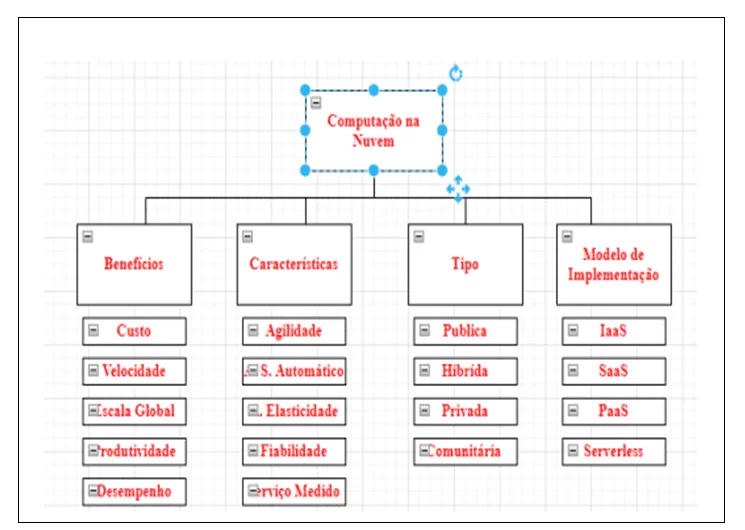
For Barros (2021, p. 29), it can be defined that cloud computing is:
é um modelo para permitir o acesso conveniente e a pedido da rede, a um conjunto partilhado de recursos de computação configuráveis, que podem ser rapidamente aprovisionados e libertados com o mínimo esforço de gestão ou interação do prestador de serviços.
Cloud computing has been used by public and private companies and government agencies, as it consists of being a computing model whose capacity confers resilience and cost optimization, allowing the performance of procedures that meet different needs. Among the benefits offered by cloud storage are “automated tools to assemble, connect, configure and reconfigure virtualized resources, and also, providing a significant increase in privacy and data protection requirements of individuals and companies” (BARROS, 2021, p . 21).
Still, with regard to digital transformation, the pillars that compose it, described by Souza (2020):
- Customer: is the fundamental agent for the success and longevity of the entire organization;
- Competition: managers must modernize their view of the competition, given the innovations brought by digital transformation, including digital platforms, which allow direct contact with their target audience;
- Data: since data sources have become unlimited, it is necessary to convert them into information that optimize decision-making processes, according to the organization’s strategies;
- Value: it is necessary to have managerial awareness about the renewal of solutions, in order to allow the desired results to be obtained;
- Business: the modernization of the management of a business comprises all the processes that involve it, from the selection of personnel, as well as training and performance analysis;
- Health: a sector highly benefited by the digital transformation, today it has modern equipment, allowing better diagnosis and treatment of different diseases, including access to disease histories and reports of patients from any location around the world;
- Education: the personalization of distance learning digital platforms stands out; the virtual environments allow differentiated assistance at a distance, courses and individual or collective interactions, in addition to the dissemination of didactic materials;
- Consumption: new virtual habits offer new and innumerable modalities of consumption and, based on algorithms created by electronic channels, an individual’s search history ends up showing personalized offers.
5. TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANTAGES OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
The expression Artificial Intelligence (AI) appears in 1956, used by John McCarthy, who intended to teach machines to perform a certain function autonomously, that is, to make information systems capable of reproducing the way human intelligence works (ALVES, 2022, p. 27).
Based on statistics and mathematical principles, it was defined as a subfield of Computer Science, which aims to make machines more intelligent and autonomous and that works according to programming algorithms that allow them to understand patterns and make decisions alone (ENGINEERING DO BRASIL, 2022 ).
Alves (2022, p. 07) argues that “AI has overcome the barriers of the impossible, making business faster, smarter and safer”. Haenlein and Kaplan (2019, apud ALVES, 2022, p. 24) refer that AI is the ability of a system to interpret external data, learning them to “mimic specific tasks and processes similar to human knowledge”.
Its evolution comes from the growth of the integrated circuit and the development of personal computers, and, at present, it collaborates in the protection of businesses in different segments (ENGINEERING DO BRASIL, 2022).
Among the various possibilities of use for AI, highlighted by Engineering Do Brasil (2022), are:
- Personal assistants: when used for direct communication with humans, such as, for example, in electronic messages and access to bank accounts. Its programming allows you to respond to requests made and automate the tasks resulting from them;
- Monitoring: in security systems, their algorithms are programmed to issue alerts and inform that something wrong may be happening;
- Customer service: applies, for example, to electronic telephone menus where specific requests must be made, to direct the customer to the sector of interest;
- Behavioral analysis of consumers: allows greater perception of the type/style of customer, optimizing the marketing sector’s campaigns to better meet the expectations of this customer. It even collaborates for the grouping of customers who demonstrate the same desires.
Among the benefits provided by the use of AI in the aforementioned modalities is the increase in the productivity of organizations.
6. ERP SYSTEM
An ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning system “is a solution for optimizing all the organization’s operational processes, allowing greater efficiency and productivity, in addition to cost reduction” (BRESSANIN, 2021, apud TEODORO, 2022, p. 207). It is a management system that properly supports the integration of the various areas of an organization, including: purchases, sales, inventories, administration, human resources, management levels and direction, all on a single platform.
Valentine et al. (2014, p. 113), explain how the architecture of the ERP System works. They teach that every ERP system has a “single database, which operates on a common platform, which interacts with an integrated set of applications, consolidating all business operations in a simple computational environment”.
With this, they use flatter and more flexible operational structures, providing greater consistency to the information entered in the system and optimizing the decision-making process of the higher levels of the organization. Despite being considered a more generic type of solution, ERP systems, in addition to offering processes that include the best practices for business, allow, based on their functionalities, to obtain gains in productivity and speed for the company that implements them, due to the fact that they can be customized, according to the needs of the contracting company (VALENTIM et al., 2014).
Among the functionalities offered by an ERP System, the basic ones comprise a total of 7, which facilitate communication between the different units. The maintenance management module, which comprises 5 other features, is not related to the first features (VALENTIM et al., 2014). Among the great advantages of using an ERP system are updates, which are always possible, as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3. Survival of an ERP System
In turn, Table 4 highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using the ERP system
Table 4. Advantages and disadvantages of the ERP system
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Eliminate the use of manual interfaces | Using an ERP alone does not make a company truly integrated |
| Optimize information flow and quality within the organization | High costs that often do not prove the cost/benefit ratio |
| Optimize the decision-making process | Package vendor dependency |
| Eliminate activity redundancy | It makes modules dependent on each other, if the system fails, the whole company can stop |
| Reduce response time limits | Greater complexity in implementation |
| Reduce the time of management processes | Increased difficulty in updating the system |
Source: Capelli et al. (2014, p. 4).
7. SAP SYSTEM
Of German origin, the company Systems, Applications, Products in Data Processing – SAP is today “one of the world’s leading producers of software for managing business processes” (PORTAL IDEA, n.d.). Created in 1972, the SAP company emerged from the union of five IBM consultants, who envisaged the development of a “standard software package to run on the mainframe”.
After a few versions, the SAP system (System Analysis Programmentwicklung) appears, software that consists of the Development of Programs for Systems Analysis and that avoids duplicate data records, in addition to unifying and centralizing all the departments of a company, since , on a daily basis, is constantly fed with new data/information by its collaborators (ROSA, 2021).
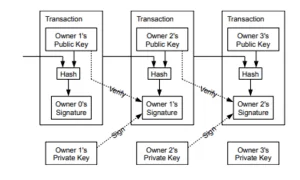
A SAP system consists of the development of “several fully integrated modules, which cover virtually all aspects of business management”, bringing together the following characteristics: “custom-made system; modular; online information; information hierarchy; integration with different areas of the company” (ROSA, 2021, p. 2). Its three-tier client-server architecture is a configuration that allows for the flexibility and scalability necessary for optimal execution, with each tier consisting of presentation, application, and database.
In this way, the SAP system provides chain facilities to the internal processes of an organization, through easy access to updated data, greater agility, operational efficiency, agile experiences for customers, ease of management and decision making, and consequent increase in profits.
It is important to point out that SAP has a policy that the information contained in its database “is not visible nor can it be extracted directly without proper authorizations and credentials. Therefore, given these two reasons, all communication with the outside world is (and should always be) via the SAP application system and not through the DB” (ROSA, 2021, p. 12).
In turn, an SAP ERP system is a product considered by specialists as “central in the infrastructure of a business” (ROSA, 2021, p. 13). The existing integration concentrates all the information entered into this system on a daily basis, allowing the management areas, such as: administration, accounting, finance, purchasing, storage, sales, human resources, to develop their activities with the necessary security for the proper functioning of the company.
The main purpose of a SAP ERP System is to provide integrated solutions, functionalities, centralization and agility of information, as well as protection against eventual corruption actions and integration with “partner systems, among them, can be mentioned the software Oracle BS, Outsystems, Microsoft TibCO etc.”, (ROSA, 2021).
Among the many functionalities of the SAP ERP System, Motta; Silva and Castor (2020) refer to the security provided by this system, which, combined with the use of the cloud, allows for significant improvements to Compliance processes and management, aiming at replacing the Governance, Risks and Compliance (GRC) suite. Among the attributes that the use of the cloud offers to Compliance are:
controle de acesso, gestão de riscos, controles internos, governança e integridade em sistemas SAP que se utilizam da Computação em Nuvem (in cloud). Por fim, destaca-se que, com o IAG, é possível mitigar riscos associados a conflitos de segregação de funções (SoD) e ao acesso crítico para soluções locais (on premise) e na nuvem (in cloud). Tais soluções possuem a característica de residirem em sites fora das fronteiras físicas das organizações (MOTTA; SILVA e CASTOR, 2020, p. 55).
The SAP ERP system adapts to the customer’s reality and, for that, it only needs adjustments in the operational modules, since it serves the following areas: “management of human capital; production planning; materials management; project system; sales and distribution; maintenance; finance and control; quality management” (ROSA, 2021, p. 4).
It is considered “a reservoir system of very valuable information, whose use is restricted to ‘operational analysts’” (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018, p. 25). However, the same authors point out that all the success in efficiently conducting the processing of operational transactions and the transparency conferred by the SAP ERP system does not reduce the main deficiencies in the relationship between the management systems of its database based on it.
8. SAP SYSTEM AND ITS EVOLUTION
Faced with the emergence of new technologies, especially from the internet, changes began to reach, with increasing speed, people’s lives, whether in the personal or within organizations. In this sense, Bhattacharjee et al. (2018) refer that, until the 1970s, the existing departments in companies operated practically in isolation, which made the activities and the good performance of the management of the different areas much more laborious and, in turn, of the direction and decision-making.
Since different technologies brought agility to internal organizational processes, the introduction of SAP ERP, which took place almost 40 years ago, allowed the synchronization of areas and departments in different sectors – whether industrial, commercial or services – raising skills for growth of business, in general, and all of this is due to the creation of a database as a technological basis (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018).
During all this time, according to Bhattacharjee et al. (2018, p. 26),
diferentes especialistas trabalharam no desenvolvimento de vários programas de armazenamento de dados (EDW) dos quais os dados de um ou de vários SAP ERP são extraídos, transformados e carregados (ETL), em um grande banco de dados que se torna a fonte primária para todas as análises e suporte à decisão gerencial dentro da organização.
Among the verified weaknesses are: the data latency associated with the ETL process, which makes real-time decision-making unfeasible, and also the fact that it is a solution that prevents business users from being able to trace the root cause of any problem that may be observed in the transaction system (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018).
To better illustrate the composition of a SAP S/4HANA system, figure 3 is inserted.
Figure 3. Modules of an SAP S/4HANA System
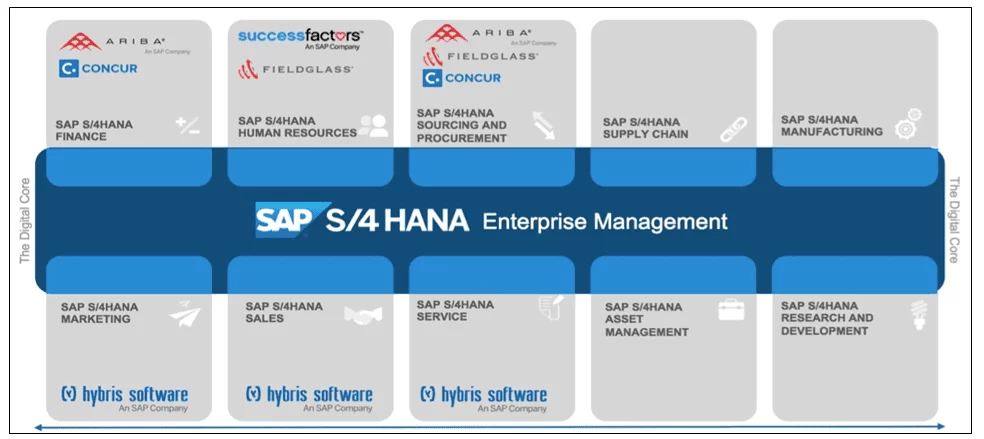
Although it is not obvious, it takes a great effort to develop more up-to-date versions of an SAP ERP system, in order to not only meet new needs, but, at the same time, correct any flaws/deficiencies that have been verified. For technology specialists and professionals, achieving the ambitious goals of companies and businesses are highly challenging tasks, as reported by Bhattacharjee et al. (2018).
In this sense, the creation of an in-memory database, such as SAP HANA, appears as a simple but fundamental evolutionary step, since it allowed product managers to design a business system that serves several objectives, that is, both to transaction processing as well as analytical processing, all in a single database (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018).
It was in 2015 that the company SAP launched its first ERP based on SAP HANA, focusing on financial processes, and which was branded as SAP S/4HANA 1503, or SAP Simple Finance. From this, new versions emerged to include all functional processes of organizations, leading their customers to also adopt the same type of SAP S/4HANA system (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018).
Figure 4 demonstrates the different versions of SAP S/4HANA.
Figure 4. Evolution of SAP S/4HANA

According to the explanation of Bhattacharjee et al. (2018, p. 27),
SAP S/4HANA é a abreviação de SAP Business Suite 4 SAP HANA, é a mais nova geração do conjunto de soluções empresariais (Business Suite) da SAP. […] É um produto novo, desenvolvido na plataforma in-memory que é a mais avançada do momento – SAP HANA – e nos princípios modernos de design com a experiência de usuário (UX) do SAP Fiori.
SAP S/4HANA simplifies all transactions such as “customer adoption, data model, user experience, decision making, business processes and models) and innovations (Internet of Things, Big Data, enterprise networks and “Mobile- First”,” collaborating on the necessary improvements in the management of organizations’ businesses, promoting a greater digital and commercial economy, in addition to keeping all those with common interests connected (BHATTACHARJEE et al., 2018, p. 27).
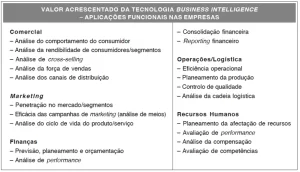
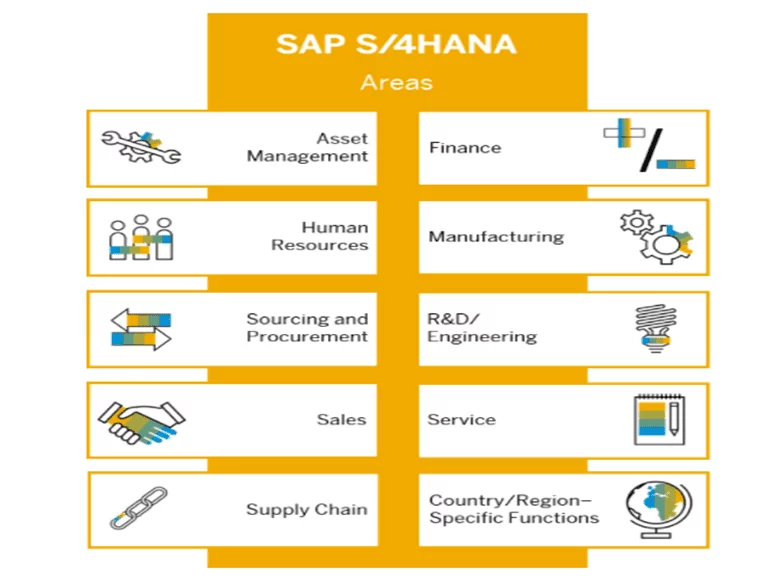
Among the modules contained in S/4HANA, Bhattacharjee et al. (2018), highlight: finance and controllership, human resources, purchasing, supply chain, manufacturing, marketing, sales and distribution, services, asset management, research and development, taxes and location, as shown in figure 5.
Figure 5. S/4HANA modules
9. CONCLUSION
The new scenario created by the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic stirred up themes that were already known to companies, but which were dormant. With regard to Information Technology, its requirements and volatility, it is important to reflect on the level at which organizations around the world are positioned, with regard to innovation and transformation in business.
It is essential that companies invest in new technologies and subsequent updates, whether in equipment, software or systems that allow their maintenance and projection in their segment of activity, or they will be doomed to failure.
Investing in technology is to bring about improvements in your internal processes, speed up deliveries and make life easier for the user, resulting in business projection, increased revenue and more agility for corporations.
The adoption of ERP systems, such as SAP S/4HANA, is a great example of this meeting between success and prosperity, linked to technology.
SAP can bring improvements in aspects such as customer service, inventory organization, purchasing processes and reducing product losses to a minimum, in addition to agility in sales processes, ease of asset management, optimizing tax calculations and the consolidation of information at what may be a global level.
Thus, it is concluded that smart companies are those that choose to adopt innovative technologies to obtain more satisfactory results, with greater speed and economy.
REFERENCES
ALVES, Afonso Violante. O potencial da Inteligência Artificial na Gestão. Dissertação (Mestrado em Gestão com Especialização em Gestão de Serviços) – Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Católica Porto Business School. Porto, 2022.
BARROS, Inocêncio Neto. Proteção de dados na computação em nuvem. Dissertação (Mestrado em Informática) – Instituto Superior de Tecnologias Avançadas de Lisboa. Lisboa, 2021.
BHATTACHARJEE, Deb; KHANDALKAR, Vishal; THOMPSON, Falguni; VAZQUEZ, Guillermo B. Logistics with SAP S/4HANA. An Introduction. Satzpro, Krefeld (Alemanha), 2018.
CAPELLI, Andressa Lacerda; STORK, Emanuela; SCHUNSKI, Fernanda; TOAZZA, Mieli; LEONI, Thais. Implementação e avaliação do sistema ERP-SAP na empresa JOHN Deere Brasil – fábrica de tratores. Caderno de Administração, vol. 8, n. 1., p. 38-49, 2014. Disponível em: https://revistas.pucsp.br/index.php/caadm/article/view/21135. Acesso em: 02 jan. 2023.
DELOITTE. Investimento em segurança cibernética pode acelerar a transformação digital no Brasil, aponta estudo da Deloitte. Deloitte, s.d. Disponível em: https://www2.deloitte.com/br/pt/footerlinks/pressreleasespage/Release-Estrategias-Futuro-Cibernetico.html. Acesso em: 16 nov. 2022.
DENECKEN, Sven. SAP S/4HANA – Frequently Asked Questions – Part 9 – Q42015 update. SAP Community – Blog, novembro de 2015. Disponível em: https://blogs.sap.com/2015/11/16/sap-s4hana-frequently-asked-questions-part-9-q42015-update/. Acesso em: 15 dez. 2022.
ENGINEERING DO BRASIL. Inteligência Artificial para negócios: quais os seus impactos positivos? Engineering The Digital Transformation Company, novembro de 2022. Disponível em: https://blog.engdb.com.br/inteligencia-artificial-para-negocios/. Acesso em: 22 nov 2022.
FERRETTI, Valdomiro Coimbra. SAP Activate: A nova metodologia para implementar ERP SAP alinhada com Métodos Ágeis. Slide Player, 2017. Disponível em: https://slideplayer.com.br/slide/12222236/. Acesso em: 15 dez. 2022.
FIA BUSINESS SCHOOL. Transformação Digital: O que é, Principais Causas e Impactos. Fia Business School, junho 2021. Disponível em: https://fia.com.br/blog/transformacao-digital/#:~:text=Transformação%20digital%20é%20uma%20mudança,sido%20impactada%20por%20esse%20processo. Acesso em: 12 dez. 2022.
FURR, Nathan; OZCAN, Pinar; EISENHARDT, Kathleen M. O Que é a Transformação Digital? Tensões Fundamentais enfrentadas pelas Empresas estabelecidas no Cenário Mundial. Iberoamerican Journal of competitive intelligence, vol. 12, n. 01, p. e0410, 2022. Disponível em: https://iberoamericanic.org/rev/article/view/410/477. Acesso em: 16 nov. 2022.
LONGO, Marcelo. A relação entre a transformação digital e a cibersegurança. Nextcode Blog, 2022. Disponível em: https://nxcd.com.br/blog/2022/05/a-relacao-entre-a-transformacao-digital-e-a-ciberseguranca. Acesso em: 16 nov. 2022.
MARRA, Fabiane Barbosa. Desafios Do Direito Na Era Da Internet: Uma Breve Análise Sobre Os Crimes Cibernéticos. Rev. Campo Jurídico, Barreiras-BA, v. 7, n. 2, p. 145-167, jul./dez., 2019. Disponível em: DOI: https://doi.org/10.37497/revcampojur.v7i2.289. Acesso em: 22 jul. 2022.
MOTTA, Ana Carolina de Gouvea Dantas; SILVA, Fernando Cesar Almeida; CASTOR, Emiliano Carlos Serpa. Transformação digital e Compliance: gestão do trabalho com ERP numa organização que aprende. Revista Carioca de Ciência, Tecnologia e Educação (online), Rio de Janeiro, v. 05, n. 02, 2020. ISSN 2596-058X. Disponível em: https://recite.unicarioca.edu.br/rccte/index.php/rccte/article/view/176/180. Acesso em: 16 nov. 2022.
PORTAL IDEA. O que é sistema SAP? Como ele funciona? Portal Idea, s.d. Disponível em: https://portalidea.com.br/cursos/bsico-em-sistema-de-manuteno-sap-apostila01.pdf. Acesso em: 15 nov. 2022.
ROSA, Jorge Miguel Reis A. Os principais produtos SAP em ambiente empresarial no contexto de Big Data. Relatório de Estágio (Mestrado em Analítica e Inteligência Organizacional) – Escola Superior de Tecnologia de Tomar, Instituto Politécnico de Tomar. Portugal, 2021.
SANTOS, Levi Alves dos. Os ataques ransomware e a camada de proteção em sistemas governamentais. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento, ano 07, ed. 08, vol. 04, pp. 132-161, agosto de 2022. ISSN: 2448-0959. Disponível em: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/tecnologia/ataques-ransomware. DOI: 10.32749/nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/tecnologia/ataques-ransomware. Acesso em: 16 nov. 2022.
SAP. O que é ERP? SAP, s.d.a. Disponível em: https://www.sap.com/brazil/insights/what-is-erp.html. Acesso em: 15 nov. 2022.
SAP. SAP Help Portal Documentation. SAP, s.d.b. Disponível em: https://help.sap.com/docs/SAP_S4HANA_ON-PREMISE/8308e6d301d54584a33cd04a9861bc52/31ca9d0a259c436cbada9cffc5b5bfd5.html. Acesso em: 15 dez. 2022.
SOUZA, Isadora. Transformação digital nas empresas: 11 exemplos de digitalização de processos para negócios. Eficaz Marketing, agosto de 2020. Disponível em: https://eficazmarketing.com/blog/transformacao-digital-nas-empresas-11-exemplos-digitalizacao-de-processos/. Acesso em: 03 dez. 2022.
TEODORO, Douglas Diego Rocha. Arquitetura de infraestrutura em nuvem e o modelo zero trust como estratégia de cibersegurança. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento, ano 07, ed. 11, vol. 13, pp. 204-232, novembro de 2022. ISSN: 2448-0959. Disponível em: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/tecnologia/modelo-zero-trust; DOI: 10.32749/nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/tecnologia/modelo-zero-trust. Acesso em: 03 dez. 2022.
TRIBUNAL DE CONTAS DA UNIÃO – TCU. Boas práticas em segurança da informação. 4. ed. Brasília: TCU, Secretaria de Fiscalização de Tecnologia da Informação, 2012.
VALENTIM, Onivaldo Aparecido; POLITANO, Paulo Rogério; PEREIRA, Néocles Alves; ARAÚJO FILHO, Targino de. Análise comparativa entre a implementação e atualização do sistema ERP R/3 da SAP considerando os fatores críticos de sucesso descritos na literatura: um estudo de caso em uma empresa do segmento de bebidas. Gest. Prod., São Carlos, v. 21, n. 1, p. 111-124, 2014. Disponível em: https://www.scielo.br/j/gp/a/KYVmhdHxR6wGPnxbPYwxQ8R/?format=pdf&lang=pt. Acesso em: 15 nov. 2022.
[1] Postgraduate Lato Sensu in Project Management, Degree in Biological Sciences. ORCID: 0000-0002-8666-8372.
Sent: December, 2022.
Approved: December, 2022.