SILVA, Raquel Chianca [2], CAVALCANTI, Carmen Suely de Miranda [3]
SILVA, Raquel Chianca; CAVALCANTI, Carmen Suely de Miranda. Care for the Caregiver: an experiment with the caretaker of the hospitalized patients in the ER Clovis Sampson. Multidisciplinary Core scientific journal of knowledge. 03 year, Ed. 06, vol. 07, pp. 59-80, June 2018. ISSN:2448-0959
Summary
Objective to analyze the importance of the role of the Social services by the caregiver of a patient in the emergency room Clovis Sampson. The analysis is based on the experience of training in first aid, health institution Sampson Clovis linked to health system that integrates the complex Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel/Er Clovis Sampson (CHMWG/PSCS). The intervention developed aimed to work the quality of life of the caregiver. The exercise was the medium used to awaken the importance of quality of life. It was used for construction of this documentary and bibliographic research article, involving discussions favouring the health policy, the role of the Social services in the field of health, the discussion on chaperone in the context of the National Policy Humanization, among other necessary discussions. Among the authors include Trinity (2001), Lee (2009), war (2000). Was still source of research data obtained through observation of daily professional. Concludes about the importance of direct more attention to caregiver of hospitalized patients in the CHMWG/PSCS; whether in preserving the welfare of companion, whether in preserving the patient's well-being, contributing to a healthy lifestyle and prevention of non-communicable chronic diseases.
Keywords: Social Service, Caregiver, physical activity.
1. Introduction
This article aims to analyse the importance of the role of the Social services by the caregiver of a patient in the emergency room Clovis Sampson. The focus of the analysis was the internship experience in Social work with escorts of inpatients on clinical observation of emergency room Clovis Sampson (PSCS). It is understanding that discuss the professional performance in a service of this nature requires the thought of a set of conditions that inform health care processing.
The interest in the study of caregivers of patients came from observation carried out during the internship in Social Service in t[4]he hospital complex Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel Er Clovis Sampson (CHMWG/PSCS), urgent and emergency hospital of hometown. Specifically, the intervention developed in Er Clovis Sampson-Note I and II-spaces that meet patients enter the emergency room and await the procedures arising from this service. The patients in this sector remain under observation and/or are released for discharge, or follow to intensive care units (Icus), Surgical Center or Hospital wards to Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel. There are also patients who are transferred to the Hospital John Machado that is configured as a rear hospital.
In this space are met the clinics of orthopedics, internal medicine, cardiovascular complaints, among others. Pick up seniors (mostly), young men and women. Throughout that period remain in this sector the patient is entitled to a date.
During the training course in Social work in the ER Clovis Sampson identified a reality characterized by significant number of elderly patients with chronic diseases. These patients remain, in this sector, in difficult conditions. On stretchers in the hallways or in overcrowded wards. Their caregivers or remain standing next to the stretchers, or spend the night sitting in uncomfortable chairs.
This fact attracted our attention to the extent to take care of the other requires a self-care. This care is attention, caution, caution, dedication, care, charge and responsibility. Take care is to serve, is to offer to each other, in the form of service, the result of his talents, preparation and choices; is practice.
Considering this issue we direct our speech from the perspective of the caregiver. Interventional proposal aimed at awakening to the importance of the quality of life of the caregiver as a way to ensure the care of the patient. The exercise was the medium used to awaken this importance. We share the idea that physical activity is an instrument of great importance, not only for the promotion of health, but also for the prevention of chronic diseases. This successful experience motivated us to develop stage, as the object of this article, the review of the same.
To achieve the objectives proposed the article is structured in three sections, in addition to the Introduction and closing remarks. The second section presents the CHMWG/PSCS placing it in the context of the unified health system (SUS); the third section is the Social services in the context of the CHMWG/PSCS analyzing tasks and competencies in the area of health; in the fourth section the focus turns to the object of study, namely, the role of the Social Care Service with the caregiver from the analysis of the intervention held together with caregivers of hospitalized patients in the ER Clovis Sampson. The intervention carried out by the caregiver is object of analysis in this section of the article.
The methodological procedures used in the construction of the article consisted of documentary and bibliographical research, involving discussions favouring the health policy, the role of the Social services in the field of health, the discussion on chaperone in National Humanization policy, among other necessary discussions. Among the authors include Trinity (2001), Lee (2009), war (2000). Was still source of research data obtained through observation of daily professional.
We stress the importance of direct more attention to caregiver of the hospitalized patients in CHMWG/PSCS; whether in preserving the well-being of this caregiver and patient, contributing to a healthy lifestyle and prevention of non-communicable chronic diseases.
2. The hospital complex Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel/er Clovis Sampson in the context of the unified health system
We began our reflection the context institutional space in which developed on stage. Such contextualisation is justified to the extent that, as we said above, the experience of training was set up as an object of study.
CHMWG/PSCS activities were started with the inauguration of the Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel (HMWG) on 14 March 1971, at this time received the title of General Hospital and emergency room for Christmas. Its activities were initiated on 31 March 1973, when it was renamed Monsignor John Gurgel Hospital in honour of the then Governor of the State of Rio Grande do Norte[5]. Currently, it is located on Avenida Senador Salgado Filho, Tirol in NatalRN. city
Is an institution of public nature linked to the national health policy and, consequently, integrates the unified health system (SUS). To situate us about this nature is essential to discuss some key points about the Constitution of the SUS.
Health in Brazil had in the health reform movement,[6] dating back to the early 1980, a watershed. One of the results and strategies of this movement was the construction of the single health system (SUS). A system that was the result of struggles and mobilization of health professionals, articulated the popular movement.
It is important to consider that the fight that ended in the SUS was pervaded by a fundamental participation of representative entities of the population: residents, unions, professional associations, political parties and Parliament. A result of this struggle is clearly explicit in 1988 on the Federal Constitution of Brazil, which in your time considers health as your article 196 as:
Everyone's right and duty of the State, ensuring through social and economic policies with a view to reducing the risk of disease and other diseases and to universal and egalitarian ACE shares and services for your promotion, protection and recovery. (BRAZIL, 1988)
In this sense, health is provided for constitutional point of view, as a right which in theory is ensured to Brazilian citizens. Therefore, the Organic Health Law (LOS) nº 8,080 of 1993 supports the principles of the unified health system (SUS):
I-universality of access to health services at all levels of assistance;
II-Completeness, perceived as articulated and continuous set of actions and preventive and curative services, individual and collective, required for each case in all levels of complexity of the system;
III-preservation of the autonomy of the people in the defense of your physical and moral integrity;
IV-Equality of health care, without prejudice or privileges of any kind;
V-right to information, people, about your health;
VI-dissemination of information about the potential health services and your use by the user;
VII-Use of epidemiology to priority-setting, resource allocation and programmatic guidance;
VIII-community participation. (BRAZIL, 1990).
In the context of the SUS, the CHMWG/PSCS is the only hospital in the metropolitan region of Natal back to urgent and emergency care. According to Lee (2009) the emergence of services of attention to urgencies and emergencies is dated from the early 20th century. However, in 2002, by Ordinance GM 2048/2002 (BRAZIL, 2006) were laid down the rules for the organisation of public and private services of attention to the emergency room. However the strengthening of those services only if he realized from the GM 1600/20111 (BRAZIL, 2006; 2011) w[7]hich established National policy of attention to Urgency.
Working in line with the guidelines of the national policy of Attention to the emergency room, the CHMWG/PSCS is the only hospital in the metropolitan region of Natal of high compl[8]exity; relying on the services of burned, orthopedics, Neurology and neurosurgery. Is a hospital complex that has structure to 284 beds, these are 45 ICU, distributed among Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel and Er Clovis Sampson, intended for service in various specialties, like clinica medica, general surgery , cardiology and orthopedics.
Important to understand the dynamics of functioning of CHMWG/PSCS, situate it in the context of classification of units in urgent and emergency care recommended by Ordinance 2048/2002, establishing the systems of technical regulation Urgent and emergency. According to this Ordinance the urgency and emergency services are classified in two types: hospital units in urgent and emergency care[9] and reference Units.
In this study, the reference Units are installed in hospitals, General or specialized, able to provide emergency assistance and medium complexity and emergen[10]ce of third level and high complexity. Is while the reference Unit is situated the CHMWG/PSCS.
According to Leal and Alves et al. (2016, p. 3-4) the reference Units are also divided into types, as follows:
the) type i: are installed at specialized hospitals and effect service of urgencies/emergencies clinical and surgical in nature, in the areas of Paediatrics Department of orthopedics or Cardiology or;
b) type II: are those located in general hospitals; aims to meet the urgencies/emergencies clinical and surgical in nature;
c) type III: are installed in general hospitals and effect service of clinical, surgical and trauma nature.
Analyzing this Division we can classify the CHMWG/PSCS as a reference Unit of type III a time if set up as a unit installed in general hospital and that nature care clinic, surgical and trauma.
The standardization of this policy has the functioning of these services requires a multidisciplinary[11] team indispensable minimum, present and able to attend the urgencies and emergencies in their specific areas of professional activity. As a member of this team, the Social worker.
It is important to consider that despite experiencing numerous structural difficulties such as lack of ambulances, with reduced number of doctors, professional failure of diversified areas, lack of beds in because of the overcrowding that characterizes it, the CHMWG/PSCS is one of the major references in the context of health care in the State of Rio Grande do Norte. Highlight that the conditions in which the health services in the country, it becomes challenging to relate what recommends the SUS regarding health guarantee as a right, with the current conditions of access and use of these services under the SUS , characterized by overcrowding, shortage of human and material resources, inadequacy between supply and demand of emergency medical care ". (GIGLIO-JACQUEMOT, 2005, p. 13).
Once inserted the CHMWG/PSCS in the context of the SUS, we situate your operating structure. This, during the period in which we conduct our training course, was composed of the following sectors: the Er Clovis Sampson with the following structure-Clinical Care III; Note III box; Politrauma and observation; General INTENSIVE CARE UNIT; Pediatric Icu; Recovery Center. The Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel showing in your structure: four (4) Wards; one (1) Cardiac ICU; one (1) General ICU (Bernadette); one (1) burn treatment centre (CTQ).
Taking into account the guidelines of the National Health Policy, the CHMWG/PSCS had, on that occasion, an interprofessional team composed of 1,800 employees, of which about 200 are from third party companies[12]. The permanent team was composed of 30 doctors at every turn and professionals who could have your requested services at any time.
In July 2003, the hospital was inserted in the integrated system of Financial Administration of the State, winning independence for planning and executing your supply and expenditure related to the maintenance of the structure. Currently, it is possible the permanent maintenance of equipment thanks to a contract signed with 17 contractors, ranging from CT scanners and x-ray machines of laundry, kitchen and lifts. (PSCS, 2015)
According to the CHMWG Portal/PSCS institution's mission is:
Inpatient offer of reference to children and adults in a situation of emergency clinics, surgeries and diseases of external causes, particularly the trauma and contribute to the training and qualification of human resources in health in the light of the ethical values and humanitarians. (HMWG, PSCS, 2015)
Has a vision, "the recognition of the society by providing reference services with high quality, in their most relevant dimensions, in the area of hospital assistance and health education". (HMWG-PSCS, 2015)
Considering the probationary period, the CHMWG had the following departments: direction of Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel and Er Clovis Sampson; Coordination of health surveillance; Hospital Medical Director Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel and administrative direction and Hospital financial Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel.
Among the programs and projects developed to highlight the program complex Hospital Class and access and quality core hospital (NAQH). Let's look at the specifics of each of these projects.
The Hospital was deployed Class Program for almost two years, serving children between the ages of 2 to 14 years. Already have been answered more than 300 children. Has as main objective to minimize the losses incurred during the academic school clearance, due to the need of hospitalization in a hospital unit. Has a partnership with the Municipal Education (EMS) and inpatients in the pediatric ward of the third floor and burn treatment centre (CTQ).
Already the core of Access and Hospital Quality, works with servers each HMWG sector. This aims to gather information, assess the data obtained and apply actions aimed at raising the hospital assistance integrating employees to a new working methodology (PSCS, 2015).
Stand out among the achievements of the Core deployment of K[13]anban, workshops clarification SOS Emergency Program policy, the[14] preparation of service flows by specialty and the adoption of the Protocol of Manchester[15]. Together, these actions have changed parameters and gave a new face to way to welcome and assist users of the unified health system (SUS) in the hospital complex.
Next, we place the Social services in the context of the hospital complex Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel/Er Clovis Sampson.
3. The social service in the hospital complex Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel/er Clovis Sampson
The Social Service as Iamamoto (2009, p. 22), is a specialization of the work, a particular profession in social and technical division of the collective work of the society ". Intervention as the social issue as the author States:
[…] is nothing but the expression of the process of formation and development of the working class and your ticket in the political scenario of society, demanding recognition as your class by the business community and the State. (IAMAMOTO; CARVALHO, 2009, p. 77).
And a profession that has an ethical political project which aims to direct the Professional category, in contemporary times, assuming a corporate commitment, democratic, supporting the social struggles, social movements, in order to guide citizens on their rights and duties, backed by the Federal Constitution of 1988.
According to the code of ethics of the Social worker are several fundamental principles of the profession, including:
VI. Commitment to the Elimination of all forms of prejudice, encouraging respect for diversity, participation of socially discriminated groups and discussion of differences;
VII. The guarantee of pluralism, through the respect existing democratic professionals currents and ACE their theoretical expressions and commitment to constant improvement;
VIII. Option for a professional design that is linked to the process of building a new corporate order, without domination, exploitation of class, ethnicity and gender;
X. Commitment with the quality of services provided to the population and with the intellectual improvement, in terms of professional competence;
XI. Office of the Social services without discrimination, not discriminate for reasons of insertion of social class, gender, ethnicity, religion, nationality, sexual orientation, gender identity, age, physical condition. (CFESS, 1993, p. 23-24).
Important record that the Social worker is a generalist professional acting in various spaces occupational partner, among others: health, social security, social assistance, education.
Specifying the area of health, it can be considered that your insertion occurs together with public and private companies. Works in partnership with other professionals, seeking to ensure compliance with the rights of users, sometimes neglected, by the public health system. His work is focused on the promotion of the empowerment of the user, so that they can be an agent in the process of changing your own reality.
On the other hand, with the implementation of the single health system (SUS):
[…] changes of technological, organisational and political orders began to require new forms of work organization, determined by the hierarchy by level of complexity, reality comes requiring Social Service Professional assignments and to give you skills with a new form of public policy, in this particular case, health policies. (COSTA, 2009, p. 41).
The actions of professional social workers are made possible, in particular through the framework health promotion conceptual and programmatic guidelines expressed by the Ministry of health (2006), among which stand out:
Subjective dimension and social appreciation in all the attention and management practices in the SUS, strengthening the commitment to the rights of the citizen, with respect to issues of gender, ethnicity, race, sexual orientation and specific populations (Indians, quilombo, bordering, settlers and etc.);
Strengthening of multidisciplinary teamwork, fostering the transversality and the grouping;
Support for the construction of cooperative networks, supportive and committed to health and production with the production of subject;
Construction of autonomy and role of subjects and collectives involved in SUS network;
Co-responsibility of those in management processes and attention;
Strengthening social control participatory nature in all instances that manage the SUS;
Commitment to the democratization of labor relations and enhancement of health professionals by stimulating processes of permanent education. (Ministry of health, 2006, p. 125).
In the view of Valencia (2002), the Social worker acting in the context of health seeks to break with social care and focused practices that reproduce the dominant values that prioritizes the doctor-patient relationship, where the purpose is the cure of diseases. It should also recognize the institution as an adversarial space of struggle, to be able to unhide the relations of domination, and establish strategies to meet the limits imposed by her.
In this sense it is up to the professional Social Service is capable, politically and ethically methodology, particularly in the field of health policy. Should take into account, for the development of their actions, the duties and responsibilities attached to them, backed by the professional code of ethics, the law regulating the profession, law nº 8,662 of 1993 and, finally, that oa laws Assistant need to use your everyday on social professional, among them: the Federal Constitution of Brazil of 1988, the Maria da Penha Law, statute of the elderly and children and teenagers, Labor Laws, parameters for performance of Social worker in the health area, between others.
In professional practice, in this area, the Social service professionals use some instruments in the context of the instrumentality which are indispensable for your practice. According to Guerra (2000), the instrumentality is a historical partner of the property profession, by allowing the meeting the demands and the range of professional and social goals. Constitutes a concrete condition of social recognition of the profession, as it will be throughout a set of knowledge and techniques that have a result more effective before the demand received.
Second Trinity (2001), trigger the technical-operative instrumental that constitutes a set of different tools and techniques used in the sphere of material production, whose base is the transformation of material objects. Among the instruments operating technicians that the social worker of CHMWG/PSCS uses one can list:
- Daily visit the patient in the Hospital (census): visit held the bed bed daily, in order to verify the control of occupancy of beds and vague, but also listen to users and guide them as the rules to be followed, as well as the verification of copies of personal documents of patients on the charts;
- Standards guidelines to be followed by the escorts. Guidelines on the prevention of contagious diseases that are present in the hospital sector;
- Social interview held in your most users to fill out the social monitoring to have information on oa patient who will carry out the admission in the hospital;
- Guidelines for Social Benefits such as Insurance of personal data caused by motor vehicles of Roads (DPVAT), exams, the SUS Card, among others;
- Information about the State of the patient to the families in the sector, politrauma, ICU Recovery Center (CRO);
- A record of the date, action that guarantees the permanence of the companion/caregiver by the patient during hospitalization;
- Release of Declaration of Death, which is filled by the medical and Social services delivered to the body and release of the fourth Routing Registry officer;
- High information to relatives, as well as car request for patients in need and can't afford to move.
As you can understand, the instruments are essential in any rational process of intervention, however, are built from the purposes laid down in the planning of the action taken by the Social worker. It is important to have an understanding that to locate the place occupied by the tools is necessary to know what are the professional goals, taking always into consideration that they are constructed from a theoretical reflection, ethics and politics.
As already elucidated the roles and responsibilities[16] of the Social service professionals are guided and direct-driven and duties of the professional code of ethics and the law of regulation of the profession paragraph 8,662.
The Social Service in CHMWG/PSCS is the gateway to users and their relatives, companions and/or caregivers. The Board of social workers, during our training period, was composed of 30 social workers that divided its activities between the Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel and Er Clovis. All acting professionals were female working in scale system, i.e., on duty[17].
It's worth pointing out that, professional oa are faced constantly with the bureaucratization, precariousness and scrapping of health policy, however is on these limitations that the Professional is invited to acting and plot strategies for quality care and so determined to users.
It is pertinent to add that the audience attended by the CHMWG/PSCS is heterogeneous, if constituting, men, women, children, adolescents and the elderly. The demand comes to CHMWG/PSCS forwarded and/or brought by ambulance from [18]the Interior of Rio Grande do Norte, is an emergency room reference to any State; referred by other hospitals or units of Ready attendance (UPA); conducted by the family; or even runs unattended.
The social workers in the exercise of their practices seek to watch users who find themselves in line with the principles and guidelines of the unified health system (SUS). In this sense, intervention, despite the infrastructural and human resource limitations, is targeting to ensure the rights of the user population, which according to the Ministry of health (2007) are:
-have access to the set of necessary actions and services for the protection and recovery of your health;
-be met with attention and respect, in a personalized manner and with continuity, in place and decent environment, clean, safe and appropriate care;
-not be discriminated against or suffer restriction or denial of service, in the actions and health services, on grounds of age, race, gender, sexual orientation, genetic characteristics, social or economic conditions, cultural, political or religious convictions, the State of health or condition of carrier of Pathology, disability or pre-existing injury. (Ministry of health, 2007, p. 144).
Among the problems which they face these professionals we detach the service space, both in the emergency room, the Hospital Walfredo Gurgel. The room for the customer service of the Social Service is divided by the professionals in attendance at the same time. So, some situations that should be sensitive, are exposed or, when you realize the situation, other professionals and users end up waiting outside the room.
Despite the limitation imposed by the health care system, through a set of knowledge that express themselves in theoretical-methodological, ethical dimension-and technical-instrumental policy of your do professional comes enabling proposals able to go beyond the demand presented. Many times, resource constraints, make it difficult to build a professional practice where the priority is the user.
The performance of Social Service becomes effective by the patient and caregiver/companion to the extent that the latter is a preponderant factor to restore the health of your patient. This segment, since the period of observation of the stage got our attention, whether the conditions to which they are subjected in the CHMWG/PSCS, whether by the difficulties it faces to ensure the presence next to your patient. That look directed our intervention. Interventional proposal, then examined, turned to actions aimed at the care with the caregiver.
4. Care for the caregiver: the internship in Social work in the ER Clovis Sampson
Our object appropriate intervention, care for the caregiver started the Interventional step. We left understanding that care assumes a complex relationship between professionals, family, public and institutional context in various conditions and even in adverse dynamics of power. (FALEIROS, 2013). Still, for Faleiros (2013, p. 88), from the perspective of critical Social services, the care cannot be reduced only to a personal relationship, but builds to a value that attaches itself to the professional work and is part of a relationship of inclusion, listening and recognition the other and your otherness as a way of reception and quality of attention. And with respect to the care, says;
The watch requires a inter-dependencies between who cares and who's care since the human connection of caring is based on Exchange, on communication and on mutual contribution between the professional or the coach and the public attended (AGICH, 2008, p. 45).
The target audience of our intervention consisted of caregivers of patients in the Observation I and II of the Er Clovis Sampson. There are two situations when we report to that segment: 1. Patients accompanied by family members, and 2. Patients who were in the care of a professional caregiver.
This sector of the Er is characterized by receive patients without age restriction, by level of urgency and emergency, are admitted only when there is need for observation of the patient or in some cases of treatments that require short or long hospitalization.
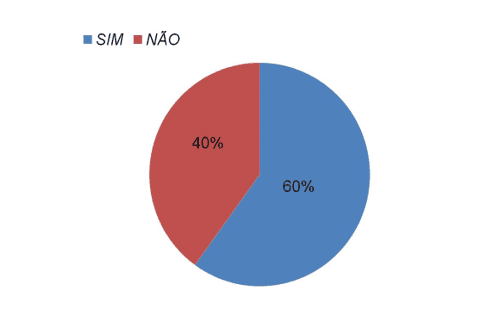
To identify the knowledge that caregivers have about the reality of your patient health apply with this caregivers, in visits to the bed, a small questionnaire to identify the level of knowledge of your disease patient following question "Sir/Madam have knowledge about what is chronic disease". The questionnaire was applied with caregivers and happened in the period between August and September (2015). For an answer we found that the majority, 60 percent of caregivers reported knowing your patient's condition. On the other hand, 40% reported having no knowledge about the disease of your patient. The chart below shows the results above recorded.
Everyday experience showed us a complex reality and inhumane for caregivers of those patients. Overcrowded wards without room for a proper treatment, patients in the hallways on stretchers, caregivers beside the beds and/or stretchers standing or in plastic chairs on which they spent days, we observed situations where escorts were asleep on cardboard under the stretchers for their patients. A space of illness, where besides the patients gradually escorts/caregivers would be sick.
Facing this reality the question put it: what could be done to improve the objective conditions of that context? We return our attention to the quality of life of those caregivers. Given the difficulties we chose a job back to health to the caregiver. We look at physical activity, specifically aerobic activities. Established for that partnership with three physical education university students Potiguar (Unp).
According to Adami (2015), aerobic activities are those that involve multiple muscle groups, so rhythmic, continuously and for a long period of time. This mode of exercise provides health benefits, because it improves the quality of life and reduces the likelihood of disease. Among the benefits that provides the aerobic exercises help "prevent cardiovascular disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, arthritis. Strengthens the heart; helps keep the good cholesterol, strengthens the respiratory system, decreases stress and reduces body fat. (BITTAR, 2014, p. 1)
In fact, the activity served as a showcase for attendees regarding the possibility of physical exercises, but the most important was to reflect to them about the importance of conducting some kind of regular physical activity, and that This practice is associated with the prevention and treatment of numerous diseases of modernity.
Among the best known are the prevention or control of cardiovascular disease, hypertension or diabetes. However, every day is more diffused the need to exercise regularly to prevent or control the development of dementia, Alzheimer's and depression, cancer, musculoskeletal injuries, osteoporosis, avoid eating disorders, hypertension, diabetes as well as chronic and degenerative diseases, among others[19].
For Moreira (2010), individually, the benefits of physical activity include physiological, psychological and social aspects. The physiology can be perceived immediately. They are: the level of glucose control, stimulus for activation of Catecholamines and improvement in sleep quality. Already in the medium term we can find an improvement in cardiorrespiratório system, improvement of muscle mass and overall strength and endurance levels, maintenance of adequate levels of flexibility, coordination and balance. And with regard to the psychological benefits argues:
[…] can be perceived immediate and medium term are to reduce the levels of stress and anxiety, improve the State of mind (General well-being), better mental health and cognitive. And finally realize the safe itself, individuals with a better social and cultural integration, having their social functions preserved and possibly expanded, running until the depression. And factors such as these may be characterised and defined as social benefits. (MOREIRA, 2010, p. 2)
The moment meant physical activity also scored with information to participants with regard to physical exercises that can be done at home, providing the health benefits, as for the prevention and minimization of chronic diseases. Physical activities are among the elements able to contribute to the prevention and minimization of chronic non-communicable diseases (NCD).
Based on National policy Playbook of Humanization of care and management in the health system-SUS Humanizes, we understand how critical appreciation of the different subjects involved in the production process: users, workers and managers. In this sense, the caregiver cannot be forgotten in the process of treatment.
The Ministry of health aimed to offer quality assistance to users of SUS instituted more recently national Humanization policy (HNP) aiming to ensure security, the attention and the respect of the health services.
The humanization in this context is seen not as a program, more like public policy crossing cuts across the different actions/and managing instances of the single Health System. According to the National policy of Humanization (2010), ' humanization, in this process as:
-Enhancement of the different subjects involved in the production process: users, workers and managers;
-Promotion of autonomy and the role of these subjects and collectives;
-Increase in the degree of shared responsibility in the production of health and subject;
-Establishment of ties of solidarity and collective participation in the management process;
-Mapping and interaction with the social collective and subjective demands of health;
-Defence of SUS that recognizes the diversity of the Brazilian people and to all offers the same attention to health, irrespective of age, race, colour, origin, gender and sexual orientation;
-Change in attention and management models in your inseparability, focusing on the needs of citizens, health and production process of health work, valuing employees and social relations at work;
-Proposal for a collective work for the SUS is more welcoming, more agile, and more resolutivo. (Ministry of health, 2010, p. 7)
In this context of care with the caregiver, it was observed that little by little the participants were passing information regarding physical exercises that can be done at home by providing the health benefits, such as for prevention and minimization among the chronic diseases they were coming.
Just had a moment of physical activity, held at the Auditorium of space observation II, lasting half an hour and after the end of the exercise, were given informational brochures, produced six physical exercises, socializing could be made in House. This material also stressed the importance of exercising, an action which contributes to avoid the harm of the sedentary lifestyle, that is the Group of chronic disease.
To terminate the activity was asked to 10 participants had enjoyed the activity performed and if they were invited they would do again. All responded that they liked and they'd do again. One of the participants commented "Interesting, liked it, took a bit of stress." (escort, 45 years)
In due course, we question the three students of physical education that were part of the activity, that they had found the experience. All three replied: "A very rich experience, had never participated in a hospital, moreover, is to be able to take a bit of awareness and importance of physical activity in daily life insert of the people".
It was gratifying to hear from everyone present who were very satisfied with the work performed and that each, in your uniqueness, contributed and learned from hands-on work carried out. Closed activities with the certainty that the objectives have been achieved.
Final considerations
The period of internship at the hospital complex Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel/Er Clovis Sampson was of great relevance to the formative process of this study for the opportunity to meet and experience the daily life of a healthcare institution, providing the knowledge of the institution, knowing your physical structure as the main sectors that operates the Social Service duties and competencies. At the same time one can meet the various demands that reach the Social Service and the various strategies to effect the guarantee of the right to health.
The internship process made it possible to live the experience of direct contact with the reality of professional practice of social worker in the area of health, but also the social reality experienced on a daily basis, and, in addition, provided the articulation of theory and practice make it professional. In this context, one can combine the practical knowledge gained in stage experience with the theoretical content acquired during the formative process of the course of Social Service. It can be considered a period that contributed in the process of learning and enrichment of knowledge that is essential in the process of any professional training, but that does not end, as should be continuous, since the reality is dynamic and contradictory.
With the analysis of the intervention, well developed to highlight effectiveness of a work by the caregiver as a key element in the implementation of the national policy of Humanisation in the processes of attention to health.
Finally, it is interesting to consider how the intervention performed, this, in fact, even with the difficulty encountered, managed to achieve the proposed objectives. In this sense it can be considered that the result was positive about what was expected, because those who participated in the intervention came out satisfied and enlightened about the specifics of care that revolve around chronic diseases and the possibility to prevent them through physical activity.
References
ADAMI, Anna. Aerobic Exercises. Bureau of Labor Statistics-Browsing and learning. 2015. Available in: <http: www.infoescola.com/educacao-fisica/exercicios-aerobicos/="">.</http:> Access in: 24 2015 11.
AGICH, George. Dependency and autonomy in old age. An ethical model for the care of far term. São Paulo: Loyola/São Camilo, 2008.
Brazil. Ministry of health. National policy Attention to the emergency room. 3. Ed. Brasilia: Publishing House of the Ministry of health, 2006.
Brazil. Ministry of health. Available at: http://www.saude.gov.br/saudelegis. Access in: 10/06/2016.
Brazil. Organic law of health. National Health Council. Law No. 8,080. September, 1990. Available at: http://conselho.saude.gov.br/legislacao/lei8080.htm. Access in: 10/06/2016.
Brazil. Constitution of the Federative Republic of. 1988. Available in: <http: www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/constituicao/constituicaocompilado.htm="">.</http:> Access in: 22 04 2015.
Brazil. Minister of health. SOS emergency relief programme in the context of network attention to urgencies and emergencies (RUE). Ministerial Order n° 1,663, 06 August 2012. Available in: <http: bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2012/prt1663_06_08_2012.htm="">.</http:> Access in: 05 10 2016.
Brazil. National Council of Secretaries of health. Media assistance and high complexity in SUS. CONASS, 2007. Available in: <http: bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/colec_progestores_livro9.pdf="">.</http:> Access in: 28 04 2015.
BITTAR, Julio. The 5 Major benefits of aerobic exercise. World. Copacabana Runners. 2013. Available in: <http: www.mundoboaforma.com.br/5-maiores-beneficios-dos-exercicios-aerobicos/="">.</http:> Access in: 24 2015 11.
CFESS. Federal Council of Social Service. Parameters for the actions of social workers in the health sector. Brasilia, March, 2009.
CFESS. Federal Council of Social Service. Code of ethics for Social worker. Available in:<www. cfess.></www. cfess.> org.br > ZIP CODE _ CFESS-SITE >, retrieved: 22 04 2015.
COSTA, Maria Dalva Horace. The work in the Health services and the inclusion of the social workers, 2009.
FALEIROS, Vicente de Paula. Challenges of nursing in Social work: a critical perspective. Catholic University of Brasília (UCB). Florianópolis. 2013.
The State Government of Rio Grande do Norte. Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel Er Clovis Sampson. Available at: <http: www.walfredogurgel.rn.gov.br/index.asp="">, accessed: 26 03 2015.</http:>
WAR, Yolanda. Instrumentality of the work process and Social Service. Social Service Society, no. 62 &. São Paulo, Cortez, 2000.
GIGLIO-JACQUEMOT, A.. Urgencies and emergencies in health: professional prospects and users. Rio de Janeiro: Editora FIOCRUZ, 2005.
Hospital Complex. Formation of the hospital complex. Federal University of Rio de Janeiro-UFRJ Campus. Available in: < http://www.ch.ufrj.br/=""> . Access in: 05/01/2017.
IAMAMOTO. M. V.; CARVALHO, r. Social Relations and Social Service in Brazil. São Paulo, Cortez CELATS, 2009.
LEE, L.. Emergency care in Brazil. 2009. 31 f. Work of conclusion of course (specialization in Nursing in Critical Patients ducts). University of Southern Santa Catarina-UNESC, Criciúma.
LOYAL, Roberta Adamoli Santin; Alves, Jaslene Lee; XAVIER Arnaldo; AX, Patricia Mara; CAETANO, Patricia da Silva. Social and political service of Attention to the urgency and emergency at SUS: the experience of the HU-UFSC. Available in: <http: cress-sc.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/serviço-social-e-política-de-atenção-a-urgência-e-emergência-no-sus3.pdf="">.</http:> Access in: 10/06/2016.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Primer of health users of SUS. Available in: <www.bvsms.saude.gov.brbvspublicações cartilha_="" cor.pdf="">.</www.bvsms.saude.gov.brbvspublicações> Access in: 25 04 2015.
Moreira, Ramon Tesafye. Contributions of physical activity to healthy aging process. Digital Magazine. 15 year. November, 2010. Available in: <http: www.efdeportes.com/efd150/atividade-fisica-para-o-envelhecimento-saudavel.htm="">.</http:> Access in: 22 2015 11.
NORTHEAST, The Newspaper. Monsignor James Gurgel. The Northeast. Available at: http://www.onordeste.com/onordeste/enciclopediaNordeste/index.php? title = Monsignor + James + Gurgel & ltr = m&id _ perso = 1246. Access in: 13/06/2016.
PEDUZZI, Marina. Multidisciplinary team of health: concept and typology. Public Health Magazine. São Paulo, 2001.
CITY HALL. Fruit of a whole new way to build. Understand how does the Manchester Protocol. 2010. Available in: <http: www.frutal.mg.gov.br/noticias/enfermeira-explica-atendimento-atraves-do-protocolo-de-manchester.html="">.</http:> Access in: 29 04 2015.
Health. National policy Playbook of humanization of care and Management in the health system-SUS Humanizes. Text book, 2010.
SINDPDPR. Union workers in computer science and information technology. Available in: <http: www.sindpdpr.org.br/faq/que-e-terceirizacao="">.</http:> Access in: 18 04 2015.
SHAH. Maria Inês Nascimento Fonseca. The duty of the Social services in Basic Health Units-UBS in France: reflection of this practice under a new look. FRANCA, 2004. Available in: <http: base.repositorio.unesp.br/bitstream/handle/11449/98540/sousa_minf_me_fran.pdf?sequence="1">.</http:> Access in: 25 04 2015.
Health. Physical exercise is recommended to prevent disease. The morning paper Online. 2013. Available in: <http: www.jmonline.com.br/novo/?noticias,7,saude,80508="">.</http:> Access in: 22 2015 11.
TRINITY, Mably. Historical aspects of the transexualizador process in Rio de Janeiro. 1. Ed. – Cambridge: Gramma, 2016.
TRINITY, Rosa Lucia Prédes. Unraveling the socio-historical determinations of technical-instrumental Social service operating in articulation between social demands and professional designs. Journal of the Brazilian Association of education and research in Social work, n° 4, year II. Brasilia. 2001
VAKAUTAWALE, Ana María. The practice of Social work: contidiano, formation and altenitivas in healthcare. 4. Ed. São Paulo: Cortez, 2007
[1] Scientific article to Potiguar University-Unp, as part of the requirements for obtaining the title of Bachelor of Social work.
[2] Student in Social work at the University.
[3] Academic Supervisor. Social Worker. MA in education. Professor at Universidade Potiguar.
[4] The term "complex" does not mean "complicated", meaning as the name indicates: with "Plexus", that is, with "network". The word network or Plexus indicates interconnection between autonomous parts, with interdependence between them. Each unit in the network, keeping your identity or autonomy becomes different when within the network. The whole does not equal the sum of its parts, can be greater than, less than or equal to the sum of its parts, but it will certainly be different. To build a complex system we must associate the idea of unity on one side with the diversity or multiplicity of other side. Available in: < http://www.ch.ufrj.br/=""> </>. Access in: 05/01/2017.
[5] Governor Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel, a political and religious, the people elected the Rio Grande for another mission: to govern the State. In this new mission continued acting with the same serenity and honesty. Available at: http://www.onordeste.com/onordeste/enciclopediaNordeste/indexphp?titulo=Monsenhor+Walfredo+Gurgel<r=m&id_perso=1246. Access in: 13/06/2016.
[6] The health reform movement-engendered from the indignation of sectors of society with the dramatic health situation in Brazil-guided his actions from the outset by the questioning of such reality. Furthermore, it can be affirmed that the brazilian health reform was born of the struggle against the dictatorship, with the theme "health and Democracy", and it was structured primarily in universities, in the trade union movement, the popular movement and regional experiences Organization of services. (TRINITY, 2016, p. 100)
[7] This ministerial order reshapes national policy Attention to the emergency room and setting up the network of Attention to the emergency room in the SUS.
[8] High complexity is a set of procedure that, in the context of the SUS, involves high technology and high cost, in order to give the population access to qualified service integrating them to the other levels of health care (basic and medium attention complexity). (CONASS, 2007, p. 18).
[9] The study about Loyal; Adams et al. (2016) highlight that the hospital units of urgent and emergency services are divided into two types: type I and type II. Type I units are those located in general hospitals small businesses able to provide emergency assistance and emergency assistance to the first level of medium complexity. The hospital units in urgent and emergency care type II are those installed in midsize general hospitals able to provide emergency assistance and emergency second level hospital assistance of medium complexity.
[10] To ensure the effectiveness of the actions to the attention to health is classified into three levels of warning: the basic attention, the average complexity and high complexity. The basic attention is characterized by a set of health actions within individual and collective, that include the promotion and protection of health, the prevention of diseases, treatment and maintenance on health (CONASS, 2007, p. 16). The average complexity consists of actions and services that aim to meet the main problems and aggravations of population health, whose complexity of care in clinical practice demands the availability of skilled professionals and the use of technological resources, to support diagnosis and treatment. (CONASS, 2007, p. 17).
[11] Multidisciplinary team is a collective working mode that is configured on the reciprocal relationship between the multiple technical interventions and the interaction of different professional areas. (PEDUZZI, 2001, p. 108)
[12] Outsourcing is the phenomenon by which a company hires a worker to provide its services to a second company-borrower. The receiving, benefits of the workforce, more does not create employment bond with the employee, because the contracting company is placed between them. Available in: <http: www.sindpdpr.org.br/faq/que-e-terceirizacao="">.</http:> Access in: 18 04 2015.
[13] The Kanban is a system of Hospital Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel-Er Clovis Sampson related to patients, identifying the name, age, the date that oa patient entered and which sector is: Ward, ICU, cardiac ICU Bernadete, Center burn treatment (CTQ), Clinical Care, Note I and II (OBS), Politrauma, ICU, ICU General Pediatrics and Recovery Center (CRO), used by professionals in the field of health.
[14] The SOS Emergency Programme is an action priority strategy for the implementation of the Hospital Component of RUE, held in conjunction with the States, Federal District and Municipalities for the qualification of the staff and management of health system users (SUS) in the largest and most complex Hospital emergency entrance doors of the SUS. Available in: < http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2012/prt1663_06_08_2012.html=""> </>. Access in: 05 10 2016
[15] The Manchester Protocol is a system that the patient is not serviced by order of arrival, but according to the risk or severity that he submit to enter the emergency room. Available in: <http: www.frutal.mg.gov.br/noticias/enfermeira-explica-atendimento-atraves-do-protocolo-de="" manchester.html="">.</http:> Access in: 29 04 2015.
[16] It is based on document of the Federal Council of Social Service entitled "parameters for performance of social workers in health" (2009).
[17] On call is where the social worker receives and hears people, most often excluded from their most basic rights and in need of care. Are people marked by unemployment, starvation, abandonment, by disease, by social and emotional needs, for the loss of dignity. (SHAH, 2004, p. 53).
[18] 70% is the interior (Brazil, Ceará-Mirim, iron Sticks, John Cairns and other interiors of Rio Grande Do Norte). According to information by the Hospital employee Monsignor Walfredo Gurgel, Interview took place on 15 April 2015.
[19] Largest information see: < http://www.jmonline.com.br/novo/?noticias,7,saude,80508=""> </>, accessed: 22 2015 11.