SOUZA, Pâmela Thariele Silva de [1]
TEIXEIRA, Márcia Cristina [2]
SOUZA, Pâmela Thariele Silva de; e, TEIXEIRA, Márcia Cristina. Resistance to change restrictive factor to organizational development-case study in a laboratory of clinical analyses. Multidisciplinary Core Scientific knowledge magazine, 1 Year. Vol. 8. pp. 107-143. September 2016. ISSN. 2448-0959
SUMMARY
In the midst of a globalized and competitive country, companies need to innovate and deploy organizational changes that are successful. This article presents a case study aiming to make an analysis of the company's organizational environment object of study to check for resistance to change and which tool the Manager uses to manage it. It was proposed in this research demonstrate the importance of the communication manager with employees in the process of implementation of changes and the necessity of managing resistance to change so that the organization can achieve their goals and remain on the market. To achieve the objectives of this research was applied questionnaire with employees and was held an interview with the Manager of the company, where it was possible to conclude through research data that the best strategy for the organization is conducting training for their employees in order to reduce the impacts caused by lack of preparation. Also it is necessary a leader responsible for monitoring of the changes sought by the organization.
Keywords: change, resistance, organization, communication.
INTRODUCTION
The transformations of the current scenario and technological innovations have led organizations to suit the processes of change as an opportunity for growth. Once the company acknowledges the positive role that may be, it's up to her to reflect on the importance and what impacts that resistance can cause in the development of the company. Such an effort could result in the development and implementation of models and processes as tools to manage resistance to change, since such models can provide competitive strategies for organizations to reach their goals and continue being leaders in the market.
However, the resistance on the part of organizations and individuals which they composed, may cause barriers and hinder the implementation of successful organizational change, so if the resistance is not only identified, but also managed for the Organization to achieve its goals.
This research was applied to analyze if the resistance to organizational change affects the development of the laboratory of clinical analyses, having as specific objectives: to present concepts of organizational change, definitions and types of resistance to change, identify through bibliographical reference the main factors of resistance to change and how it can affect the organizational development, check tools used by the company Manager to manage resistance to change and propose strategies and fundamental templates Manager for implementation of changes.
The present work is relevant for bringing contributions to the target company of research and to introduce models that will allow us to identify and deal with resistance at change. Also will serve as a support for students and may enhance their knowledge on the subject. The study and analysis of the topic become opportune, because the management tools of the changes that will be developed in this work could be taken by the Manager of the company for the results to be achieved as effectively as possible. The research may provide the company with knowledge that will help in managing resistance to change, and may result in competitive advantages for the organization.
2. BASIC THEORY
This step deals with the theoretical basis of the article and provides essential information to understand the importance of change for individuals and organizations. Will show also how resistance can be overcome so that the deployment process for change to be successful.
2.1 organizational development
Organizational development is the means by which organizations can adapt to market requirements and be able to respond to changes (MOREIRA, 2012). You can conceptualize how a planned change approach whose main focus is to change the people, nature and the quality of their working relationships. In short, emphasizes the cultural change as a basis for organizational change (CHIAVENATO, 1997 apud MOREIRA, 2012).
Chiavenato defines as a tool whose purpose is to "analyze the organizational culture, change the behavior and values, improve the organizational climate and the managerial styles and consolidate these changes to increase the efficiency of the Organization as a whole, the team and the individual" (CHIAVENATO, 2006, p. 164).
Carranza (2012) in turn defines organizational development as planned change aiming at the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization. Such changes can be culture, organizational structure and dynamic. Through the change of behavior is possible for employees, their values and attitudes, since it is impossible to carry out organizational changes without any change in the structure of the organization. It is also the purpose of organizational development to evaluate the impact that the changes may cause both the domestic and external environment.
2.2 Organizational Culture
Organizational culture can be defined as "shared beliefs and values system that develops within an organization and guides the behavior of its members. "(MATOS, MATOS ALMEIDA, 2007, p. 255-256).
Realize that each company has its own culture, so to deploy permanent changes that will be necessary to achieve organizational culture is, because it can influence the perception of the employee to the processes of change.
Silva (2008, p. 43) defines Organizational Culture as follows:
Organizational culture is a solid base of corporate principles and ideals that are the soul of the modern enterprise. Organizational culture encompasses a set of perceptions, thoughts and feelings common to stand out in the workplace, extrapolating the physical boundaries of the Organization and influencing the macro environment in which the company is inserted. In the so-called global savings, she will represent the way in which the company relates to the market, and the way that developers will cope with the rapid transformations of the work environment.
Developing a culture of change is crucial in the deployment process of change, because without culture is impossible to obtain successful results, even if the change is well planned. (BREGION, 2013).
2.3 organizational change
Survival depends on how organisations the same respond to changes in your environment, because organizations can achieve the success it is necessary that they have flexibility in the face of a new reality in the globalized market. (BREGION, 2013).
Organizational change "means any change, planned or unplanned, occurred in the Organization, arising from factors internal and/or external to the organization that brings any impact on the results and/or in the relations between people at work. "(DO, 2000 apud SALEM, 2009, p. 21). Chiavenato (2003) States that the world is in constant change, so organizations need to adapt in search of survival in this dynamic and competitive environment. The author also points out that the change means disruption and transformation "(…) the inability of the processing makes the Organization ineffective and condemns the extinction. "(CERIBEL, MERLO, 2013, p. 02).
The organizational change aims to generate structural transformations, cultural, technological, human, among others. These changes can impact in parts or in the Organization as a whole. (WOOD, 1995 apud SALEM, 2014, p. 07). It is noticed, so that the change can provide significant changes in the way we think of individuals so it is possible to affirm that its focus is the individual development, because through this it is possible to achieve the organizational performance.
In table 1 it is possible to identify internal and external factors considered as causes of organizational change.
Table 1: causes of organizational change
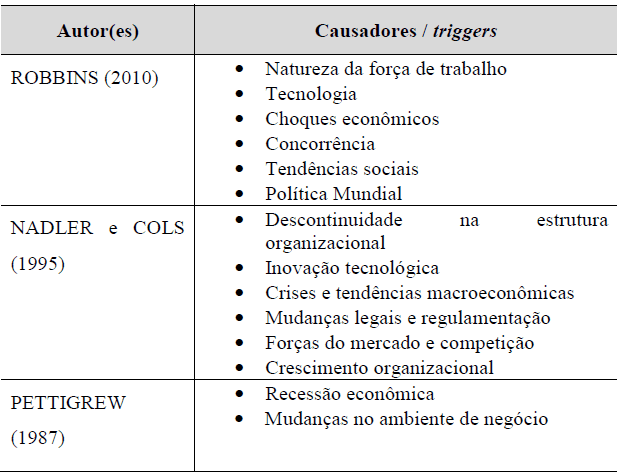
ng (BASHEER, 2004, apud SALEM, 2014, p. 18)
2.4 change process
As Chiavenato (2010) the change is composed of three steps:
1-Thawing: regarded as the initial phase consisting of the abandonment of old ideas and practices, namely, change of current standards of behavior for a new one. Defrosting is intended to ensure that the individual understands the need for change. Without thawing the tendency is that the employee return to habitual patterns of behavior.
2-Change: is the process of learning and discovery of new attitudes, values and behaviours. In this step occurs the ID (the individual understands the effectiveness of new attitude and accept) and internalizing (the attitude becomes part of the normal pattern of behavior). During this step there is the emergence of ideas and practices causing people to think and perform differently.
3-Refreezing: final step where the stabilization of change. Its purpose is to incorporate new ideas and practices definitely. Consists in incorporating the current practice standard learned that become part of the behavior of the individual.
2.5 resistance to change
"One of the greatest discoveries more well documented in research on organizational behavior and people's organizations and its members resist change" (ROBBINS, 2005, p. 425). Bortolotti, Souza and Andrade (s/a) claim that the change causes resistance, because of the fear of the unknown. People suffer a reaction process when faced with the need for change, especially when it comes with a sense that threatens to situations where the individual feels secure.
One of the strongest people's reactions change is the sense of loss coupled with the conflict to accept something new. Even when the change seems to point to improvements like promotion, expansion, etc., among others, this psychological process affects everyone. (SCOTT and JAFFE apud BORTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, S/A, p. 08).
One can see that:
The resistance arises due to some factors inherent to the process of change and the individual perceptions of the consequences of change. The impossibility of knowing the future, the existing difficulty in the transition between the current and proposed State, the difficulty in dealing with new and complex conditions, in addition to negative experiences with changes previously occurring cause there is fear about change. (1997, apud CERIBELI, MERLO, 2013, p. 06).
In certain situations the resistance can be seen from the positive point, when is intended to generate discussion on decisions to be taken resulting, therefore in better choices. The resistance may be considered negative when it tends to hinder the progress of the organization. In short, the resistance to change as critical and creative source is considered a common process, but the same becomes harmful when it prevents the implementation of changes in the organization.
Chiavenato (apud FREITAS, 2010, p. 17-18) points out that the resistance to change can be a result of logical, psychological or sociological aspects, namely:
Logical aspects: logical resistance stems from the time and effort required for a person to adjust to change, including new duties and tasks that need to be learned. These are the actual costs imposed on people. When you believe that the move will be favorable in the long run for people, they clearly show predisposed to pay short-term investment.
Psychological aspects: psychological resistance is "logic" in terms of attitudes and feelings of the people about the change. People may feel fear of the unknown, suspicious of the leadership of the Manager or realize that your job security is threatened. Even if the organization does not believe that there is justification for these feelings, they should be recognized as real.
Sociological aspects: the sociological resistance is the "logic" in terms of interest groups and social values involved. Social values are powerful forces, and must be carefully considered. There are political, Trade Union values colizações and opposites values of different communities that can affect the behavior of people on the changes. At the level of small groups, for example, there are co-workers who may be laid off because of changes. People can find out if the change is conscious in their social values or if they hold the team spirit.
2.6 Individual and organizational Sources of resistance to change
You can sort the resistance to change in two categories, the first being at the individual level and the other to the organizational level. (CERIBELI, MERLO, 2013).
Table 2: key barriers to organizational change

(BARON and GREENBERG, 1999, apud SOARES, 2007, p. 51)
2.7 forms of resistance
Judson and Mendes (1996, 2001 apud BOTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, s/a) reported that the resistance to change manifest – if in the following ways:
1. Spontaneous resistance: the spontaneous resistance has the main features: constant complaints, absenteeism, low productivity, damaged relations with customers and increase information retention.
2. Organized resistance: your manifestation occurs through the opposition strategy. This opposition may be individual or collective. Among the main examples of this resistance stands out: requests for meetings, work conflicts and collective manifestations.
3. Rational resistance: according to the authors rational resistance are the fears.
4. Irrational resistance: based on emotions.
5. Active resistance: considered the easiest way to be identified as explicit resistance, however, is the form of resistance more difficult to manage, because the individual objections against the proposed change, by reason of having formed an opinion, thus ends up questioning the manner of implementation of change.
6. Passive resistance: is the most subtle and it causes negative effects superior to active resistance. Its purpose is to prevent the implementation of the change is carried out. She can manifest through maneuvers that cause impact on stocks, the reduction in the pace of actions related to change in the increase of activities whose focus is to divert the focus of the people as well as your time. This resistance is also characterized by the attitude of apathy in the work, that is, the individual does not seek innovative solutions to the problems, demonstrate lack of motivation and uncooperative with the change process.
7. Personal withdrawal: can express themselves through the decrease in the pace of work, low productivity, learning difficulty and may lead the individual to shut down the company.
8. Indifference: it takes an individual to present apathetic reaction and lose interest in the work and just do what is imposed, but without protest. It hinders the understanding of the nature of the change.
9. Passive resignation: Considered as a reaction of cooperation by means of pressure, that is, the individual needs to be supervised and controlled, it means that the change did not succeed and may generate backlash.
10. Voluntary cooperation: desired reaction by agents of change happens when the individual believes in and supports the implementation of ideas and actions.
Already Maurer (1996, apud BORTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, s/a) complements the resistance can also perform the following ways:
- Confusion: form of impediment to the event of the change;
- Immediate criticism: Rejection by the change before the same be detailed;
- Disclaimer: Resignation in accepting that things have changed;
- Malicious obedience: the individual simulates in agree with the change when in fact does not comply;
- Easy agreement: Presents little resistance, but prevents the realization of being agreed;
- Deflection Causes change of focus;
- Silence: Hampers the way of dealing with the resistance;
It is noticed that the resistance to change can manifest in different ways, so knowing their sources and causes it is possible to use strategies to overcome the resistance so that the same is not deterrent factor for the achievement of goals and organizational development.
2.8 overcoming resistance to change
Resistance is an attitude contrary to the change, barriers and hampers effective implementation of organizational changes, so the first step to deploy changes, whatever, is resistance to change. After the discovery of the resistance change manager needs to adopt strategies to deal with this resistance. (BORTOLOTTI, JÚNIOR, ANDRADE, 2011).
Robins (2005) suggests six tactics that change agents can use to face the resistance.
- Education and communication: communication with employees is a medium that can be used to minimize the resistance, because it is assumed that the sources of resistance are the lack of communication and information. Individual discussions, memoranda, reports and presentations in groups are media that can be used in this process.
- Participation: people tend to resist Change when they are not involved in his decision, so it is necessary that the opponents to be entered into the decision-making process, so that they can contribute significantly. The involvement could reduce the resistance and bring improvements in the final decision.
- Facilitation: the efforts supporters are to be used by the agents of change, in order to reduce it. These efforts may include: counselling and therapy, training and even paid leave, and are used when the individual presents like reactions, fear and anxiety.
- Negotiation: this method is used when the resistance comes from a powerful source. In this case the change agent can offer rewards that meet the individual needs of opponents to the change.
- Manipulation and Cooptation: Considered as an influence in disguise, implies the employee to accept the changes, that is, are easy ways to get support of opponents to the change and can lead change agents lose their credibility if opponents realize they're being manipulated.
- Coercion: is the use of direct threats on the resistant, among the main examples stands out: threat of transfer, loss of promotions, letter of recommendation and negative performance evaluations.
2.9 change management
One can define change management as a set of techniques and tools whose purpose is to manage the human side of change and reduce the impact of the new organizational practices in people for the results to be achieved effectively. (Rabbit, 2012).
An organizational change process needs to be well structured for the deployment management to be successful. Therefore it is necessary the following steps (Kotter, 1997, apud CERIBELLI, MERLO, 2013):
1. Establishment of a sense of urgency;
2. Training of people with influence to lead change;
3. Change efforts and targeting strategies that allow the achievement of change;
4. Communication of objectives for those involved in the process of change;
5. Give permission to the employee when necessary and train them for new responsibilities;
6. Development of short-term change project to be maintained in the long term;
7. Consolidation of gains of more changes;
8. Modification of the organizational culture;
According to the author it can be concluded that the efficiency is achieved through organizational agents flexibility and that the expected results for the process are predictable.
2.10 change Deployment
For organizational change programmes are successfully deployed it is not enough to make changes only in the workplace, if necessary also a change of attitude and behavior of the people, that is, the first consists of individual behavior change, because it will be possible to change organizationally. (CHIAVENATO, 2010).
The planned change is intended to enable the Organization to adapt to changes in their environment and behavior of its employees. The agents of change are responsible for the management and implementation of activities, therefore they possess a vision of the future that others do not have. (BREGION, 2013). Chiavenato (2010) States that the agent of change is who initiates the process of change. Is the person responsible for making the changes occurring in the organization.
3.1 plan or Outline of research
This article was methodologically sketchy qualitative and quantitative form, because, as Roesch (2009) through the quantitative method it is possible to use standardized data that allow the researcher to conduct its analysis based on the use of statistics. Already the qualitative method in turn is intended to provide more detailed investigations, habits, attitudes, behavior tendencies. (MARCONI and LAKATOS, 2008).
The search can also be considered exploratory because it aims to develop, clarify concepts and ideas and aims at the formulation of precise problems or hypotheses that can be tested in subsequent studies. This research consists of the bibliographic survey, interviews and case studies. Are typically used when you want to get an overview of the facts (GIL, 2008).
3.2 definition of area or target population
This survey was conducted by the company Manager along with 11 employees, as these can provide relevant information to the same conclusion.
3.3 collection plans and Instruments
In this article interview techniques were used with the Manager and application of questionnaires to employees. Roesch makes the following observation:
A project can combine techniques developed in one or the other paradigm. In the case of primary data collection through interviews, questionnaires, observation or testing, it is important to specify in this section of the data source (the people who will be interviewed and the documents will be analyzed), when they will be raised and through which instruments (attaching the instruments, as script for interviews or questionnaire). (ROESCH, 2009, p. 128)
Through the interview with Project Manager, was obtained through interviews, relevant data for research and for the organization. Since the interview makes it possible to record observations such as: appearance, behavior, and attitudes of the respondent.
The questionnaire was another model adopted in this research because it is the form used to collect data and allows you to measure exactly what you wish. It is also the means used to obtain answers to the questions logically related to a central problem. The questionnaire applied to employees contained open-ended questions where it was allowed to get free answers and also close-ended questions, whose purpose was to obtain more precise answers.
3.4 data analysis plan
Whereas in quantitative research the data are processed, the data of this research were analyzed through electronic tabulation and Excel charts for interpretation of the questionnaires. It was also used in the present research the content analysis is a technique that "works with the content, hopes to understand the thoughts of the subject, through the content expressed in the text. (CAREGNATO and MUTTI, 2006, apud GERHARDT and SILVEIRA, 2009, p. 86).
For greater reliability in research and interpretation of the data, we used the method of triangulation of data since its use becomes necessary when the researcher uses two different methods in an attempt to confirm, validate or report results within a single study. In this model it is possible to use quantitative and qualitative methods to integrate the results of both methods during the stage of interpretation (CRESWELL, 2007).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The lab, located in the State of Rondônia, operates in the field of clinical analyses and currently has 12 employees. It was founded in October 1993, with the goal of adding a safe option in results in clinical analyses. Gradually, with the Manager and his staff became increasingly recognized by quality standards obtained in results generating full reliability to the customers.
4.1 research conducted with employees
A research on resistance to organizational change in a laboratory of clinical analyses, case study object. To obtain the results, applied a questionnaire with open and closed questions, to eleven employees of the organization under study. The data were released in a spreadsheet, enabling this way the verification of a data obtained more clearly where it was possible to identify: one of the 37 respondents% of respondents have completed high school, 27 percent are attending higher education, 18% of respondents have not completed elementary school, 9% have completed higher education and only 9% have expertise. As for sex: 91% of our employees are female and 9% of males. How to age: 28% of employees have of the 31 35 years, 27% have over 51 years .18% have between 36 to 45 years the other 18% have until 25 years of age and the remaining 9% are between 46 to 50 years.
Chart 1-time service
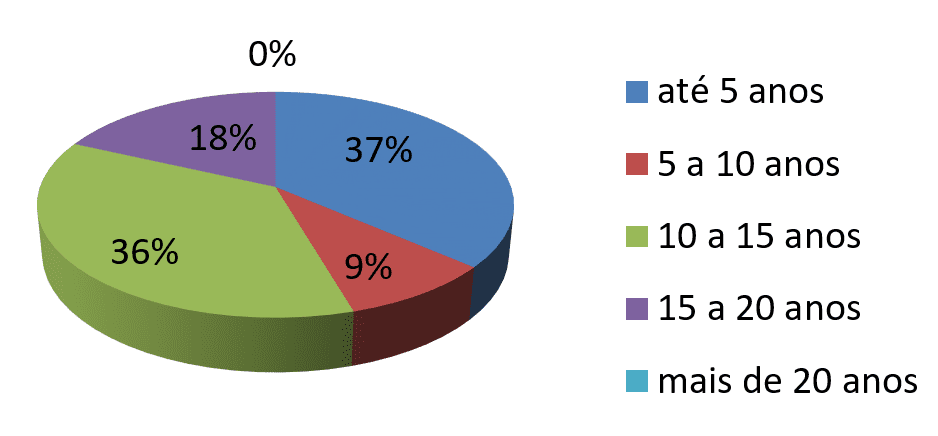
time: research data
In the graph 1 it was possible to identify that 37% of colaborardes have until 5 years length of service in the enterprise and that 63% of employees have between 5 to 15 years. You can see through the data that developers are accustomed to routine tasks and this factor has generated demotivation and stagnation causing them to fall into the comfort zone.
Being several years at the same company and performing the same function developers tend to oppose against the innovations proposed by the organization running only what is imposed. It is also common that the Professional with several years of company become inflexible and believe that your way of performing tasks is always correct.
Was asked to the employees who are responsible for organizational change processes in the company, it was possible to identify through the answers that the employees were unanimous to respond to senior management, namely, management is responsible for the implementation of organizational change. Through the data collected note that employees do not have autônomia to deploy any kind of organizational change process.
Was asked for developers to change it is necessary to abandon the current behavior, through this question the employees claimed to experience changes necessary to abandon old ways and habits acquired over time. Also stressed that change must occur from the principle of innovation, and that takes leadership, focus and determination. According to the same change implies out of the vicious circle and accept what is being proposed. Some officials have claimed that there is no need to abandon the current behavior as the way they don't change. Note through this statement some resistance, because every change implies abandonment of current behavior and old habits acquired and is related to whether it changes in personal life, in a structure, a methodology or process.
Chart 2-the process of change is difficult for the developer
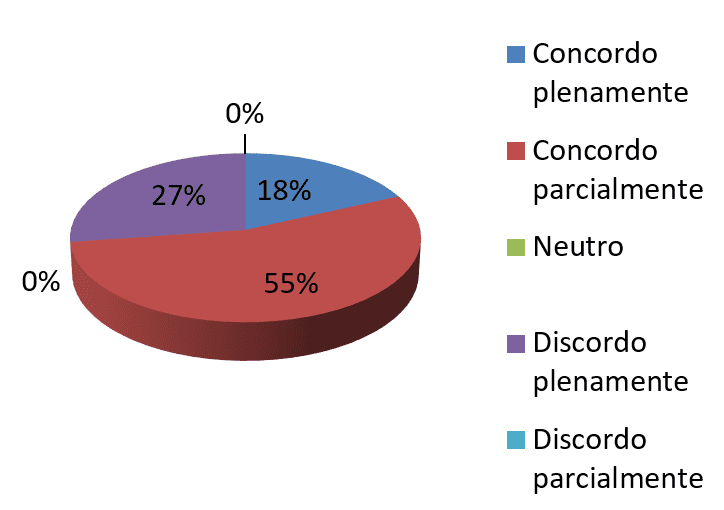
rFonte: research data
The chart 2 it turns out that more than half of employees agree partially, being 55% 27% do not agree and only 18% agree fully. Generally people tend to resist change due to fears of the past, that is, any desired change that turned into failure, also because of the feeling of fear and uncertainty that arise when the individual is faced with changes, since Exchange right by uncertain implies a challenge to be overcome.
Graph 3-I disagree with the proposal for change when I don't understand
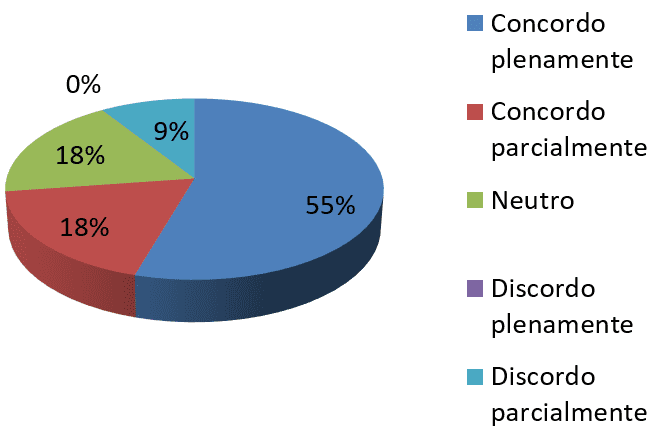
nd. Source: survey data
According to the survey 55% of employees, i.e. more than half agree fully, 18% agree partly and 18% were neutral in relation to the statement and only 9% disagreed. It is crucial that the Administration be able to convey clearly the strategies required for the deployment of changes and where you plan to arrive because that way the employees involved will be able to achieve the goals expected by the company.
Note that 91% of employees agree fully that to change it is necessary to establish the goal of transformation that aims, already 9% of respondents agree partially. The goal is critical and needs to be communicated to employees because the change without planning and objectives will not be successful and will not achieve the expected results.
4 graph-Accept a change is connected to an emotional process
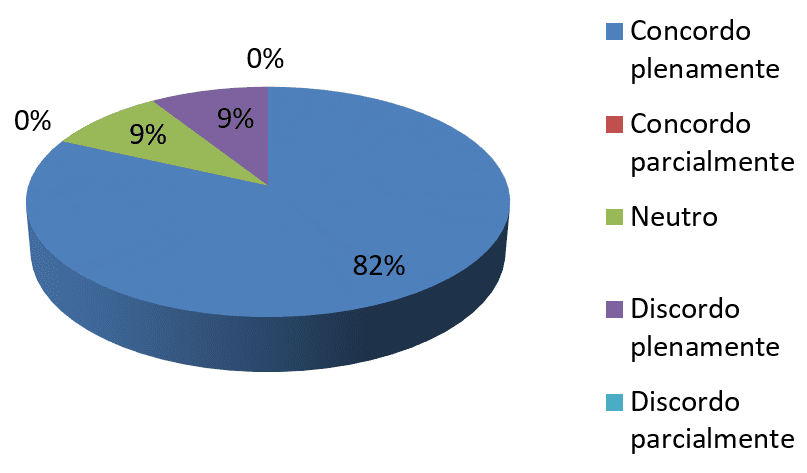
s. Source: survey data
It is observed that 82% of respondents agree fully that accept a change is connected to an emotional process, whether in personal life or in the workplace, already 9% remained neutral and other 9% do not agree that the change is linked to an emotional process is in personal life or on your desktop. Negative emotions such as fear, anger, sadness, guilt, insecurity and the difficulties to understand the changes are a result of emotional resistance.
Chart 5-Change is a process of pain anxiety for people
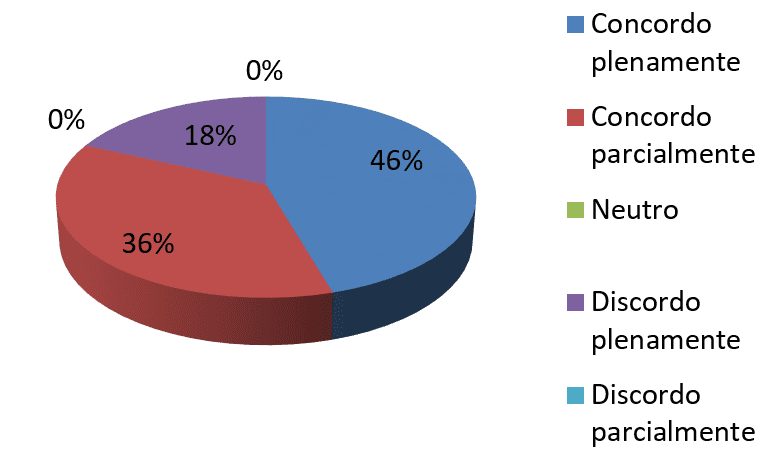
As 46% respondents fully agree and 36% agree partly, but not necessarily 18% agree that the change is linked to a process of pain and anxiety for the people. Through this data it is possible to validate that the change is linked to a psychological aspect (Chiavenato, 2010).
It was also possible to see through the data, 82% of employees agree fully that criticise and disapprove the changes is easier than trying to compromise with them, and 18% disagree partially. Maurer (1996, apud BORTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, S/A) States that the immediate criticism is considered to be one of the forms of resistance to change that is intended to cause rejection by the change before the same be detailed.
Chart 6-My work rate decreases when there is a change in the process
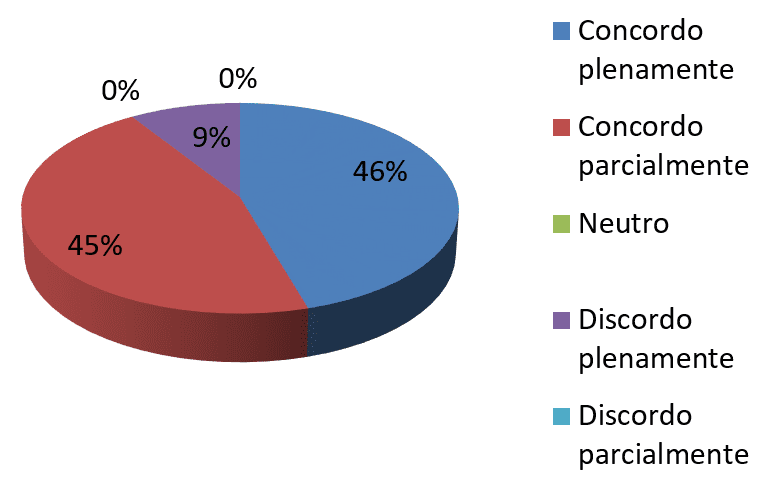
Source: survey data
As chart 6 data was found that 46% agreed fully, 45% agreed in part and 9% believe that the deployment of changes does not interfere in his work rate. Judson and Mendes (1996, 2001 apud BOTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, s/a) reported that the decrease in the pace of work and low productivity, when the individual is in a process of adaptation to change, occurs due to personal withdrawal which is one of the forms of resistance, as it may hinder the progress of change in the organization.
Graph 7-afraid of the unknown
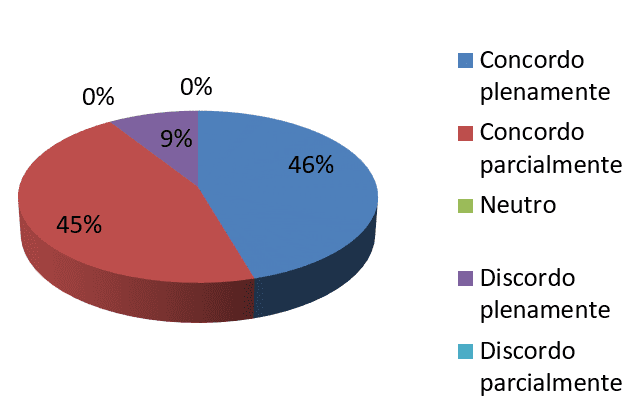
Source: survey data
You can view the chart explicitly through 7 that 46% of employees agree fully and 45% agree 9% partly in contrast claim without fear of the unknown. As organizational behavior research reveals people and organizations tend to resist changes by the following factor: fear of the unknown, because working with something you know is more comfortable for the developer. With the following statement: to accept a change is easier when you know what the results will be positive, all employees agreed. You can tell this because the fear of the unknown becomes a kind of barrier causing in this way some resistance on the part of the team making the deployment process of changes in the organization.
In respect of the role of the leader in deployment and change management note that all employees maintain that the transition process of change is much easier when there's a leader able to conduct it. You can see through the data obtained to the leadership is fundamental to the changes occurring in the Organization and to be successful. The leader is the person responsible for the implementation of changes, by communication to the employees and by the involvement of the same, and also the motivation of the team before, during and after the deployment process.
It was found through the survey data that 37% of respondents of the company agree fully that when a member of the group disagrees with the change the others try to convince you that the change will be positive. This factor shows that the developers have team spirit and commitment which greatly facilitates the mutual motivation and achievement of expected goals with change. 36% disagree 18% remained fully neutral and 9% agree partially.
Graph 8-the culture of the Organization undermines the process of organizational change
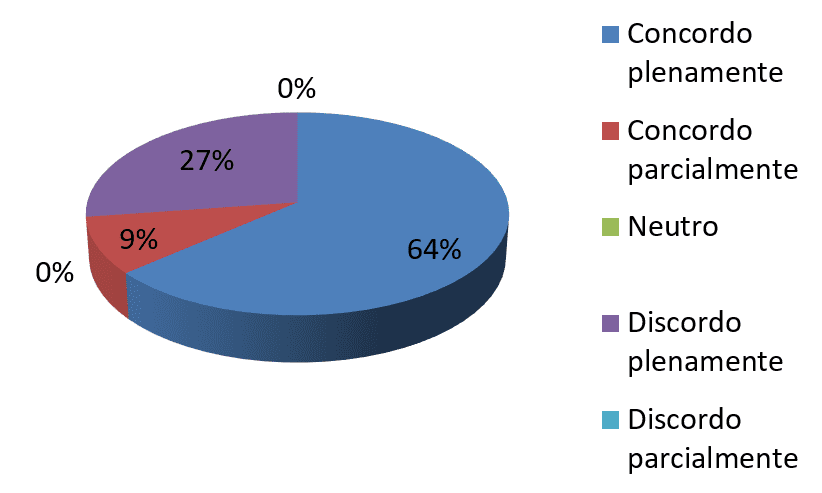
Since every company has its own culture and that the deployment of changes depends on the culture of the Organization and of its work, was asked to the employees about the culture of the Organization and if the same harms the process of organizational change. Note that 64% of employees agree fully that the company culture at study affect the deployment of changes, with 27% disagree 9% agree fully and partially. It is essential that the company develop a culture of change, because without it is impossible to obtain successful results even if the change is well planned (BREGION 2013).
Graph 9-All desired by the organization change is communicated to employees
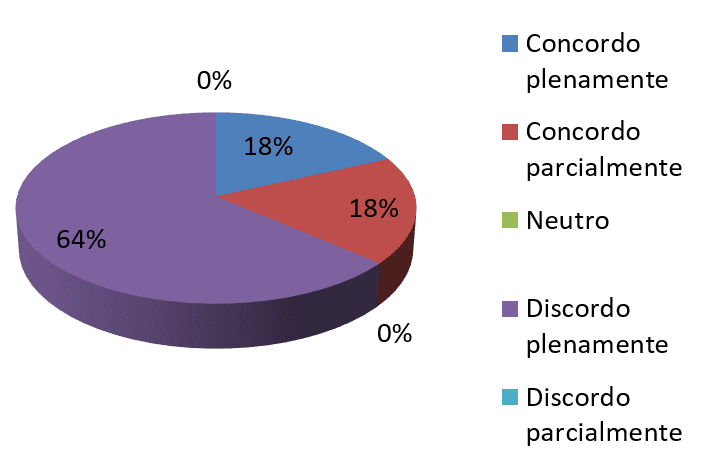
s. Source: survey data
Through 9 chart, it turns out that more than half of employees, totaling 64% claim that the changes sought by the Organization are not communicated to all team members, 18% already agreed fully and the other 18% agreed in part. Using the data obtained was prompted to tell employees about the importance of communication before, during and after the deployment process. According to the same communication makes them schedule for changes, because without it the deployment does not occur so successful. They stated also that she is crucial because employees will be attentive and prepared psychologically for training if you need.
The developers stressed the importance of the leader in the process of communication on the changes as well as the sharing of results. As the same any process of change must be parsed and planned and mostly explanatory form release to developers because communication allows guide colleagues and employees about workplace improvements and better results in the company's performance.
All employees fully agreed that a change be deployed the entire organization must be willing to change, that is, the change has to come from both parties, since the operational level management until, there needs to be change in behaviours of everyone involved.
91% of respondents agree fully that in the enterprise, the deployment of a change happens even if the contributors do not agree with her, and 9% of respondents agree partially. These data reveal the lack of participation of employees during the decision-making process of organizational change, since they may collaborate with innovative ideas and solutions for the company. Employee participation makes him feel part of the process and ends up resulting in commitment to what is being proposed by the agent of change.
Graph 10-When I'm statement in relation to the implementation of change in organization:
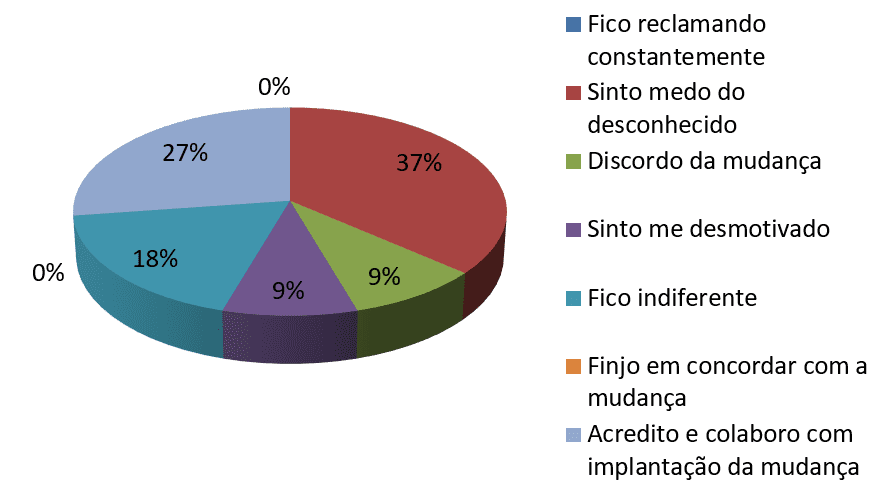
açãoFonte: research data
Analyzing the graph 10 you can see through the data the main forms of resistance to change on the part of the company's employees. The hypothetical situation raised: when I reported in relation to the implementation of change in organization, aimed to identify the main forms of resistance to change in the Organization, in this way it was possible to identify that 37% of employees feel fear of the unknown. This type of resistance is connected to psychological aspects and is inherent to human beings being regarded as something normal. Individuals tend to react in the face of situations where they run into the need for change, especially when it comes to threaten your comfort zone, but this fear must be overcome and should not prevent the changes occurring in the organization.
Already 18% responded that stay indifferent when they are reported in relation to the implementation of change in the organization. The indifference is one of the forms of resistance whose purpose is to get developer to lose interest in work and just do what is imposed, but without protest, so the developer does not engage in the process, hindering the implementation of the changes.
Only 9% answered that disagree with change when they are notified of deployment. This type of resistance is easily identified and can be considered for active resistance, but it is one of the hardest types to be treated as due the developer has opinion just opposing and criticizing the deployment and how the change will be carried out.
Among survey respondents, 9% admitted they feel unmotivated when they are notified of deployment of changes in the organization. This motivation is linked to passive resistance and causes negative effects superior to active resistance, because the developer might end up slowing your pace of work and search for innovative solutions and not cooperate with the change process by preventing the implantation of the change is carried out.
27% said they already believe and collaborate with the implementation of changes in the organization. This type of reaction is regarded as voluntary cooperation and occurs when the individual believes in and supports the implementation of ideas and actions related to changes and is the kind of targeted reaction by agents of change (JUDSON and MENDES, 2001 1996 apud BOTOLOTTI, SOUZA, ANDRADE, s/a).
4.2 interview with Lab Manager
For the collection of information through field research, was prepared a script for interview with the Manager of the company in order to verify that the resistance to change affects organizational development. The interview was conducted as follows:
That Manager was asked to explain his views on when an enterprise should provoke an organizational change, according to the same organizations must always be evolving in order to keep informed of events in general the purpose to ask the Manager of your opinion was to identify if the company seeks innovation and is in constant transformation. You can see through the opinion of the manager that the company acknowledges the need to constantly evolve and be updated of developments in all areas. Also notable is the concern of the Manager to be updated about technological factors and also the competition, since the same was the factor that determined the need to change the company's work force was:
"The working environment itself needs to be aware of the technological updating and constant monitoring of competitors who need change the workforce" (Manager).
It is observed through the Manager's account that it recognizes the importance of technological innovation and competition to cause organizational changes. Whereas organizations wishing to keep on the market will have to be in constant improvement and always seeking to be up-to-date.
Asked if the Manager if the motivation for organizational change originated from personal perception, or external pressure on the part of employees and customers or originated from responsible for the administration of the company. He stated that the motivation arose due to personal factors and external pressure, as participation in conferences always orients the personal perception and external pressure from the competitors finish driving the organizational change. The Manager's response signals that the factor that has led to more company to get organizational change is the very competition that makes the business owner seek innovative solutions as a strategy to stay in the market where competition has become increasingly fierce.
Also asked if the transition process of change has been no communication with the employees, the manager stated that there was, but through this response was not possible to clearly identify the type of communication and if the same occurs in detail and if you can achieve the goals, because according to the results obtained with the questionnaire applied to employees the company has failed in your communication process in relation to implementation of changes. It turns out that more than half of the employees claim that the changes sought by the Organization are not communicated to all team members, it can be observed that there are flaws in the process of communication between management and employees.
Again asked the Manager if the change was structured and designed with the team of managers and employees in order to find out if there is a concern on the part of the Manager of the team involved in the process of implementation of changes, the response was as follows:
"In a way yes because we carry out visits to our customers informing the changes we're always communicating the officials of changes and those that occur" (Manager).
As the Manager for the concern to keep its partners about changes in the company, so the owner carries out frequent visits to their clients to keep them informed about update of prices, on innovations in the company or in a specific process, but it should be noted again that wasn't the way it is performed detailed communication with their employees and how they are inserted in the process of change. You can see through the interview with the developers that they feel the need to be inserted into the process of change, and can give suggestions for improvements and also present your point of view, take your questions to understand the reason for the change and also participate not only in the implementation of the change, but also have freedom to make suggestions for innovative changes to the owner of the company.
Asked what disadvantages and difficulties to fulfill the established planning with the change, the Manager said:
"It's usually the difficulty of assimilation of change by the collaborative team" (Manager).
You can tell by the Manager talks lack of communication is the critical point of the organization. Asked employees if they receive training when there is any change or deployment process and if the same was satisfactory, it can be concluded that all were unanimous on the answer no and that when there are changes in the company she only is applied, but there is a kind of training before their application.
The developers have cited learning in practice from the mistakes and successes and that when there are any changes are communicated on the subject and learn in their own practice of work. These difficulties of assimilation of change on the part of employees can be resolved with training, monitoring and evaluation so that the developer is prepared and qualified when you change deployment thus avoiding the occurrence of errors and waste of time.
The Manager was asked if he had been created a team to lead the process of change and the same replied that there was no creation, there was only the leadership of the owner manager of the company.
The Manager was requested to name the main challenges faced in the implementation of the change, the purpose of this question is to check if there is resistance on the part of employees and if the same is considered a challenge to be overcome, but through talks the Manager cannot identify at any time that he consider the resistance of his team of collaborators as a challenge in the implementation of changes and that his biggest challenge is the competitors.
So wondered how the management faced resistance from employees regarding the change. According to the Manager was as follows:
"So only motivating employees to leave the comfort zone" (Manager).
Meet the source of resistance is fundamental to be able to adopt strategies to overcome it. It is notable through the Manager's assertion that he admits that there is resistance on the part of his team of collaborators, but that it does not have appropriate strategies used such as communication with employees participation in decision of change, the insertion of the opponents in the process of change so that they can somehow contribute significantly the use of training, therapy and advice if the resistance do psychological factors, compensation and rewards for those who engage in achieving the expected results with the change, and in cases where the employees oppose in order to prevent the implementation of the change manager you can use the following methods: transfer threats, lost promotions, recommendations and negative performance evaluations. These tools if used, will make resistance is minimized (ROBINS .2005).
In this case we suggest to the Manager to first establish the objectives to be achieved with the changes and perform a deployment management of changes in the organization by setting a leader responsible for planning. The plan should contain the type of desired change, the date of their deployment and end, where the change will occur, who will be responsible for its implementation, the people who will be affected by the same and costs that the company will get with this change.
After the completion of the plan of action the leader should meet with the employees to present the goals of the organization with the implementation of change and the gains made with the same, after the communication is necessary for the leader of opportunity for employees are making suggestions and also to clarify possible doubts so there is no failure in the communication process.
Held communication and script developers are made aware of the objectives is the time to make the change, whether in a particular area, or particular service, until it extends to the whole organization. It is recommended that the switch be deployed gradually because the leader may be doing the monitoring along with the Manager, if is possible to correct them.
The training is fundamental in this process because it tends to reduce the resistance that arises because the developer did not feel prepared for the implementation of change. The leader will be able to adopt the following tools such as: lectures, preparation of explanatory material, meetings for questions, stage, video lessons. Training in certain cases of change should be carried out before, during and after your deployment.
The leader must also make constant and regular follow-up, in order to identify difficulties that might arise during the process, to be correcting the flaws. The evaluation is also an important tool and allows the results to be analyzed in a certain period of time. The leader must stipulate the period in which they will be performing this evaluation be weekly, or every 15 days, the ideal that the assessment is made in the short term, because the leader can in some cases be redirecting your actions if you find faults and obstacles.
After the final deployment of the change is necessary for the leader to conduct another meeting with the Manager and the employees so that it can provide feedback necessary to report whether the goals were achieved and to share the results of change.
CONCLUSION
This research had as main objective to analyze if the resistance to organizational change affects the development of the laboratory of clinical analyses. It was observed that the company search for innovation and seeks to be ahead of the competition. It was noticed that the employees have admitted presenting resistance when they are faced with situations that threaten their comfort zone.
Given the above, it was noticed that currently there are gaps in the communications process manager-collaborator during deployment of changes, which contribute to the solidification of the resistance on the part of the collaborative team, because they recognized the importance of communication in business, primarily as a way to get trace goals to be achieved with the changes proposed by the management.
It was identified that the training during the implementation of changes, just not in the lab, this factor has been one of the causes of resistance, because the training contributes to preparation of the employee to perform the changes proposed by the company, and so that they learn to deal with the fears and uncertainty that arise during the deployment process.
It is believed finally that this study has reached its goal and contributed to the target organization of field research, because through it was possible to identify the resistance on the part of employees and lack of communication on the part of management in the process of implementation of changes. The present study has provided the Manager tools and suggestions so that it can manage the resistance organizationally, that will result in competitive advantages for the company.
6. REFERENCES
BORTOLOTTI, Silvana Ligia Vicenzi. ; Junior. Alfonso Farias de Souza; Dalton Francisco de Andrade; Resistance to organizational change-cognitive, behavioral and affective Reflections; VII National Congress .2011 Management Excellence.
BORTOLOTTI, Silvana Ligia Vicenzi. ; Souza, Biswajit Agarwal. ; Dalton Francisco de Andrade; Resistance a useful tool in organisational change.
BREGION, Viviani, Organizational Culture: a case study in an institution of higher education. 2013. 79 f. Monograph-Faculdade Cenecista de Capivari-FACECAP undergraduate degree in business administration, 2013.
CARRANZA, Giovanna, TRT-PE 6 Region Administration-personnel management Textbook; 2012.
CERIBELI, Harrison Bachion and MERLO, Edgard Monfort, organizational change: a multicasos study; Faculty of Economics, administration and Accounting Department of Administration-University of São Paulo-Ribeirão Preto-SP, Brazil, 2013.
Amado Luiz Cervo-scientific methodology. -4 ª ed.-São Paulo: Makron Books .1996.
CHIAVENATO, Neena, introduction to the general theory of Management: a comprehensive overview of modern management of organizations; 7. ed.rev. and current.-Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2003-6th reprint
CHIAVENATO, Neena, General and Public Administration; 6. Ed. reimp. Oxford: Elsevier, 2006.
CHIAVENATO, Neena, people management: the new role of human resources in organizations; 3. Ed., London: Elsevier, 2010.
Rabbit, Naira Cenachi, change management: development and implementation of a methodology applied to MRS logistica. 2012. 80 f. Monograph-Instituto Militar de Engenharia.
How to develop research projects: language and method/Roberto s. Kahlmeyer-Mertens …[et al.].-Rio de Janeiro: Editora FGVP .2007.
CRESWELL, John w.-Research Design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods.-2. ed.-London: New Haven .2007.
FREITAS, Flavio Ozório., organizacioanal Culture and its relation to resistance to change: the perception of TLI-Espirito Santo Research Institute Foundation in accounting, economics and finance; Victory, 2010.
GIL, Antonio Carlos-methods and techniques of social research 6. ed. São Paulo: Atlas .2008.
GIL, Antonio Carlos .1946-how to write research projects/Antônio Carlos Gil. 4. ed. São Paulo: Atlas .2002.
LAKATOS, Eva Maria, Scientific Methodology/Eva Maria Lakatos, Marina de Andrade Marconi. -5. Ed. -2. reimp.-São Paulo: Atlas .2008
Matos, José R. Gilvomar; Matos, Rosa Maria B.; Gardar Almeida Ribeiro; Analysis of the enterprise environment: the organized chaos to the strategic planning of organizations; Rio de Janeiro: E-papers, 2007
Research methods/T[organizado por]atiana Engel Gerhardt and Denise Tolfo Silveira; coordinated by Open University of Brazil-UAB/UFRGS and the Technology degree course-planning and management for Rural development of SEAD/UFRGS.-Porto Alegre: UFRGS Publisher .2009.
Moreira, Elen Gongora, organizational climate; Curitiba, PR: IESDE: Brazil, 2012.
PRODANOV, Cleber Cristiano, methodology of scientific work: m[recurso eletrônico]ethods and techniques of research and scholarly work. -2. ed-Novo Hamburgo: Freevale .2013.
ROBBINS, Stephen p., 1943-organizational behavior; 11. Ed., New York: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005.
ROESCH, Sylvia Maria Azevedo, internship and Research Project in administration: guides for stage, completion works, dissertations and case studies. -3. ed.-reimpr.-4 São Paulo: Atlas, 2009.
SANTOS, Marcel de Souza e Silva, management of organizational change: a theoretical review, 2,014,106 f. Dissertation (maester) – Brazilian School of public administration and companies, Academic and research training centre.
SANTOS, Marco Antônio Pires Camargo, organizational process Maturity: a study in a multinational industry welding sector, 2009.96 f. Dissertation (Master's Thesis)-Universidade FUMEC. Faculty of business sciences.
SILVA, Walter Franco Lopes da, benefits and services; Curitiba: Brazil IESDE s.a., 2008.
SOARES, Helena Teixiera Magalhães, organizational change and its impact on the behaviour of individuals in an organization of the third sector, 2,007,169 f. Dissertation (maester) – Faculdades Integradas de Pedro Leopoldo.
APPENDICES
Questionnaire applied to employees of the laboratory
1. Educational level achieved:
- () Primary education incomplete
- () Primary education complete
- () High school incomplete
- () Complete high school
- () Upper incomplete
- () Complete Upper
- () Specialization
2. Time of service in the enterprise
- () up to 5 years
- () of 5 to 10 years
- () of 10 to 15 years
- () of 15 to 20 years
- () more than 20 years
3. Gender:
- () male
- () female
4. Age:
- () up to 25 years
- () of 26 years to 30 years
- () of 31 to 35 years
- () of the 36 45anos
- () of 46 to 50 years
- () above 51 years
5. What are the responsible for organizational change processes in the company in which you work? That is, who participates in the process of deploying a new structure or a new process?
- () Top management
- () All employees, regardless of position held
- () Anyone who has full authority and power
6. The transition from "old" to "new" is difficult for the developer.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
7. When I disagree with a proposed change, or do not understand well, normally I feel confused and question whether the changes are really necessary.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
8. Accept a change is connected to an emotional process, whether in personal life or on your desktop.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
9. Accept a change is easier when you know what the results will be positive.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
10. Change is a process of pain anxiety for the people.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
11. It is easier to criticise and disapprove the changes than trying to compromise with them.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
12. My work rate decreases when there is a change in the process.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
13. I'm afraid of the unknown, I prefer to work with what I already know.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
14. The transition from "old" to "new" it's easier when there's a leader able to drive change.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
15. In our Organization, when the group disagrees with the change, no one agrees with her.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
16. The culture of the Organization, or of the people who work here, is detrimental to the process of organizational change
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
17. All desired by the organization change is communicated to all team members.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
18. For a change is implemented across the Organization must be willing to change.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
19. To change it is necessary to establish the goal of transformation that is intended to achieve.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
20. In our Organization, the deployment of a change happens even if the contributors do not agree with her.
- () I fully agree
- () I agree partially
- () Neutral
- () Strongly disagree
- () Disagree partially
21. When I reported in relation to the implementation of change in organization:
- () I'm complaining constantly, I shorten my work rate.
- () I feel fear of the unknown
- () Disagree with the change and try to convince the team that she will not be required.
- () I feel unmotivated and not cooperate with the deployment of the change proposal
- () I'm indifferent (not agree and not disagree), I'd rather not get involved in the process
- () Pretend to agree with the change when really I do not agree.
- () I believe, accept and cooperate so that the process of change is deployed.
22. To change it is necessary to abandon the current behavior? Give your opinion.
_____________________________________________________________________
23. What is the importance of communication in the process of implementation of changes?
_____________________________________________________________________
24. When there are any changes in deployment Organization employees receive training? The training is satisfactory and meets the goals?
_____________________________________________________________________
25. In the organization there is a responsible person to assess whether the deployed change is occurring as expected?
_____________________________________________________________________
Questions for interview with project manager
- In your opinion, when an enterprise should provoke an organizational change?
- What is the factor that most determined the need to change the work force in the Organization?
- The motivation for change originated from personal perception, or external pressure (employees and/or customers) or request of the senior management?
- There was no communication in the process of transition?
- The change has been structured and designed with the team of managers and employees?
- What disadvantages and difficulties to comply with the established planning.
- Was created a team to lead the process of change?
- Was created a team to lead the process of change?
- What are the main challenges to implementing the change?
- As the administration faced resistance from employees regarding the change?
- What are the strategies adopted to overcome the barriers found?
- One of the six tactics that change agents can use to face the resistance choice which best suits to eliminate the resistance in your organization:
() Education and Communication
() Participation/involvement
() Training, counseling, therapies paid leave if the developer introduce reactions such as fear and anxiety.
() Negotiation: offers of compensation and rewards
() Handling and Cooptation: induce the employee to accept the changes
() Coercion: threat of transfer, loss of promotions, letter of recommendation and negative performance evaluations.
[1] 7° the academic course in administration of CEULJI/ULBRA. Email: [email protected]
[2] Expert, Master Teacher of the course of CEULJ administration/ULBRA. Email: [email protected]