PRIETO, Manoel Jose [1]
PRIETO, Manoel Jose. Mathematical logic to the elementary school. Multidisciplinary Core scientific journal of knowledge. 03 year, Ed. 04, vol. 05, pp. 54-76, April 2018. ISSN:2448-0959
Summary
The search object discussed in this article is the introduction of Mathematical Logic in all years of elementary school, on a regular basis, programmatic and systemic. It is expected to achieve greater speed in the process of training of young people by connecting them in your near future to growing demands for intellectual capital required by the global market. We discussed often, in teachers ' rooms, questions about the teaching and learning of these students and, invariably, there are numerous considerations as to the effectiveness of the methodologies employed. Recurring issues such as family, social, cognitive, educational models, among others, can hardly be answered without further analysis. Through bibliographical research, study the intellectual functions in Logical and emotional field that, together, have great importance in cognitive development of these students and can give subsidies to responses expected in that context. Once the logical values in human relations are not always easy to be understood or identified, we will seek to reveal them through teaching interdisciplinary projects, problems, situations, technical and investigative methods scientific, so that these students develop better their skills and abilities and are favored in your adulthood, both ethics as professionally.
Keywords: reasoning, logic, mathematics, elementary.
Introduction
The Logical Mathematician comprises a set of techniques, methods and procedures, organized, organized, triggered and, sequentially structured through the interactions between the multiple Functional Intelligences promoted by brain, facilitate understanding and problem-solving. Can be developed through the use of methodological, didactic-pedagogical resources and still teaching and learning objects of technical and/or scientific throughout elementary school.
When we discuss the factors that hinder the teaching and learning of elementary school students faced with questions whose answers are not so simple to be satisfied. Among others, we can cite: what to teach, how and when to teach, the ethical and moral values, social responsibility, new technologies, the speed of access to information, globalization, sustainability, greater demand for quality of life, the preparation for the future, the differences and trends cultural partners, social inclusion and educational policies.
We intend to demonstrate in this study, it is possible to use logical reasoning, systemic mathematician, and program continued in all years of primary education, to promote the access of these students to real-world problems, respecting the objectives outlined by the law of Guidelines and Bases of education and the national curriculum Parameters.
We will deal with in this research, the strategy and the instrumentalization of some methods and processes, as well as some objects of teaching and learning that can be applied through the Logical Mathematician to obtain greater speed in process of training, development and maturity. Make them realize and recognize the importance of your multiple intelligences and how to use them in the transformation of the environment in which they live.
The cognitive areas to be worked with the purpose to develop the intellectual functions of students throughout elementary school, through the Logical mathematician, will be supported in the contributions offered mainly by Howard Gardner in your work on multiple intelligences, by Daniel Goleman in your work on the Emotional Quotient, by Jean Piaget, though unintentionally, laid the foundations of constructivism and John Dewey, American philosopher and pedagogue influenced Anísio Teixeira, one of the creators of the New school movement occurred in Brazil in the 30. Learning to potentialize, assess situations problem with logical content and propose solutions, these young people can become good agents transformers of society, critical and conscious citizens of their social responsibilities.
The method to be used shall be that of research, literature review and experience reports of work linked to this area.
The polls will be held in physical and virtual libraries, international and national scientific articles, PhD theses, specialized sites and academic papers, all with due recognition.
As for the experience, only those whose results were significant and contributed effectively to the rationale of these studies.
Development
Consolidate the Logic of systemic form, and continued in programmatic all years of elementary school, through the use of methods, teaching and didactic tools objects-pedagogical, for the development of the functions Intellectuals requires resources and methodological expertise of teachers, as stated by Galuch, Sforni (2009, p. 123). "the teacher's mediation is essential, because the individual appropriates the meaning only to be inserted into suitable environments, whether literate or scientific literacy teachers".
Frequently asked whenever we discussed education, mainly in the classrooms of teachers: When and what is truly important to teach? What methods, education systems and practices more effective? What are the expected results and that time will come. How to relate the knowledge with the permanent demands of society?
We reflect on the complexity of factors that interfere in the dynamics of teaching and Learning Systems such as: the family involvement, commitment to studies, attention deficits, cognitive limitations, the possible conflicts between generations, (X, Y, Z, Alpha, digital natives), both of whom teach with who learns and, updating and training of teachers. Nevertheless, are also remembered, among other things, the ethical and moral values, social responsibility, new technologies, the speed of access to information, globalization, sustainability, greater demand for quality of life, the preparation for the future, the differences and trends, minorities and cultural partners, social inclusion.
To get the answers we will start using the law of Guidelines and Bases of education and the national curriculum Parameters that guide us, mainly in the area of mathematics, making the students, among other productions, acquire:
I-the development of the ability to learn, taking as basic media full mastery of reading, writing and calculation;
II-the understanding of the natural and social environment, political system, of technology, of Arts and of the values on which society is based;
III-the development of learning capacity, with a view to the acquisition of knowledge and skills and the formation of attitudes and values;
IV-the strengthening of the family ties, the bonds of human solidarity and mutual tolerance in which sits the social life. (BRAZIL. LDB-Law of Guidelines and Bases of education no. 9,394 of December 20, 1996).
And yet, know:
- Use the different languages: verbal, math, graphics.
- Position of critical, responsible and constructive manner in different social situations.
- Understand Member, dependent and transformer agent environment.
- Understand the citizenship,
- Position-critical way
- Meet fundamental characteristics of Brazil and valuing the diversity of the cultural heritage of Brazil,
- Develop knowledge of yourself and a sense of confidence in your abilities, affective, cognitive, physical, ethical, aesthetic.
- Learn to use different sources of information and technological resources to acquire and build knowledge;
- Question reality formulating problems and trying to solve them using logical thought. (BRAZIL. PNE-national plan of education law No. 13005, of 25 June 2014).
Logical values (true or false) that exist in human relations are not always easy to be understood or identified and to study them the professor, motivate, guide, organize and direct, his students proposing activities that stimulate your multiple intelligences, without inhibiting the creative process and interfere in their stages of development. Second, Copying (1978, p. 19): "the study of logic is the study of the methods and principles used to distinguish correct from incorrect reasoning".
Know the limitations and interests of students will facilitate the achievement of the proposed objectives already from the initial series of elementary school. For Gardner, (1995, p. 21):
The biggest challenge is to get to know each child as she really is; know what she's capable of and education focus on the capabilities, strengths and interests of the child. The teacher is an anthropologist, you observe the child carefully, and an adviser, which helps the child to achieve the goals, the school district or the nation.
Experience shows us that by using problem situations involving cross-cutting issues and to relate the disciplines, we give more sense to study objects, activate the logical reasoning and motivate students to take ownership of knowledge. According to Abar, (2006), "logical learning helps students in reasoning, understanding of basic concepts, in formal verification of programs and better prepares them for understanding the content of more advanced topics".
Note that if these challenges are not achieved, we can compromise the future of these young people, as CITES Rauber (et al., 2003), "it is common to find University students with difficulties to interpret what they are reading, because they have not been literate for understand what is "behind" that which is written, that is, the real meaning and context ".
The motivation and stimulus to multiple intelligences and logical reasoning.
HOWARD GARDNER

"The emergence of new technologies requires us to educate children differently" (GARDNER).
It seems that latent, in today's world, the human skills and abilities should be expanded and integrated into the global information system, promoted by new technologies, such that the human being: "able to direct its objectives, values, thoughts and actions in relation to a network of interactivity that share the production of meaning and functioning of social responsibilities "(GARDNER, 2004, p. 254).
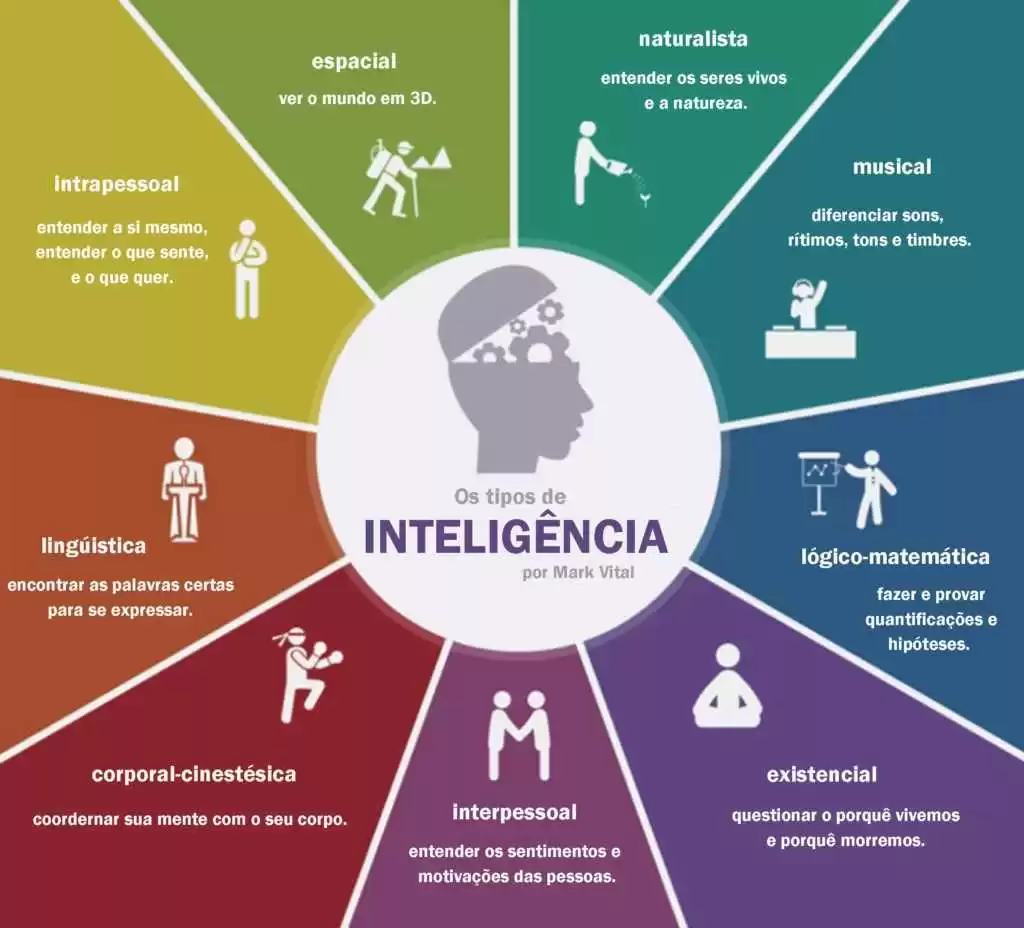
Howard Gardner, multiple intelligences theory in your calls for various types of intelligences, illustrated below, and which together or associated enable resolve or understand problems of the most diverse orders, even if not in all these are with equal development.
Intelligence implies the ability to solve problems or develop products that are important in a particular environment or cultural community. The ability to solve problems allows the person to address a situation in which a target must be achieved and find the appropriate solution to this goal (GARDNER, 1995, p. 21).
THE TYPES OF INTELLIGENCE – MARK VITAL
Thomas Armstrong Gardner scholar infers:
Multiple intelligences is a cognitive model that attempts to describe how individuals use their brains to solve problems and create products, your theory to show how the human mind operates on the content of the world. The wits he found so far are: linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal and intrapersonal, naturalist (ARMSTRONG, 1995, p. 14)
and yet, (2001, p. 14-15) discusses the set of wits mentioned in Gardner's theory explaining each one of them:
Linguistic intelligence: the ability to use the words, with sensitivity to the sounds, rhythms and meanings of the same, the ability to convey ideas. Gardner shows us that this is used with greater intensity by poets. The children she appears in the ability to tell stories and reporting experiences.
Interpersonal intelligence: This aims at intelligence ability to perceive changes in moods, intentions, motivations and feelings of other people. You'll notice more in teachers, politicians and psychotherapists, children can observe those who enjoy leading other children, because they are sensitive to the needs of others.
Intrapersonal intelligence: is intelligence more staff on the other, corresponds to the kind of intelligence in which the person has the ability to have access to their own feelings, ideas and dreams, uses them to solve personal problems.
Logical-mathematical intelligence: the remarkable point in this intelligence is the child with special ability to count and make mathematical calculations and to create your reasoning practices notations.
Musical intelligence: the manifestation of this intelligence through the skill and sensitivity to rhythm, tone or melody and timbre of a musical piece. The small child with special musical ability realizes different sounds in your environment and sings to herself since she was a kid.
Spatial intelligence: the ability to perceive the visual and spatial world accurately. The child has the ability to manipulate shapes or objects mentally and, from the initial perceptions, create tension, balance and composition, in a visual or spatial representation. Is present in the artists, engineers and architects us. In young children, the potential is observed in the ability to wrap-head and other space games and attention to Visual details.
Body-kinesthetic intelligence: Note-If your skill in using the whole body to express ideas and feelings (for example, as an actor, MIME artist, dancer or athlete) and ease-of-use of hands to produce or transform things (for example, as craftsman, sculptor, assembler or surgeons). It also includes specific physical skills such as coordination, balance, dexterity, strength, and others.
Naturalist intelligence: linked to the plant and animal life, also known as biological or ecological Intelligence. We can see in gardeners, landscape, the nature lover to the florist. It is the ability to identify members of the same species, recognize the existence of different species and map relationships between different species.
Although there are some criticisms about the work of Gardner, your theory has wide acceptance in the educational area. Maybe we can answer the how to teach. Weinreich-Hast spells
What does Gardner gave us a contribution? Your new way of conceiving the intelligence frees the psychology of a limited paradigm, based on a unitary model of intelligence. A model of multiple intelligences will facilitate the exploitation of a wide range of mental activities. This fact is particularly important, considering that the cognitive models and information processing have dominated the psychological research for several years (WEINREICH-HAST, 1984, p. 22).
Some strategies to stimulate Multiple intelligences through logical reasoning in school environment.
Perhaps the first one is that not all people have the same skills and learn the same way. Live in various sociocultural environments, establish relationships with the environment, too, differently which ultimately encourage learning and cognitive performance. For Borges (2003, apud Dantas, 2005, p. 3) "individuals have different life histories because they interact with the medium differently, soon, know and learn different forms".
According to Agarwal (2005, p. 104), multiple intelligences can be encouraged in class as follows:
Linguistic intelligence: "progressive physical image Description. Verbal word games. Teaching a foreign language when possible. Language games; ".
Logical-mathematical intelligence: "replacing the mechanical count by count. Perception of the sets. Notions of scale. Mathematical games; ".
Spatial intelligence: "Reading with interactive participation. Beginning literacy of cartographic signs or not. Beginning of swimming lessons when possible. Analytical and descriptive examination of old photos. Space games; ".
Musical intelligence: "description of facts and experiences the language sound landscapes. Musical games; ".
Body/Kinesthetic intelligence: "playful Games. Body games ".
Interpersonal and Intrapersonal intelligence: "parental involvement initiatives in a probate program of personal feelings. Help the child understand and identify your emotions; ".
Naturalist intelligence: "Games involving interactive adventures between the child and the discovery of nature". Games naturalists;
Some strategies for parents stimulate the multiple intelligences of their children in social and family environment.
It is necessary a great effort for the education of these young people, not only on the part of teachers, but also of parents and guardians, so that these intelligences can be stimulated in other environment not the school. Antunes (2005, p. 112) suggests some strategies that, in some cases, can also be used for students of 9 to 14 years.
Table 1-strategies for parents stimulate Multiple intelligences
| Ages Intelligences | Of the five to eight years of age |
| Linguistic Intelligence | -Encourage the child to tell stories and perform readings; -Develop questions with guesses. Ex: what are we going to do if it rains today? -Avoid one-word answers, explain the "why" of things, even if the child does not ask; -Encourage her to write the words you know. Develop the joke to write tickets. Perform linguistic games. |
| Logical-Mathematical Intelligence | -Stimulate mathematical games games; -Make the kid figure out how to play dominoes; -Bring cash home and place objects, then ask the child the amount of objects that fit into each box; -Make sure the child understands what are hours, asking that she represents in the hours digits views in an analog clock. |
| Spatial Intelligence | Teach the child to cut magazines; -Ask the child for this separate heads of bodies and figures and make new characters; -Make the child distinguish objects that are "above" or "below"; -Let the children play with strategic games (chess, puzzles, among others); -Counting your day. Extend the narrative questions and stimulating the comparison between the day before and today; -Work with the perception of laterality and perform spatial games. |
| Musical Intelligence | -Make sure the child participate in identification of sounds; -Excursions with the child for the purpose of this hearing natural sounds; -Introduce the child various types of music and musical games. |
| Body/Kinesthetic Intelligence | -Create activities that stimulate motor skills, such as running, jumping, climbing stairs, among others; Teach the child to use scissors; Let the child move en masse to model; -Child tie knots in ropes. |
| Interpersonal and Intrapersonal intelligence | -Encourage the child to name their feelings, causing her to discover the meaning of "joy", "sorrow", "anger", among others; -Praise the child with moderation, please do so to discover the things she's good; -Stimulate your self-esteem and help her deal with her feelings by giving name to what you feel. |
| Naturalistic Intelligence | -Perform with your child personal gain; -Organize visits to the field and make the child discover the differences between animals and plants; |
Source: Antunes (2005, p. 112)
As the games and their relationships with Multiple Intelligences can be used in the development of logical reasoning.
For Agarwal (1998, p. 13), "the game helps build new discoveries, develop your personality and symbolizes a pedagogical instrument that takes the professor to driver condition and learning evaluator Stimulator.".
Some strategies may be employed as a means of bringing the student of self-knowledge and if you get the acting and interacting in the socio-cultural environment in which this uploaded.
Some games may be worked through theatrical performances in such a way that allows multiple intelligences to stimuli.
LINGUISTICS: rhymes, nursery rhymes, tongue twisters, riddles, choose formulas, symbolic games, dramatic games, songs.
Logical-mathematical: bingos, puzzles, memory games, chessboards, playing cards, rhythmic games, target games, charades, pitches: Chair and ring, bowling, Dodgeball, target shooting, biroca, Betis.
Or VISUAL SPACE: takers work with rope, hide-and-go-seek, hopscotch, normal and burned in circle games pitches, "basketball", memory games, elastic, hopscotch, goat-blind, activities of drawing, painting, collage, sculpture, games of imagination and building games that explore the different spaces (House, school, circus, place, forest, city, plants, rivers).
BODY-KINESTHETIC: imitation, role play, charades, dances, producing objects for play, motor circuit, games that involve motor skills of locomotion, manipulation and stabilization: walking, running, jumping, throwing, receiving, bounce, kick, swing, balance, spinning, up, pull, carry.
Musical: the Lullaby songs, songs of different styles, play songs, nursery rhymes, nursery rhymes, rhythmic activities and in tune, mnemonics and various dances.
PERSONAL INTELLIGENCES: the jokes of papers representation, dramatic games, theatre, dances, cantigas de roda, competitive games, the games of inhibition (statue, stop, hard-soft, peekaboo).
PICTORIAL INTELLIGENCE: knowledge, appreciation and reproduction/rereading of artistic compositions, the knowledge of art history, (movements, life and works of the great artists) and the development of the expressive capacity of the child, through the field of elements of graphic languages, musical and verbal body.
NATURALISTIC INTELLIGENCE: collections of natural products, exploration activities and adventures in forests, Woods, streams, walk to the Zoo, identifying the voices of animals, animal imitation games, role play costumes related to nature (endangered animal, forest being devastated, pollution by garbage), imaginary trips (teacher motivates the child to perform imaginary trips, experiencing different situations), in natural environments (rivers, Woods), games with names of animals and plants which make it possible to extend the knowledge and the respect for nature (LIMA, 2003, Phd Thesis).
JEAN PIAGET

"The operative structures are not innate intelligence" (PIAGET).
Piaget's contributions to the Logical-mathematical development are more noticeable in the Operative phase-when concrete breaks out the principle of abstraction and in subsequent Operative Formal logic consolidates. Maybe we can start answering to teach how to teach and especially when teaching.
Piaget (1985, p. 126) says, "to educate is to adapt the individual to the social environment".
As La Taille; Okoro and Dan (1992, p. 17), ' (…) the logic for the final form of Piaget. It is a system of operations, that is, actions that have become reversible and likely to be composed with each other ".
In the Operative phase-concrete (7 to 12 years), the child enters the elementary school where it begins to be developed and structured your logical thinking. Begins dealing with concepts, with numbers, establishes relationships time x space, realize sequences and starts the stage of abstraction. La Taille (1992, p. 17), "the ability to think simultaneously the initial state and the final State of any transformation performed on objects (for example, the absence of conservation of quantity when transvaza the contents of a glass to another B smaller diameter) highlights this stage and gives a basis for the next stage ".
The Logical-Formal Operative Stage, (12 to 16 years) consolidates the intellectual structures of logical reasoning or logical-mathematical-deductive, which will extend until adulthood. (PIAGET, 1985)
At this stage the student becomes able to understand and discuss increasingly complex problems logically, sequential and triggered by having your cognitive ability most developed. We can then introduce objects of teaching and learning, pedagogical resources that can leverage your potential for logical reasoning.
In this case we can understand how Learning Objects: "any digital resource that can be reused for education support" (WILEY, 2001, p. 7).
There are some websites that offer practical examples and guidance on how to apply these resources and promote improvements in the learning of mathematics and science in General. For example, the IVEN project-international network of Virtual Education, SEED-Secretariat for distance education, in consortium with other countries of Latin America. There we find a book whose title is: Learning Objects A pedagogical resource proposal (pdf), available at <http: rived.mec.gov.br/artigos/livro.pdf="">.</http:>
It is a material rich in proposals which enables the development of Logical Deductive Reasoning, inductive and that meets the purpose of this article, that is adding value to the learning of the Basic Cycle education.
We must not forget that, whatever the technological impact on Education systems, teaching and learning and the educators, will still exist behind the human element.
Education is much more than its technological supports: embodies a formative principle, is a social and cultural task, whatever the transformations that try, will continue depending on, first of all, their human components, their ideals and values (BRUNNER, 2001, apud BRASLAVSKY, 2004 p. 77).
JOHN DEWEY

John Dewey is still considered by many as one of the greatest thinkers of the twentieth century, in the area of education. Contributed significantly to the democratization of education, having influenced the Brazilian Anísio Teixeira, founder of the new school movement that occurred in Brazil in the thirties. Your ideas endure and maintain the thesis of an Active, progressive School, Instrumentalist, where students are the protagonists.
In schools equipped with laboratories, shops and gardens, to freely introduce dramatizations, games and sports, there are opportunities to play situations in life, and to acquire and apply information and ideas in a progressive impulse of experience continued. The ideas are not segregated, are not isolated islands. Animate and enrich the normal course of life. Information is revitalized by your function; the place it occupies on the line of action. (DEWEY, 1916)
To John Dewey, "the teacher who arouses enthusiasm in his students achieved something that no sum of systematical methods for more accurate they are, can get" (DEWEY, 1979, p. 6).
Second Digiorgi (1922, p. 24), are five steps of learning to Dewey:
1. Activity: the starting point of any learning in school, as well as in life, the school must play the best possible is any that is already being carried out; This activity that occurs spontaneously and which corresponds to the interest of the learner.
2. Problem: all activity, to be carried out, raises problems that hinder your continuity and/or development. Is this the origin of thought: this always comes from a problematic situation. The starting point of the thought is the attempt to venture, to overcome a problematic situation.
3. Data collection: the professor and students should collect data (all data type) that may help overcome the problematic situation.
4. Hypothesis: this data, once collected, will allow the formulation of one or more explanatory hypotheses.
5. Experimentation: this hypothesis should be tested in order to verify your validity. If it is valid, it will solve the problem, and the activity will continue until they encounter a new problem.
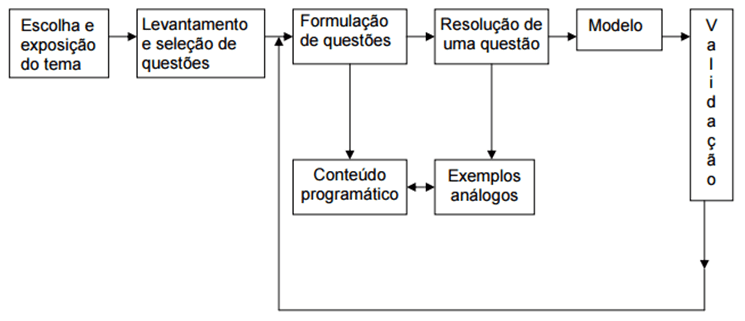
Based on these ideas, we can employ modeling schemes for solving mathematical problems such as suggested by Biembengut; Hein (2003, p. 22).
According to Dewey (2012, p. 3) "the teacher should introduce the school content in the form of questions or problems and never give advance answers or solutions ready".
It is clear, then, that by this principle we can propose a problem situation and start an investigative process with technical and/or scientific resources, in which they can use the knowledge gained and compare them with reality.
Here we find the ideal environment to propose the so-called Teaching Interdisciplinary Projects:-Financial Education Project; Environmental Education Project; Project Build Model Airplanes; Media project in the classroom; among others.
Learn through interdisciplinarity, collecting and selecting data, testing hypotheses proposing solutions, near these young people from the real world.
"real interest is the sign of any material, object, ability, or whatever, is being appreciated in accordance with what currently compete for the progressive March of an action, with which the person has identified" (DEWEY, 1978, p. 86).
DANIEL GOLEMAN

Of course we couldn't help but also mention the motivational factor and, to this end, we will consider the theory to the development of emotional intelligence by Daniel Goleman, (1998, apud Salem, 2011, p. 21). "… ability to identify our own feelings and those of others, to give him confidence and us manage emotions in us and in our relationships. "
According to Goleman (1998, apud Salem, 2011, p. 19), emotional intelligence can be categorized into five skills.
- Emotional self-awareness-recognize their own emotions and feelings when they occur;
- Emotional control-dealing with their own feelings, adapting them to each situation;
- Self-Motivation-driving emotions in the service of a goal or personal fulfilment;
- Recognition of emotions in other people-recognizing emotions in others and empathy of feelings; and.
- Interpersonal relationships skills-interaction with other individuals using social skills.
The first three are people skills and interpersonal the last two. As far as the first are essential to the self-knowledge, the latter are important in:
- Group organization-essential skill of leadership, which involves initiative and coordination of the efforts of a group as well as the ability to obtain recognition of the leadership group and a spontaneous cooperation.
- Negotiation of solutions-feature of the mediator, preventing and resolving conflicts.
- Empathy-the ability to, to identify and understand the wishes and feelings of the individuals, react appropriately in order to channel it to the common interest.
- Social sensitivity is the ability to detect and identify feelings and motives of people.
If seized by educators, these concepts can make a significant contribution in the process of training of young people for adult life. According to Goleman (1998, p. 15).
The parameters of the job market are changing. We're being judged by new criteria. It doesn't matter just how smart, or our training or our level of specialization, but also how we deal with ourselves and with others.
To develop skills and abilities related to emotional self-control, self-knowledge, respect for diversity, control of frustrations, among others, we can use theatrical games by wide range of real life situations that can be simulated. So, we will give greater contribution to emotional side of these young men for your future. According to Spolin (2007, p. 29):
The theatre games can bring freshness and vitality to the classroom. The workshops of theatre games are not designated as hobby of the curriculum, but rather as a complement to school learning, expanding awareness of problems and ideas central to the intellectual development of the students.
In article published by Claudia Gasparini (examination, 06/04/15 and 14/06/15) we can see how we are evaluated in adulthood in matters of emotional intelligence. Are positive and negative aspects which leads us to reflect some of the causes could not be on our fundamental training.
5 attitudes typical of those who have no emotional intelligence
Here are some features of postures who doesn't have emotional intelligence at work, experts say ears per scan.
- Do not recognize their weaknesses
According to Santos, the wave of "selfies" is not without reason: the self-centered are loose. The problem is that the excessive self-confidence is often not proportional to the competence of the vain. "These people lack self-awareness, the ability to recognize their vulnerabilities, and not only its forces," he said.
The professional who acts all the time as a "champion" has a very poor perception of yourself – and your relationship with the environment. "He doesn't know the impression that is causing us other, unaware of the time to talk and to remain silent," he says.
- Distrust of their own emotions
Aldan explains that many professionals try to rationalise-and thereby deny – his own emotions. "Unfortunately this is the keynote of the corporate world, that results depend only on the right," he says.
The price you pay for it is high. "If you disconnect what you're feeling, it is precisely there that will determine your emotional behaviour, unconsciously," he says.
- Don't see the other
Little intelligent professionals under the emotional angle usually have difficulties to "read" other people. "They lack sensitivity to realize the intentions of others, verbal and non verbal cues from what others are feeling," said Santos.
The problem of not seeing colleagues and bosses do you lose the opportunity to learn from them. "If we stay concentrated too much on ourselves, whether by excess self-confidence or self-criticism, it's hard to connect with each other, recognize their contributions," he says.
- Don't know what they want
Who has little emotional intelligence is often hostage to the opinion of others, according to Aldan. "They are professionals without their own initiative, following the direction of the majority," he says.
The problem is that lack self-knowledge. "Those who do not know each other well has no goals, no vision of the future, and ends up at the mercy of circumstances. Unfortunately, this is the case of most people today ", says the CEO of Kronberg.
- Are fickle
The control of emotions is a emotional competence that make much lack in corporate environments. "One day the person is great, cheerful, telling jokes. The other, reacts so intemperate and rave for smaller reasons, "says Santos.
The emotionally competent professional, in contrast, can inspire confidence and bring peace to the desktop. "Is someone whose colleagues like to have around, that positively affects the environment," says the psychologist.
"There are two main reasons for this: the heavy use of technologies and activities that make us increasingly isolated, overwhelmed and disconnected from other people". (Examination, 2015)
10 signs that you have emotional intelligence at work
According to the American consultant Travis Bradberry, co-author of the book "Emotional intelligence 2.0" (Perseus Books, 2009).
- You know describe their emotions with words you need
Have an extensive "emotional vocabulary" is a rare ability, according to the consultant. Just say you're feeling "badly" is very different to describe as "perplexed", "frustrated" or "anxious", for example. People with emotional intelligence you know managing your own feelings because they know exactly what they are. - Do you know your weakest side
According to Bradbury, know what are their main vulnerabilities is essential in time to administer your behavior. "Having a high QE means knowing their strengths, and how to use them to your favor, but also prevent their weaknesses from distracting you," he writes. - You're a good judge
The ability to interpret the feelings, intentions and motivations of other people is another typical sign of this kind of intelligence. If you have a keen and sensitive trial in respect of the other, is likely to have a high degree of emotional competence. - You are not easily offended
It's hard to put an end to the joy of those who have self-confidence. "Emotionally intelligent People are safe and have an open mind, which gives them a ' skin ' thick enough," writes consultant. This means identifying, criticism and aggression of others – and even make fun of yourself once in a while. - You are able to say "no"
Take negative comments in sports does not mean being passive. Have emotional competence implies also know put limits. Second Bradberry, reject new tasks and appointments assertively is hard, but brings important gains for the mental and physical health. - You forgive yourself
Who has dominion over you feel usually contemplate their own failings so quiet-but don't ignore them. "Dwell on their mistakes brings anxiety and shyness, while forget them altogether can make repeated," writes consultant. It's like a "rope" notes Bradberry, in that only the most competent can walk without stumbling. - You don't cultivate grudges
So how are able to forgive your own mistakes, people with emotional intelligence also tend to "absolve" the other. Grief and anger are two ingredients for stress and even diseases like high blood pressure. Who can dominate his own feelings, of course, prefer to run those triggers of malaise. - You are generous
Offer help without asking anything in return is a typical feature of who has emotional intelligence, says Bradberry. "These people build strong relationships because they're always thinking of others," he writes. - You neutralize people "toxic"
At the time of dealing with difficult bosses, colleagues or professional with high QE identifies his own feelings such as frustration or anger, and prevents them from becoming loose. In addition, he seeks to respect the point of view of the person "toxic" and seeks to find positive solutions to the two parties. - You don't seek perfection
"People with emotional intelligence don't see perfection as a goal, because they know that it doesn't exist," writes Bradberry. On the inevitability of the problems, they do not complain about the past and just move on. (Examination, 2015).
Final Considerations
The globalized world promoted greater economic integration and socio-scientific advances due to the large communications area, made possible by information technology. Human relations have become complex and require faster processing and technical training, especially in the emotional field, as CITES Goleman (1998, p. 21): "A growing number of companies coming noting that the stimulus to the skills related to emotional intelligence is a vital component of any organization's management philosophy ".
When Gardner emphasizes the importance of developing the multiple intelligences so that people become more able to solve problems, it is clear that we need to have or create mechanisms to achieve the objectives proposed by him. "intelligence implies the ability to solve problems or develop products that are important in a particular environment or cultural community." (GARDNER, 1995, p. 21).
We saw then, Antunes suggest some activities that properly applied within schools and family will partner stimulate these intelligences, which meets Gardner proposals.
John Dewey, when proposing the method of learning through the five steps, makes it clear that the student will build a research process of problem situation, logically organized, coordinated, systematized and so will be enabling your Reasoning Logical through their intellectual functions. This answer us, as do.
For Piaget, (1985) the Logical-Formal Operative stage, which goes from 12 to 16 years consolidates the intellectual structures of logical reasoning or logical-mathematical-deductive, which will extend until adulthood. This allows us to respond when and what to teach.
The Logical Mathematician when stimulated by the interactions of multiple Functional Intelligences and emotional aspects, from the use of methodological, didactic-pedagogical resources, teaching and learning objects, all suitable to each stage of development of the student, will bring greater speed and cognitive expansion making them agents, critics and citizens understanding transformers of their social responsibilities.
The theories presented here, when associated with and explored properly by educators will apply the Logical Mathematician in all series of elementary school on a regular basis, programmatic and ongoing systemic, allowing achieve greater intensity in the process of formation of these young people.
REFERENCES
ABAR, C.. Notions of mathematical logic. 2006. Available at: <www.pucsp.br logica/="">accessed: 21.</www.pucsp.br> Mar. 17.
ANTUNES, Celso. Multiple intelligences and its stimuli. 3. Ed. Campinas: Papirus, 1998.
______. Games for the stimulation of multiple intelligences. 9. Ed. Petrópolis: Vozes, 2001.
______. Multiple intelligences and their games. Vol. 4-Spatial Intelligence. Petrópolis: Vozes, 2005.
ARMSTRONG, t. multiple intelligences in the classroom. 2. Ed. Trad. Maria Adriana Veríssimo Veronese. Porto Alegre: medical arts, 1995.
BIEMBENGUT, Maria Salett and HUH, Nelson. Mathematical modelling in teaching. 1. Ed. São Paulo: context, 2000.
Borges, Teresa Maria Machado. The preschool age child. Sao Paulo: 1. Ed. Atica, 1994.
Brazil. LDB-Law of Guidelines and Bases of education no. 9,394 of December 20, 1996. Brazil. Law No. 13005, of 25 June 2014.
BRASLAVSKY, Cecilia. Educational policies before the technological revolution, in a world of increasing interdependence and partial. In: TEDESCO, Juan Carlos (Org.). Education and new technologies: hope or uncertainty. São Paulo: Cortez, 2004. p. 77-94
BRUNNER, José Joaquín. Education in the new technologies. In: TEDESCO, Juan Carlos (Org.). Education and new technologies: hope or uncertainty. São Paulo: Cortez, 2004. p. 17-75.
5 attitudes typical of those who have no emotional intelligence-EXAME.com-Claudia Gasparini-06. Feb. 15-available at: <http: exame.abril.com.br/…/5-atitudes-tipicas-de-quem-nao-tem-inteligencia-emocional/="">accessed: 13.abr. 17 and 21.abr. 17.</http:>
Skills and abilities/INFOENEM-available at: <https: www.infoenem.com.br/competências-e-habilidades/="">accessed: March 15, 17 and 23.abr. 17.</https:>
Memory visuoespacial-functional components. Available in:<www.scielo.br/scielo.></www.scielo.br/scielo.> PHP? script = sci_arttext & pid = S0103-40142013000100004 > Access in: 23. APR 17.
COPI, Irving m. Introduction to logic. 2. Ed. São Paulo: Mestre Jou, 1978.
DEWEY, John. Democracy and education. 1916. Cap. 12. The thought on education. Helder Silvério translation finalist of the degree in physics, Physics, 2000/01 Variant. Available at:<https: www.google.com.br/url?sa="t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=6&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwimyfrp2sjTAhULkJAKHXDVDl0QFghIMAU&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.educ.fc.ul.pt%2Fdocentes%2Fopombo%2Fhfe%2Fdewey%2Fcap12.htm&usg=AFQjCNHeEU3s7wuOc860R-Rcd6_ee47oGg&sig2=bZXVKrr-j_-TZG0ErZykmw"> accessed: 29.</https:> APR 17
DEWEY, John. As we thought: reflective thinking as it relates to the educational process, a Rechallenge. 4. Ed. São Paulo: national, 1979.
DEWEY, John. Democracy and education: an introduction to philosophy of education. Trad. of Godofredo Rangel and Anísio Teixeira. 4. Ed. São Paulo: national, 1979.
______. Pedagogy of projects. Revised practical guide for elementary school I. Scale. Ed. 96, 2012.
10 signs that you have emotional intelligence at work-EXAME.com-Claudia Gasparini-14. Jun 15. Available at: <http: exame.abril.com.br/carreira/10-sinais-de-que-voce-tem-inteligencia-emocional/="">accessed: 13.</http:> Apr 21.04.17 17e.
DIGIORGI, Cristiano. New school. São Paulo: Ática, 1992. (Principles)
GALUCH, Márcia Terezinha Bellanda, SFORNI, Riyas de Faria. Conceptual and appropriation of learning written language: contributions of historical-cultural theory. EST. Endorsement. Educ., São Paulo, v. 20, n. 42, p. 111-124, jan/abr. 2009.
GARDNER, h. Structures of the mind-the theory of multiple intelligences. 1. Ed., London: Mosby, 1994.
______. Multiple intelligences theory in practice. São Paulo: New Haven, 1995.
GOLEMAN, Daniel, Working with emotional intelligence. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 1998.
In LA TAILLE; OLIVEIRA, M. K; Dantas, h. Piaget, Vygotsky, Wallon: psicogenéticas theories in discussion. 13. Ed. São Paulo: Summus, 1992 p. 11-22. Available in < https://books.google.com.br/books?isbn="8532304125"> Access in 21. APR 17.
John Dewey, the thinker who put the practice into focus-new school. Available at:<https: novaescola.org.br/conteudo/…/john-dewey-o-pensador-que-pos-a-pratica-em-f…=""> accessed: 14.</https:> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
John Dewey and Active school-by the emergence of a new school. Available at:<www.planetaeducacao.com.br ortal/artigo.asp?artigo="447"> accessed: 14.</www.planetaeducacao.com.br> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
LIMA, Jose Milton. The play and learn in the educational context: a false dichotomy. 2003. 246f. Thesis (doctorate in education)-Faculty of philosophy and science. Universidade Estadual Paulista, Marília.
Neuropsychology learning-Pepsico-Available in:<pepsic.></pepsic.> bvsalud.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0103-84862006000300006 >. Access in: 21. Mar. 17 and 23.abr. 17
Learning objects A pedagogical resource proposal (pdf). Available at: <http: rived.mec.gov.br/artigos/livro.pdf="">accessed: 14.</http:> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
______. -Book-END. PMD-Iven-Mec. Available at: <http: rived.mec.gov.br/artigos/livro.pdf="">accessed: 14.</http:> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
Pepsic-ELECTRONIC PSYCHOLOGY JOURNALS. Home Page-the brain and thought – available at: <pepsic.bvsalud.org cielo.php?script="sci_arttext&pid=S1517-24302006000100006">accessed on 09.</pepsic.bvsalud.org> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
____________. Home Page. -Verbal activity considerations-Available in:<pepsic.></pepsic.> bvsalud.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1413 … > 09 access. APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
Piaget, Jean. Genesis of logical structures. Rio de Janeiro: forensics, 1975.
____________. The birth of intelligence in children. Rio de Janeiro: Zahar, 1978.
______. Psychology and pedagogy. Rio de Janeiro: University Forensic, 1985.
RAUBER, J. ROSSETO, M.; JOCELYN, A. M.; JOCELYN, A. A.; TONIETO, C. How about some logic. Passo Fundo: Clio Books, 2003.
IVEN-International Virtual Education Network-Available in:<rived.></rived.> mec.gov.br/site_objeto_lis.php > data access on 14. APR 17 and 22.abr. 17
SANTOS, Franklin, Emotional Intelligence/Franklin Santos. 1. Ed. Recife: Clube de Autores, 2011.
SFORNI, M. S. F.; GALUCH, Maria Terezinha Bellanda. Appropriation of symbolic instruments: education (Porto Alegre), v. 32, p. 79-83, 2009.
SPOLIN theater games v.: the binder of Viola Spolin. London: Prospect, 2001.
The Theory of Multiple Intelligences – WordPress.com. Available at:<https: howardgardner01.files.wordpress.com/…/443-davis-christo…=""> accessed: 10.</https:> APR 17 and 23.abr. 17.
WEINREICH-HAST, Helen. The multiplicity of intelligences. New Scientist, Elmont, v. 102, n. 1413, p. 19-22, June 1984.
WILEY, d. Connecting learning objects to instructional design theory: definition, metaphor, and taxonomy. 2001. Available at:<www.reusability.org ead/chapters/wiley.doc=""> accessed: 22.</www.reusability.org> APR 17.
FIGURES
Figure 1: Las mejores Howard Gardner-PsicoActiva.com phrases-available at:<https: www.psicoactiva.com/blog/las-mejores-frases-de-howard-g=""> accessed: 13.</https:> APR 17.
Figure 2: the types of intelligence by Mark Vital. Available in< http://www.psiconlinews.com/2015/05/teoria-das-inteligencias-multiplas-de-gardner.html=""> </> Access in 13. APR 17.
Figure 3: Jean Piaget. Available in <http: kdfrases.com/autor/daniel-goleman="">Access in 13.</http:> APR 17.
Figure 4: John Dewey <http: www.planetaeducacao.com.br/portal/artigo.asp?artigo="447">Access in 13.</http:> APR 17.
Figure 5: BIEMBENGUT, m. S, EH, no. Mathematical Modeling. 1. Ed São Paulo: context, 2000.
Figure 6: Daniel Goleman. Available in < http://kdfrases.com/autor/daniel-goleman=""> Access in 13. APR 17.
[1] Graduate studies in Mathematics Education