INTEGRATIVE REVIEW
SILVA, Fagner Pereira da [1]
SILVA, Fagner Pereira da. Speech therapy intervention in patients diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: integrative review. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento. Year. 07, Ed. 06, Vol. 05, pp. 157-174. June 2022. ISSN: 2448-0959, Access link: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/health/speech-therapy-intervention, DOI: 10.32749/nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/health/speech-therapy-intervention
ABSTRACT
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can be characterized as a neurobiological disorder, with genetic causes, presenting, among the main symptoms, inattention, restless behaviors, as well as impulsivity problems. This disorder appears during childhood and can accompany humans throughout their life cycle. The treatment can be carried out through the association of drugs, psychotherapy and speech therapy, especially when speech disorders or writing problems are observed. In this context, the present article has as its guiding question: how can speech therapy act to reduce the problems caused by attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? Thus, the main objective of this research is to analyze, through the already published literature, the intervention of speech therapy in patients diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. For the foundation of the research, it was necessary to carry out an integrative bibliographical research, analyzing several theories related to the intervention of speech therapy in people with ADHD. For this, searches were carried out in the databases: Scielo, Pubmed, Lilacs and Medline. It is concluded through this research that the performance of speech therapists in individuals diagnosed with ADHD provides a significant reduction in multiple behaviors, significantly helping with regard to combating the main difficulties of these individuals, such as attention and impulsiveness problems, in addition to assistance to parents or guardians of people with ADHD.
Keywords: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Speech therapy, Symptoms, Treatment.
1. INTRODUCTION
With regard to the origin of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, it is possible to state that it emerged in the scientific literary field during the 20th century, being initially described in 1902, through the work of George Still. This scholar characterized this disorder as distractibility, hyperkinesia and lack of impulse control by humans (AXELSON; PENA, 2015).
In accordance with the provisions of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), it is inferred that ADHD is characterized as a disorder associated with neurodevelopment, evidenced in individuals due to various symptoms, especially during the period of childhood, especially the lack of attention, hyperactivity or somatization of these groups mentioned above, which can be divided, according to the degree, into mild, moderate or severe (AMERICAN PSYCHIATRIC ASSOCIATION, 2014).
Among the main symptoms, lack of patience, continuous distraction, impulsivity, lack of abstraction capacity for a long period of time, rejection, doubts regarding intellectual capacity and low self-esteem stand out (BARINI ; HAGE, 2015).
However, these problems can be mitigated through interventions that have as their main scope the promotion of improvements in the quality of life of people diagnosed with this disorder (RIBEIRO, 2016).
It should be noted that the interventions must occur through the joint action of several professionals, emphasizing, mainly, pedagogues, psychopedagogues, psychologists, neurologists and speech therapy professionals.
In this context, the research problem is based on the following question: how can speech therapy act to reduce the problems caused by attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?
Thus, it was defined as a general objective to analyze, through the already published literature, the intervention of speech therapy in patients diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
In accordance with the regulation of the Federal Council of Phonoaudiology, art. 1 of Law nº 6.965/1981, speech therapy has among its objects of action the development of preventive work, effective participation in the team responsible for diagnosing and performing therapies aimed at communication in a broad way, that is, in its development, in the process of improvement and in the analysis of cognitive problems (BRASIL, 1981).
Thus, it is possible to infer that the work of Speech-Language Pathology professionals is capable of providing a series of advantages for the treatment of individuals with ADHD, acting more specifically on neurofunctional difficulties through processes aimed at stimulating neuroplasticity.
This justifies the importance of the topic, as there is a continuous need to seek a better quality of life for children diagnosed with ADHD, which can be provided through the work of speech therapy professionals, who are directly responsible for performing therapeutic actions, by stimulating the cognitive process, aspiring to the proper improvement of the most diverse human skills, such as, for example, in the act of thinking, in helping the memorization process, in the capacity for self-control, in addition to improvements in attention.
2. ATTENTION DEFICIT AND HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER
Initially, it is worth analyzing the theoretical concepts related to ADHD. This disorder can be defined as a clinical condition that occurs more frequently during childhood and adolescence, originating due to the interaction of genetic factors and environmental factors (ROHDE, 2000).
Regarding its diagnosis, there is a clinical predominance, having among the main symptoms, hyperactivity, lack of attention, in addition to the issue of impulsivity in accordance with the criteria prescribed by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) (AMERICAN PSYCHIATRIC ASSOCIATION, 2014).
It should be noted that these various symptoms can compromise simple daily activities, in addition to considerably affecting school life and bringing problems to social relationships.
Research shows that changes in the executive functions of individuals diagnosed with ADHD tend to include: difficulty solving problems; cognitive inhibition; mental flexibility; behavior inhibition self-regulation; and motor control. It is inferred, therefore, that people with ADHD tend to show a series of language difficulties and an evident delay in speech, with syntactic, phonological and pragmatic (SOUZA et al., 2021).
Still, it is possible to state that several skills, such as phonological awareness, working memory and the issue related to automatic naming, can suffer a series of damages in people with ADHD, causing serious consequences for reading skills, such as a simple decoding of a word, making the student, for example, start reading properly and later invent the rest of the words or phrases. Also, it is not uncommon for difficulties related to textual comprehension to arise, that is, the inability to organize ideas, so that you can achieve success in the accuracy of answers when asked (CAPELLINI et al., 2007).
According to Martins et al. (2020), approximately 80% of people diagnosed with ADHD, who do not undergo effective treatments, demonstrate a lower performance in school and approximately 45% tend to repeat at least one year in school life. It should also be noted that Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is directly related, with about 30%, to learning problems, emphasizing dysgraphia, dyslexia (difficulty in reading) and dyscalculia.
Chart 1 demonstrates in detail the main learning problems presented by people who are diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
Chart 1 – Learning problems in people with ADHD
| Learning problems | Features | Treatment |
| Dysgraphia | Disorder that directly affects writing with the signs being identified through the action of teachers in the classroom environment, being associated with motor issues. Illegible handwriting, in addition to slow writing, such as words arranged on the board. | The treatment can occur through the action of occupational therapists, psychomotor therapists or through the performance of speech therapists with specialization in the area. It is necessary, however, to seek a doctor for the proper evaluation, to verify that there is not a more serious motor problem. It should be noted that a pediatrician can perform this service and consequently refer the case. |
| Dyslexia | Learning disorder of neurobiological origin, causing a series of impairments in the accurate and/or fluent recognition of words, considerably affecting the decoding ability and problems with spelling words. This disorder results in deficits in the phonological component of language. | Through learning strategies capable of providing the proper stimulation of the process of reading, writing and vision, thus requiring support from a multidisciplinary team made up of pedagogy, psychology and speech therapy professionals, as well as neurologists. |
| Dyscalculia | Learning disorder that manifests itself, especially in children who are of school age. Individuals with dyslexia tend to have difficulties in the process of thinking, reflecting, evaluating or reasoning in activities associated with mathematical problems. | It requires a series of pedagogical strategies, through the identification of areas in which children are more comfortable. Among the main recommendations, the following stand out: the need for an assistant teacher; Respect for the child’s teaching-learning process, requiring the resumption of content whenever necessary; advance the content according to the child’s time; Provision of materials produced with the necessary adaptations according to needs, using specific methodologies for the type of dyscalculia presented, continuously seeking to maintain the balance of time spent with explanations. In short, the repetition process without the proper understanding of the child can cause frustrations, bringing problems to the learning process and to the memorization process. |
Source: author himself (2022).
3. SPEECH THERAPY INTERVENTION IN PATIENTS DIAGNOSED WITH ADHD
Bearing in mind that one of the main symptoms of ADHD is inattention, the speech therapist will work to improve the child’s attention. In addition, the professional will be able to help with skills related to oral communication, which can also be equally impaired. In addition, it is highlighted that this disorder can “open the door” to other disorders, such as oral and written reading, for example (FREIRO, 2013).
It should be noted that the speech therapy professional has the role of acting in health promotion, prevention, evaluation and diagnosis, in addition to acting in guidance, therapy and due improvement of communication between human beings in the most varied and complex aspects (SOUZA, 2015).
It is noteworthy that among the main areas of competence of speech therapists is the continuous search for a kind of improvement of the relevant skills, especially oral language, with understanding and with the process that involves the written part (FREITAS, 2020).
In this context, speech therapists are of paramount importance in the monitoring of people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, due to the occurrence of several alterations with regard, mainly, to auditory processing, which can be both a primary cause and a subsidiary cause, capable of contributing to the expansion of problems during the school phase (SILVA and CARLINO, 2020).
Thus, the intervention of speech therapy to individuals diagnosed with ADHD aspires to the improvement of communicative skills, highlighting the process of systematizing speech and expanding the linguistic repertoire, through actions that seek to improve auditory attention skills, memory auditory, auditory closure, background figure for linguistic sounds and phonological awareness, thus influencing the acquisition of language, the process of speech development and school development, in addition to the socialization process (SIGNOR, 2013).
Also, one cannot forget that speech therapy professionals have an important role when they act to guide family members and education professionals, advising teachers and coordinators to find a more adequate and efficient way to guide people with ADHD to achieve better academic results (FONTINELE and SILVA, 2021).
4. METHODOLOGY
For the foundation of the present research, there was a need for a literary review of the integrative type, through the analysis of theories coming from researchers, based on several research sources and scientific articles present in several databases, emphasizing SCIELO ( Scientific Electronic Library Online), CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) and MEDLINE (Sistema Online de Busca e Análise de Literatura Médica).
The integrative literature review can be characterized as a method whose scope is the proper synthesis of results from research on a topic, in an orderly and comprehensive manner, thus providing a considerable amount of information on a subject/problem (MENDES; SILVEIRA; GALVÃO, 2008).
Through the integrative review, the combination of data from the theoretical and empirical literature was included in the research, thus providing an understanding with a greater breadth on the theme related to the performance of speech therapy for people diagnosed with ADHD, resulting in a framework of multiple and complex definitions, through the researched theoretical apparatus. Furthermore, the research is based on a qualitative-exploratory approach.
To achieve greater success in choosing the sources that supported this research, the search was based on the aforementioned databases, using the following descriptors: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), speech therapy, intervention, benefits.
With regard to the inclusion and exclusion process, only scientific articles prepared and published between the years 2015 and 2022 were used, and research prepared outside this period was excluded, therefore, the first criterion was based on the aspect of temporality.
The second inclusion criterion was the admission of only studies that were in their entirety, excluding those that presented only abstracts, thus avoiding distortions of the ideas presented by their respective authors.
The third inclusion and exclusion criterion was based on the idiomatic issue, using only sources that, despite being produced in other countries, were duly translated into Portuguese.
And, finally, the last inclusion and exclusion criterion was based on the issue of duplicate research in different databases. Thus, repeated searches were included only once.
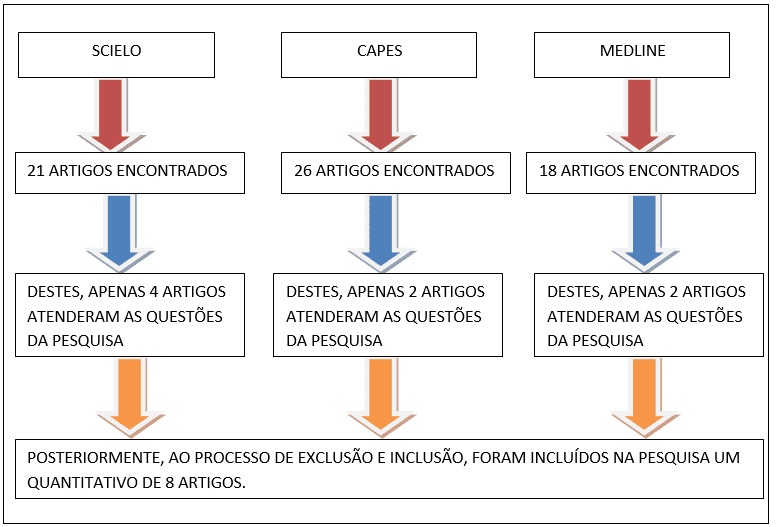
Therefore, regarding the performance of speech therapists with people with ADHD, 21 articles were identified in the Scielo database, 26 in CAPES and 18 in MEDLINE. However, after the inclusion and exclusion process, only 4 articles from Scielo, 2 articles from CAPES and 2 articles from MEDLINE were included, thus totaling a quantity of 8 articles included in this research.
5. RESULTS
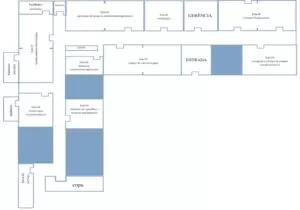
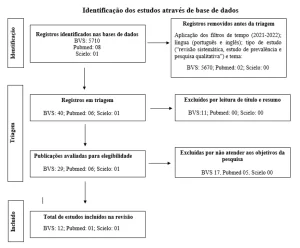
The result related to the inclusion process and the exclusion process of the sources used in this research, after a search on the SCIELO, CAPES and MEDLINE websites are shown in the flowchart below:
Flowchart 1 – Studies (post-inclusion and exclusion criteria) that supported the research according to the database
For greater systematization, there was a need to draw up Table 2, in order to demonstrate the main information (author, year of publication, title, database, objectives, methods and results) about the sources that supported the research.
Table 2: Characterization of the inserted sources that supported the research
| Author (year) Data base |
Goals | Method | Results |
| Martins RA (2020)
Phonological remediation in students with ADHD and dyslexia SCIELO |
To compare the performance of the assessment of phonological processing, reading speed and text comprehension before and after the application of a phonological remediation program in a restricted group of students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and dyslexia. | The study included 32 students from the 2nd to the 8th year of elementary school, of both sexes, diagnosed with ADHD and dyslexia according to the DSM-5, treated at the Children’s Neurology Outpatient Clinic of IPPMG/UFRJ. All patients were submitted to the phonological remediation program, which consisted of 18 weekly sessions. | The results, expressed as a z-score, indicated a statistically significant difference between the pre- and post-remediation assessments in phonological processing skills, such as syllabic and phonemic awareness, working memory and lexical access. The rhyme task was analyzed separately, as it is considered a task with a different segmentation level from other syllabic levels and, for this result, there was no significance. In addition to these, there was also a statistically significant difference in tests that measure reading speed and text comprehension. |
| Silva US (2020)
Literature review on ADHD and speech-language pathology alterations SCIELO |
Carry out a literature review on ADHD and changes in the context of language | The research was carried out using the following databases: Lilacs, Scielo, Periódicos CAPES, Virtual Health Library, regarding the approach of the articles studied, seven articles dealt with specific language themes, such as: vocabulary restriction, comprehension verbal, phonological aspects, visual-motor perception and reading disorders and just one, it traces the comparative profile of the dyslexic and the subject with ADHD. | Because it is a theme that has been growing in the context of speech therapy and in the multidisciplinary field, it needs to be further explored and studied, there are still few studies that show the speech therapy aspects and more specifically aspects of language. The articles published so far do not bring a consensus on the changes in the language scenario, which are the most recurrent and the profile of these subjects, therefore, the need for further studies on this theme is evident in order to improve the performance of Speech Therapy in this area. |
| Calixto et al. (2021)
Learning and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: an analysis of Brazilian production. SCIELO |
To investigate the topic of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – ADHD in the context of Brazilian education. | 24 articles from the Scielo Brasil database were analyzed, covering the last 10 years (2007-2017). | The articles correspond to the medical field, more specifically to clinical medicine, neurosciences, speech therapy and psychology. Most of them approach ADHD from a neurobiological perspective with drug therapy. The others point to the problem of the emergence of the large number of diagnosed and medicalized students. It is concluded that this is a new discussion that seeks a multidisciplinary look and the critical dimension of learning for people diagnosed with this disorder. |
| Birth NM (2016)
Speech-Language Pathology Disorders in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: systematic literature review SCIELO |
Systematically review scientific productions about the relationship between Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Speech Therapy and methodologically analyze observational studies on the subject | This is a systematic literature review, carried out in the databases Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System online (MEDLINE, USA), Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS, Brazil) and Indice Bibliográfica Español de Ciencias de la Salud (IBECS), in which the descriptors “Language”, “Language Development”, “Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder”, “ADHD” and “Auditory Perception” were used. | The study of scientific productions revealed that the most discussed speech-language disorders were reading disorders and that there are few publications about the relationship between auditory processing and the disorder, as well as about the performance of the speech-language pathologist in the evaluation and treatment of children with Disorder of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. |
| Silva DPC (2021)
Occurrence of changes in the assessment of central auditory processing in individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review CAPES |
To verify the occurrence of changes in the assessment of central auditory processing (PAC) in children and adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | The systematic review was conducted according to the PRISMA recommendations. The guiding question was elaborated based on the PECOS strategy, being: “Are there changes in PAC behavioral tests in children and adolescents with ADHD?”. The following descriptors were selected: “Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder” and “Auditory Perception Disorders”, in Portuguese and English. Studies indexed in the following databases were identified: Pubmed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, LILACS, LIVIVO, Proquest and Google Scholar. | The main auditory skill often altered in individuals with ADHD was temporal processing, both resolution and temporal ordering, the use of medication favored test performance, and most studies showed a low or moderate risk of bias. |
| Duarte TB (2021)
ADHD: update of studies that bring CAPES |
Gather scientific evidence on diagnosis and therapy on the subject | A review of the literature whose information was collected from databases such as Medline, Pubmed, Cochrane, Scielo, UptoDate and Bireme, with an emphasis on the last 12 years (2009-2021). | Current evidence suggests that pharmacological treatment, in association with the psychosocial approach, is more effective in the short term, with significant effects in up to 2 years. However, there are few studies with high quality evidence that analyze the use of Methylphenidate or Amphetamines in the long term. |
| Escarce AG (2020)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and speech-language disorders MEDLINE |
To verify the occurrence of cases with diagnosis or suspicion of ADHD in a Speech Therapy Outpatient Clinic of a University Hospital and the occurrence of alterations in oral language, writing, auditory processing and phonological awareness in this population. | Exploratory study, carried out in a Speech-Language Pathology Assessment Outpatient Clinic of a University Hospital | In 2016, 14 children were referred to the outpatient clinic with suspected or diagnosed Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Most presented inadequate results in the simplified assessments of auditory processing, phonological awareness and reading and writing. The present study showed changes in auditory processing, phonological awareness and reading and writing tasks. The importance of new studies is emphasized, with more robust samples, aiming to better elucidate the impacts of these alterations in patients with ADHD. |
| Moura LT (2019)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and pedagogical practices in the classroom MEDLINE |
To review in the scientific literature the pedagogical practices that should be used by teachers of students diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in the classroom. | Systematic review of literature |
After verifying the information found in the research, it is concluded that the difficulties presented by ADHD students in the teaching process can be alleviated if the school allows these students, methodologies and interventions that aim to enhance the potential and creativity of students with ADHD. Therefore, teachers play a very important role in the learning process of students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. And, as a result, they need to seek more and more knowledge about this disorder, so that they can better manage their own classes when they are faced with the difficulties of these students. |
Source: author himself (2022).
6. DISCUSSION
According to Martins et al. (2020), the role of speech therapy professionals in people diagnosed with ADHD is of paramount importance, especially through their own methods or programs, such as phonological remediation, which is able to contribute beneficially with regard to the performance of phonological processing, in the process related to reading speed, ensuring greater efficiency in the text comprehension process.
Machado-Nascimento; Kummer; Lemos (2016) states that, among the researches, the main problems related to people with ADHD are reading disorders, thus requiring more research on the performance of the speech therapist in the evaluation and treatment of children with these disorders.
The main auditory skill that suffers alteration in people diagnosed with ADHD was temporal processing, both in terms of resolution and temporal ordering. In addition, according to Silva and Assis (2021), the use of drugs tends to favor test performance, with research demonstrating a low or moderate risk of bias.
However, according to Duarte et al. (2021), drug treatment when used alone is endowed with inefficacy, with the need for a multidisciplinary follow-up that involves care in several areas, emphasizing psychopedagogy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, psychology, psychomotricity, physical education and pediatric neurology, in addition to the transmission of information, training of the respective guardians and relatives of people with ADHD and the preparation of teachers to work in the classrooms.
Escarce; Machado-Nascimento; Lemos (2020), prescribes that in cases where the existence of Auditory Processing Disorder associated with ADHD is confirmed, speech therapy has the ability to complement the effect of medication, by enhancing the level of productivity of patients diagnosed with this disorder, which mainly affects school-aged children. However, the same author states that even knowing the existence of alterations in auditory processing tasks, in phonological awareness and in reading and writing, it is necessary to carry out more research and, consequently, new samples, in order to elucidate the impacts of these alterations due to ADHD.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, according to Moura and Silva (2019) is based on three symptoms, with emphasis on: impulsivity, inattention and hyperactivity, both psychic and physical. Thus, the speech therapist has the skills to identify people’s behavior, acting so that the child’s attention is continuously improved, helping in the skills related to oral communication, which can be extremely impaired. In addition, ADHD can bring other disorders, such as, for example, written and oral and written reading.
Silva and Carlino (2020), however, states that there is still no consensus among researchers on the performance of speech therapy in people with ADHD, thus there is a need for further studies on the subject, since the articles published up to the present day they do not bring uniformity about the main alterations in the aspect associated with the language.
Similarly, Calixto et al. (2021), argues that, because this theme is a relatively new discussion, it is necessary, in this way, a breadth based on multidisciplinarity, through a critical dimension of the learning of those individuals diagnosed with ADHD.
7. FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
Given the above and answering the guiding question of this article, which aimed to answer: how can speech therapy act to reduce the problems caused by attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? It is concluded that the performance of speech therapists in people diagnosed with ADHD is important, because through their methods or programs, such as phonological remediation, there are improvements in the performance of phonological processing, increasing, in this way, the reading speed and a greater text comprehension.
In short, it is possible to state that the auditory processing disorder is directly associated with ADHD and, if ratified, speech therapy is responsible for complementing the drugs, substantially enhancing the productivity level of individuals diagnosed with this disorder.
Still, according to the research, it was possible to identify that there is still no consensus among scholars about the main benefits of speech therapy, however, it is already unanimously accepted that the advantages can occur more effectively if there is the action of a multidisciplinary team, formed by doctors , psychologists, education professionals and speech therapists.
REFERENCES
AMERICAN PSYCHIATRIC ASSOCIATION. Manual Diagnóstico e Estatístico de Transtornos Mentais– DSM-5. Tradução: Maria Inês Corrêa Nascimento. Porto Alegre: Artmed, 5° ed., 2014.
AXELSON, Valkira Trino; PENA, Perciliana. As funções executivas e o Transtorno de Déficit de Atenção e Hiperatividade (TDAH) na primeira infância. Revista Psicologia, O portal dos Psicólogos, 2015. Disponível em: https://www.psicologia.pt/artigos/ver_artigo_licenciatura.php?codigo=TL0381. Acesso: em 09 de junho de 2022.
BARINI, Nayara Salomão; HAGE, Simone Rocha De Vasconcellos. Vocabulário e compreensão verbal de escolares com Transtorno do Déficit de Atenção e Hiperatividade. CoDAS, v. 27, n. 5. p. 446-451, 2015. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20152015022. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
BRASIL. Lei n° 6.965, de 9 de dezembro de 1981. Dispõe sobre a regulamentação da profissão de Fonoaudiólogo, e determina outras providências. Presidência da República, 1981. Disponível em: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l6965.htm. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
CAPELLINI, Simone Aparecida. et al. Desempenho de escolares bons leitores, com dislexia e com transtorno do déficit de atenção e hiperatividade em nomeação automática rápida. Rev. soc. bras. fonoaudiol., 12 (2), jun. 2007. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-80342007000200008. Acesso em: 15 de junho de 2022.
CALIXTO, Francisca Graziele Costa; SOARES, Stela Lopes. Vasconcelos, Francisco Ullissis Paixão e. A aprendizagem e o transtorno do déficit de atenção e hiperatividade: uma análise da produção brasileira. Revista Contexto & Educação, 36(113), 74–84, 2021. Disponível em: DOI: https://doi.org/10.21527/2179-1309.2021.113.74-84. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
DUARTE, Thaila Brandão. et al. TDAH: atualização dos estudos que trazem diagnóstico e terapêutica baseado em evidências. Brazilian Journal of Surgery and Clinical Research – BJSCR. Vol. 35, n. 2, pp. 66-72 (Jun – Ago 2021). Disponível em: https://www.mastereditora.com.br/periodico/20210711_102005.pdf. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
ESCARCE, Andreza Gonzales; MACHADO-NASCIMENTO, Narli; LEMOS, Stela Maris Aguiar. Transtorno de Déficit de Atenção e Hiperatividade e alterações fonoaudiológicas. Distúrbios da Comunicação, 32(3): 523-528, setembro, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.23925/2176-2724.2020v32i3p523-528. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
FREITAS, Infância Bones. O uso de tecnologias móveis para auxiliar na aprendizagem de estudantes com discalculia. Dissertação apresentada ao Mestrado Profissional em Informática na Educação do Instituto Federal de Ciência e Tecnologia do Rio Grande do Sul (IFRS) – campus Porto Alegre, 2020.
FREIRO, Liliane da Costa. O aprender e o não aprender: outros olhares. TCC (graduação) – Faculdade de Educação da Universidade de Brasília. Brasília: Universidade de Brasília, 2013.
FONTINELE, Francijane de Carvalho; SILVA, Maria Lucilene da. Speech therapy intervention in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): literature review. Research, Society and Development, v. 10, n. 1, p. e19710111561, 2021. Disponível em: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php/rsd/article/view/11561. Acesso em: 15 de junho de 2022.
MARTINS, Raquel Araujo. et al. Remediação fonológica em escolares com TDAH e dislexia. CoDAS, 32 (5), 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20192019086. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
MENDES, Karina dal Sasso; SILVEIRA, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira; GALVÃO, Cristina Maria. Revisão integrativa: método de pesquisa para a incorporação de evidências na saúde e na enfermagem. Texto & Contexto – Enfermagem, v. 17, n. 4, p. 758-764, dez. 2008. Disponível em: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s0104-07072008000400018. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
MOURA, Luciana Teles; SILVA, Katiane Pedrosa Mirandola. O Transtorno de Déficit de Atenção e Hiperatividade (TDAH) e as práticas pedagógicas em sala de aula. Revista Eletrônica Acervo Saúde, n. 22, 2019. Disponível em: DOI https://doi.org/10.25248/reas.e216.2019. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
MACHADO-NASCIMENTO, Nárli; KÜMMER, Arthur Melo e; LEMOS, Stela Maris Aguiar. Alterações Fonoaudiológicas no Transtorno de Déficit de Atenção e Hiperatividade: revisão sistemática de literatura. CoDAS, 28 (6), dez. 2016. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20162015270. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
RIBEIRO, Simone Pletz. TCC e as funções executivas em crianças com TDAH. Revista Brasileira de Terapias Cognitivas, vol. 12, n. 2, pp. 126-134, 2016. ISSN 1808-5687. Disponível em: http://dx.doi.org/10.5935/1808-5687.20160019. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
ROHDE, Luis Augusto. et al. Transtorno de déficit de atenção/hiperatividade. Braz. J. Psychiatry, 22, dez. 2000. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-44462000000600003. Acesso em: 15 de junho de 2022.
SIGNOR, Rita de Cassia Fernandes. O sentido do diagnóstico de transtorno de déficit de atenção e hiperatividade para a constituição do sujeito/aprendiz. Tese apresentada ao programa de Pós-graduação em Linguística, da Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, 2013.
SILVA, Ueslane dos Santos da; CARLINO, Fabiana Cristina. Revisão de Literatura sobre o TDAH e alterações fonoaudiologias no âmbito da linguagem. In: II Congresso Sergipano Multidisciplinar: Abordagens em Saúde – Lagarto – SE, 2020. Disponível em: https://doity.com.br/anais/ii-congresso-sergipano-multidisciplinar-abordagens-em-saude-ii-cosemult/trabalho/153650. Acesso em: 09 de junho de 2022.
SILVA, Daniela Polo Camargo da; ASSIS, Zandonaity Soares Teixeira de. Ocorrência de alterações na avaliação do processamento auditivo central em indivíduos com transtorno do déficit de atenção com hiperatividade: uma revisão sistemática. TCC (graduação) – Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina. Centro de Ciências da Saúde. Fonoaudiologia. Florianópolis, 2021.
SOUZA, Isadora de Lourdes Signorini. et al. Relações entre funções executivas e TDAH em crianças e adolescentes: uma revisão sistemática. Revista da associação brasileira de psicopedagogia, volume 38, edição 116, 2021. Disponível: DOI: 10.51207/2179-4057.20210023. Acesso em: 15 de junho de 2022.
SOUZA, Sara Cristina Magalhães Estrella Silva de. Esclarecimento de pais e/ou responsáveis quanto ao tratamento fonoaudiológico realizado em crianças: Enfoque bioético. TCC (graduação) – Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina. Centro de Ciências da Saúde. Fonoaudiologia, 2015.
[1] Graduation in Speech Therapy. ORCID: 0000-0002-5184-5519.
Sent: May, 2022.
Approved: June, 2022.