REVIEW ARTICLE
ADRIÃO, Iracely Santos [1], BARBOSA, Marluce Sampaio Nobre [2]
ADRIÃO, Iracely Santos. BARBOSA, Marluce Sampaio Nobre. Nursing actions in primary care in view of the risks of hypertension during pregnancy. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento. Year 06, Ed. 09, Vol. 04, pp. 84-100. September 2021. ISSN: 2448-0959, Access Link: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/health/risks-of-hypertension, DOI: 10.32749/nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/health/risks-of-hypertension
SUMMARY
Preeclampsia presents itself as one of the hypertensive syndromes that can affect women during pregnancy, during childbirth and/or in the postpartum period up to 10 days, so that it is still a pathology that, when not properly diagnosed and treated, can cause great harm and even lead to the death of the pregnant woman and/or parturient. The main objective of this study is to know the prevention of preeclampsia in primary care by nursing. Therefore, the following question is: what are the nursing actions in Primary Care in the face of the risks of hypertension during pregnancy? The present work is based on a bibliographic research, with a qualitative approach carried out through the integrative review method. To collect the data, an investigation was carried out in the databases: Google Scholar, Pubmed, Scielo and Medline. The descriptors used were: Risks. Gestation. Hypertension. Nursing. The inclusion criteria used for sample selection were: articles available electronically published from 2015 to 2020; language Portuguese. Exclusion criteria were articles lower than 2015 and keywords that are not related to the theme. For the full analysis of the selected articles, an online platform (search in databases) was used, with the purpose of extracting (title and purpose of the articles), organizing (in table form), summarizing the information and facilitating the formation of the database. The results indicated 35 published articles, but only 15 articles, in the last five years, have as main theme the prevention and risks of preeclampsia in primary care. It is concluded that the main conducts used not only by nurses, but by the entire team working in primary care, should be based on the welcoming process focused on actions that may be determinant in the prevention of preeclampsia.
Keywords: Risks, Pregnancy, Hypertension, Nursing.
1. INTRODUCTION
We currently live in a world deeply marked by the production of knowledge in all areas, including nursing and medicine. Even with this, the number of women affected by widely known diseases, such as Specific Hypertensive Pregnancy Syndrome (SHEG), is still very large. Its incidence is high, to the point of being treated as a public health problem (ARAÚJO, et al, 2017).
If hypertensive syndromes linked to the pregnancy status of women are so important, therefore, they must be known to the authorities and health professionals, and therefore it is to be asked, because in the 21st century, such pathologies still compromise the health and often even the life of pregnant women and neonates. When it is known that the practice of prenatal examinations would identify the problem, or at least allow its early diagnosis, which in practice would allow a timely intervention (ARNALDO; CARDOZO, 2021).
All these reflections contributed and motivated the choice of the theme as the object of study, for its feasibility was partly the following problem: there has been a high rate of pregnant women who are almost always attended to presenting signs and symptoms of SHEG, especially preeclampsia. So, what are the nursing actions in Primary Care in view of the risks of hypertension during pregnancy? And as a provisional response to the problem stated, it was adopted the hypothesis that women in gestational period and even parturient s and in the postpartum period, present high preeclampsia index, because they did not have adequate prenatal follow-up (ARAÚJO et al., 2017).
Studies involving this set of information (risks of hypertension during pregnancy), help in the prevention of hypertension, since it stimulates and alerts the population to adopt changes in eating habits and in the usual practice of physical activity, as well as facilitates the drug approach of its isolated components or metabolic syndrome itself, through professionals and researchers (ARNALDO; CARDOZO, 2021).
The choice of the theme acts to bring to pregnant women information that leads them to a healthier life, because this is the main task of health professionals. And for these women in pregnancy should start to take to their day to day a healthier and natural diet, having as advice the consumption of fruits, vegetables, vegetables. Being oriented to minimize the consumption of meat, fats, fried foods, sandwiches and other forms of food harmful to health and that leads to increased hypertension (SOARES et al., 2015).
For a good quality of life, the pregnant woman considered hypertensive needs to maintain a healthy life, because many of these adher to pharmacological treatment, where blood pressure is controlled through the ingestion of tablets. There is also non-pharmacological treatment that is performed through physical activity practices, which can also be a complement to pharmacological treatment (MELO et al., 2015).
The practice of exercise is of fundamental importance for health and quality of life in general and especially for pregnant women, who have the habit of leading a sedentary life, since she is in the rest period of the profession, and begins sedentary lifestyle (SOARES et al., 2015).
The work is justified because it is of great interest to nursing and the woman who intends to be a mother. The interest in the research was also motivated due to this being a theme that brings important and fundamental information to every woman who aims to become pregnant and for the nursing area of activity.
And so the research brings teachings to a good quality of life of pregnant women, since hypertensive women need to maintain a healthy life, because many of these adher to pharmacological treatment, where blood pressure is controlled through the ingestion of tablets. There is also non-pharmacological treatment that is carried out through physical activity practices, which can also be a complement to pharmacological treatment (SANTOS; NETO, 2016).
The main objective of this work is to know the conducts of prevention of preeclampsia in primary care by nursing.
2. METHODOLOGY
Regarding the methodological procedures of the present study, the development of bibliographic research was used, i.e., a literature review of scientific articles on hypertension and pregnancy. For the present scientific research, the articles were searched in the databases of Google Scholar, Pubmed, Scielo and Medline, health journals books and scientific articles, based on materials already elaborated.
In addition, the exploratory research for Lakatos and Marconi (2010, p. 171) “the combined exploratory-descriptive studies have the objectives of describing a completely certain phenomenon, such as the study of a case for which empirical and theoretical analyses are performed”.
Therefore, the research always seeks the best approximation of the researcher with the real situation of the problems, besides, it consists of understanding in a less totalitarian way, fragmenting the opinions presented and aiming at the perspective of the perspective of the actors who are involved in the process.
In relation to the means, the procedures of bibliographic research were applied to this study. Thus, national publications, in books, articles authored by nursing professionals and journals will be part of the construction of this material (FONSECA, 2002).
Therefore, it is noticeable that, despite all the effort to raise the views of the social actors involved in the process to which the research is proposed to study, it is perceived that the theoretical basis through bibliographic survey becomes the foundation for the understanding of research.
In this study, the understanding of some authors was raised based on bibliographic research in detail in search of the view of this study. Enriching in knowledge, because it is of fundamental importance to verify the position of these authors regarding nursing and the risks of hypertension during pregnancy.
Therefore, the inclusion criteria were: articles published in Portuguese, which address nursing and the risks of hypertension during pregnancy, and which have been published and indexed in these databases from 2015 to 2020. Exclusion criteria were articles lower than 2015 and keywords that are not related to the theme. The key words used were: Risks. Gestation. Hypertension. Nursing. Data collection was also performed in the first half of 2021.
The present research had among its sources of data collection, through cataloguing and binder of bibliographic documentation, books, articles, magazines, newspapers, periodicals, and articles published on the Internet, of contemporary authors, through which several interpretations of the theme were performed. Thus, it is important to mention, the means of collecting related data, is what is expected to cultivate in the best possible way the origins and motivations of the answers found or not at the end of the research.
3. DEVELOPMENT
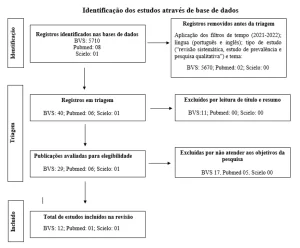
The final sample of this review consisted of 15 (fifteen) scientific articles, selected according to previously established inclusion criteria. Table 1 represents the specifications of each of the articles, distributed according to: year; periodical; authors’ name and title.
Table one. List of studies selected for year, journal, authors and title between 2015 and 2020.
| YEAR | PERIODIC | AUTHORS | TITLE |
| 2017 | Rev enferm UFPE on line | ARAÚJO, Isabella Félix Meira, et al | Síndromes hipertensivas e fatores de risco associados à gestação |
| 2021 | Revista científica multidisciplinar núcleo do conhecimento | ARNALDO, Mariany de Freitas. CARDOZO, Maryanne Neuraide Freire | Assistência de enfermagem às gestantes hipertensas na prevenção da prematuridade: revisão bibliográfica |
| 2019 | Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso | CABRAL, Gustavo Pereira | Cuidados de enfermagem a mulheres com doença hipertensiva específica da gestação: uma revisão integrativa |
| 2017 | International Nursing Congress | ENDRINGER, Deyvid Dantas; CRUZ, Monielle Lima | Representatividade do enfermeiro na assistência a gestantes com pré-eclâmpsia |
| 2015 | REBES – Revista Brasileira de Educação e Saúde | MELO, Wyara Ferreira, et al | A hipertensão gestacional e o risco de pré-eclampsia: revisão bibliográfica |
| 2018 | Brazilian Journal of Surgery and Clinical Research – BJSCR | OLIVEIRA, Leilyanne de Araújo Mendes, et al | Cuidados de enfermagem a gestante com síndrome hipertensiva: revisão integrativa. |
| 2018 | Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento | SANTOS, Keilane Carvalho. BRASILEIRO, Marislei Espíndula | Enfermagem e os cuidados Emergenciais na doença hipertensiva específica na gravidez |
| 2016 | Revista Científica da FASETE | SANTOS, Joelma Oliveira Silva; NETO, Thiago Paulo de Almeida | Atuação do enfermeiro na redução da ocorrência da pré-eclâmpsia: uma revisão integrativa |
| 2020 | Enfermagem Brasil | SARMENTO, Rayani Silva, et al | Pré-eclâmpsia na gestação: ênfase na assistência de enfermagem |
| 2016 | Centro Universitário Ritter dos Reis | TEIXEIRA, Rafaela da Rosa; MINUZZI, Renata Nolibus; TELES, Jéssica Machado | Cuidados de enfermagem à pacientes com hipertensão gestacional: um relato de experiência |
| 2017 | Rev Port Med Geral Fam | FERREIRA, Sara Santos, et al | Ácido acetilsalicílico na prevenção da pré-eclâmpsia: uma revisão baseada na evidência |
| 2015 | Ciência Y Enfermeria | KRAUZER, Ivete Maroso, et al. | Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem na atenção básica: o que dizem os enfermeiros? |
| 2015 | J. res.: fundam. care. | FERNANDES, Amélia Carolina Lopes | Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem na prevenção de infecções em unidade de terapia intensiva |
| 2015 | Escola Anna Nery Revista de Enfermagem | SOARES, Mirelle Inácio, et al | Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem: facilidades e desafios do enfermeiro na gerência da assistência |
| 2016 | Rev. Interd | MONTEIRO, M. M., et al. | Emergências obstétricas: características de casos atendidos por serviço móvel de urgência |
Source: Own authorship (2021)
3.1 FEATURES OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY
In this research we will have emphasis on a pathology that is the second leading cause of perinatal death in Brazil, which is hypertension in pregnancy, in which it carries several risks for the mother and child, thus it is necessary to regularly follow these patients and to guide changes in lifestyle and diet (ARAÚJO et al., 2017).
Blood pressure (BP) presents alterations in the interaction of neurohumoral, behavioral and environmental factors. Hypertension (AH) can be conceptualized as a syndrome of multifactorial origin, considered as one of the major problems in the area of public health being evaluated as a serious risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (ARNALDO; CARDOZO, 2021).
Women who use cigarettes and contraceptives, aged over 30 years, end up being the most affected, because they are submissive to other lung diseases. Women receive protection due to cardiovascular events that occur before menopause, in men only arise after the age of 30 (SOARES et al., 2015).
Longer-term studies have identified that they are not different from men regarding antihypertensive blood pressure response; however, it is of paramount importance to avoid the use of Angiotensin-To-Use Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE) and Angiotensin II receptor antagonists in women when they are of childbearing age and who are not using proven safe anticoncept methods (SANTOS; NETO, 2016).
The causes of hypertension are associated with a sedentary life, with inadequate intake of foods, such as excess sodium and fat or alcohol consumption, and even smoking, which is the cause of heart failure. The fact is that hypertension is a potent contributor to cardiovascular diseases, attacking and overloading the heart until one day it fails (CABRAL, 2019).
Hypertension in pregnancy is the second leading cause of maternal and perinatal death in Brazil according to data from the Ministry of Health. This shows the need to know and control this pathology. In pregnancy the woman’s organism undergoes several transformations to be able to develop the fetus that will be sheltered for about 280 days or approximately 9 months. In Brazil, the population is expected to reach the mark of 228 million inhabitants in 2025 (CABRAL, 2019).
The mortality rate according to IBGE in 2016 is that 6.6 live births per thousand inhabitants. Given these data, it is evident the need to develop research and design to better this alarming index, from the mapping of the places that have the highest gestational risk, which can intensify care for pregnant women and thus improves the mortality rate (ENDRINGER; CRUZ, 2017).
3.2 GENERAL ASPECTS OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA
It is not known for sure when the first cases of this pathology were identified, but what is known is that it has been described since the times when records began to be made, its occurrence was attributed to bad spirits, bad genius, and, more recently, sodium intake and weight gain during pregnancy (ENDRINGER; CRUZ, 2017).
It is noticed that this syndrome has caused major disorders in young pregnant women correlated with the first pregnancy, and is characterized as the main cause of maternal mortality in Brazil. In 1998, pregnancy toxemia was responsible for 21% of direct obstetric deaths (SANTOS; BRASILEIRO, 2018).
Preeclampsia is characterized as one of the hypertensive syndromes that can affect women during pregnancy, during childbirth and/or in the postpartum period up to 10 days, so that it is still a pathology that, when not properly diagnosed and treated, can cause great damage and even lead to the death of the pregnant woman and/or parturient (SARMENTO et al., 2020).
It is characterized as a systemic disease that arises from the 20th week of gestation by the triad: hypertension, edema and proteinuria and may have its condition aggravated for eclampsia, in the presence of convulsion, and/or evolve to HELLP syndrome (SANTOS; BRASILEIRO, 2018).
The causes of preeclampsia are still unknown, however, what is known is that some pregnant women are more likely to be affected by this pathology. In antiquity they referred to bad geniuses, weight gain, and too much salt intake (FERREIRA et al., 2017).
Today it is not yet known for sure the causative and triggering reasons for preeclampsia, what is known is that it has multicausals: predisposition family and genetic, endocrine-metabolic, including alteration of prostaglandin production, uteroplacental ischemia, immunological, presence of trophoblastic tissue, toxins in the maternal bloodstream, causing vasoconstriction and defective placenta (SARMENTO et al., 2020).
Preeclampsia has several etiologies that may come from hereditary and/or acquired causes due to the patient’s lifestyle or social and environmental conditions. However, what is known is that social conditions, together with a sedentary life, poor diet, and the lack of information usually derived from low schooling, favor the imminent risk of the onset of preeclampsia, in addition to others (TEIXEIRA; MINUZZI; TELES, 2016).
Hypertensive syndrome initially presents as mild preeclampsia, then progresses to severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, Hellp syndrome, CIVD (disseminated intravascular coagulation) and finally death. And these are the stages of severity of hypertensive syndrome, however, it does not necessarily need to go through all stages, and may evolve from a mild preeclampsia to Hellp Syndrome (FERREIRA et al., 2017).
Other complications of preeclampsia are: premature placental detachment as a result of placental injury at the site of implantation, acute pulmonary edema, acute renal failure due to installed glomerulopathy and cerebral hemorrhage (TEIXEIRA; MINUZZI; TELES, 2016).
O2 free radicals are identified with fat cells that are endothelium, soluble in maternal blood and very close to the vascular endothelium. They reduce the production of prostacyclin and nitric oxide that are dilated vessels, and increase vascular resistance, causing increased blood pressure (FERREIRA et al., 2017).
The only alternative to control preeclampsia and prevent it from eclampsia is the correct follow-up of prenatal care during pregnancy. Patients with mild preeclampsia need to opt for rest, always measure the frequency of blood pressure and adhere to a low-salt diet (KRAUZ et al., 2015).
Antihypertensive and anticonvulsant drugs are indicated for the control of eclampsia with greater severity, which may require the anticipation of delivery. And the disease tends to regress spontaneously with the removal of the placenta (FERNANDES, 2015).
Therefore, according to Varella (2020, p. 1), it is important to follow some recommendations:
– Se dirigir ao ginecologista antes de engravidar para uma avaliação clínica e início da administração de ácido fólico;
– Importante estar presente em todas as consultas previstas no pré-natal;
– Qualquer desatenção e a ausência de sintomas podem fazer com que uma forma leve de pré-eclâmpsia evolua com complicações;
– Realizar exercícios físicos de acordo com a fase da gestação;
– Reduzir a quantidade de sal nas refeições, não fumar e principalmente não ingerir álcool durante a gravidez (VARELLA, 2020, p. 1).
Treatment consists of bed rest (left side), in an airy and quiet place, with the use of drugs, with the intention of minimizing worsening and postponing premature labor, when possible, that is, when there is no imminent risk to the mother and fetus. However, when this is not possible, the indication is the immediate interruption of pregnancy, regardless of the gestational period (FERREIRA et al., 2017).
3.3 NURSING CARE AT WOMEN’S HEALTH CARE LEVELS
The Systematization of Nursing Care (SAE) aims at a care in a broad, dynamic way, with planning involving nursing processes as a whole, whose care counts on the harmonic participation of several professionals together with the family and the patient, building an environment conducive to recovery successfully and with less wear and tear for both the patient-family and the team (SOARES et al., 2015).
Nursing care also aims at integration into society, where its main focus is to provide quality of life to people, in order to lead to a better and broader care of their specific needs, prioritizing individuals who are under nursing care and attention, that is, those who already follow up (MONTEIRO et al., 2015).
“Planned Nursing” seeks to carry out professional guidance regarding the elaboration of a systematic planning of nursing care. The series of principles coordinated here is attributed to the nomenclature of “Therapeutic Nursing Plan”, a plan that composes the entire process of actions and decisions aimed at programming nursing care. (SOARES et al., 2015, p. 50).
It is understood that nursing care is all care or technique dispensed to a patient, and every procedure that reduced or minimized pain. When the nurse takes care of a patient, he dispenses not only attention, but connects to the client to reduce their pain, thus providing their recovery, reducing their injuries and encouraging their improvement in both physical and mental, through the action together with the health team and the family (MONTEIRO, et al., 2015).
However, planning on nursing care is a mission that presents a certain degree of complexity due to several factors: one of these factors is that the process of planning in nursing involves the harmonic participation of several people, such as the patient, the nurse and his team and the members of the health team; another reason is the indispensability of the use of reasoning, decision-making, performance and documentation; in addition to these, another preponderant reason is related to constant changes in life that affect even the most improved plans (SOARES et al., 2015).
It is observed that to perform good nursing care it is necessary to take into account several factors, one of the main factors being the ability of nurses to conduct work together with the health team, taking care of paradigms of the patient and his family. Using its ability to transmit information and, on the other hand, to know how to listen, and this constitutes a basic component for a good nursing professional (MONTEIRO et al., 2015).
The care nurse is part of a multidisciplinary team that aims at preventive and curative actions within the community through the promotion of health policies aimed at reducing the notifications of harm, through the knowledge of the causes and risks to which the population is exposed, and at the same time, sensitizing public agencies to the actions that should be implemented (KRAUZER, 2015).
When performing anamnesis in a given client, a thoughtful and holistic look should be adopted aiming not only at the underlying pathology or the one that is in evidence, but also to try to understand the reasons why it emerged, in order to seek a solution for the patient (SOARES et al., 2015).
In this data collection, nurses should draw up systematized care plans in order to promote and recover health, which had been shaken, aiming at a correct diagnosis. For Carpenito apud Fernandes, et al (2015, p. 1,581):
O diagnóstico de enfermagem baseia-se tanto nos problemas reais (voltados para o presente) quanto nos problemas potenciais (voltados para o futuro), que podem ser sintomas de disfunções fisiológicas, comportamentais, psicossociais ou espirituais.
It is understood that the nursing diagnosis is divided into two moments: a real diagnosis that is characterized by the defined manifestations already existing in the individual, i.e., impaired physical mobility, related to lower limb injury. The second is the risk diagnosis is characterized by risk factors to which the individual is exposed, vulnerable both by the environment and by his own physical immunity, that is, by the risk of infection related to the time of hospitalization (KRAUZER, 2015).
3.4 NURSING CARE AND ACTIONS IN PREVENTION PRE-ECLAMPSIA
During prenatal care some tests are requested and through these can be detected the acute or chronic pathologies that are directed to treatment so as not to harm the gestational cycle and decrease the rates of maternal and child morbidity and mortality (ARNALDO; CARDOZO, 2021).
Prenatal consultation needs to take place early in pregnancy, as a more detailed evaluation of maternal and fetal conditions can be performed. Even if pregnancy is considered a normal physiological process, several types of changes occur in the woman’s body and this causes a shorter distance between health and disease than when she is not pregnant. Prevention or at least early diagnosis of abnormal signs, and immediately an effective treatment, can act as a strategy to minimize various types of complications associated with parturition, not only during the antepartum period, but also during labor (ENDRINGER; CRUZ, 2017).
It is known that the health professional should be aware of any sign that may indicate a situation that compromises prenatal care, for this reason the nurse should perform all the steps, in addition to the request for laboratory tests (SANTOS; BRASILEIRO, 2018).
Nursing must always pay attention throughout the gestational period in order that any unplanned occurrences do not manifest themselves during this event. Health promotion and risk prevention actions during pregnancy need to focus on serving this much more specific clientele that requires all care. In this context, prenatal care, as recommended by the Ministry of Health, serves as the main way to generate the safety that clients and health professionals need to have over the consolidation of a pregnancy free of risks and complications (MONTEIRO et al., 2016).
In this bias, the nursing consultation, the follow-up of the pregnant woman during prenatal care, the attention to any clinical manifestation outside the planned and the counseling function as fundamental and need to receive proper monitoring. On the other hand, they call attention to complications related to arterial hypertension, presence of hemorrhages, bleeding and signs of preeclampsia and eclampsia, as beacons of deeper complications and mortality (SANTOS; BRASILEIRO, 2018).
Preeclampsia has its slow and gradual onset with major complications for the mother and fetus, so it is necessary that there is a good quality prenatal care that provides preventive actions and the identification of predisposing cases in order to diagnose as early as possible, to start prophylactic treatment. The events should also be recorded in the medical records so that this information is not lost and facilitates future care (MONTEIRO et al., 2016).
The professional nurse should perform already in the first consultation with the pregnant woman, a complete anamnesis obtaining as much information relevant to their current and previous health, in addition to family history, and for this should request routine tests, vitamin support, guidance on their diet, filling out their pregnant card, check their vaccination card and schedule for next consultation (ENDRINGER; CRUZ, 2017).
Nursing care in the prenatal period is of paramount importance because it monitors and identifies possible changes in its initial period, and forwards to a more accurate evaluation in a reference unit, with this correct decision-making can make a difference, and provide the pregnant woman with greater safety and characterize a true preventive care, it is worth mentioning that the nursing professional is a protagonist of incalculable importance in prenatal care, because it is precisely because it has the greatest bond with pregnant women (SANTOS; BRASILEIRO, 2018).
4. FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
The study, constructed from a review of specialized literature, allowed an analysis on the prevention of preeclampsia in primary care, and for this purpose, made a brief history about the incidence of this pathology, as well as its concepts and characteristics.
In addition, it was appropriate to describe the contributions of nursing care in Primary Care. Therefore, it is understood that to perform good nursing care it is necessary to take into account several factors, one of the main factors being the ability of nurses to conduct work together with the health team, taking care of paradigms of the patient and his family. Using its ability to transmit information and on the other hand know how to listen, and this constitutes basic components for a good nursing professional
Preeclampsia, although it is a pathology or a syndrome that can affect women in a state of pregnancy, is still characterized as a public health problem, despite the entire development of science, including in the nursing area and in the medical area, precisely the triggering reason for the study, which part of the problem proposed in the introduction, which, according to the researchers, was treated in depth, so that the data obtained were consistent and the results from them can be generalized to the entire population studied.
Thus, using articles that were found focusing on the theme of this study, it arouses the need to make many other publications on the prevention of preeclampsia. Most studies focus more on the role of nurses in the humanization of professional/user contact at the time of acute or chronic pain in emergency services than on the prevention of preeclampsia in primary care.
So, what are the nursing actions in Primary Care in view of the risks of hypertension during pregnancy? In response to the problem, it is worth noting that the nursing professional working in a health unit should hold lectures in order to raise awareness about the importance of prenatal care as quickly as possible to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a good evolution of the concept and labor.
In this sense, it is concluded that the main conducts used not only by nurses, but by the entire team working in primary care, should be centered on the reception process, focused on actions that can be determinant in the prevention of preeclampsia. Thus, it is extremely important to publish more studies focusing on the prevention of preeclampsia in primary care.
REFERENCES
ARAÚJO, Isabella Félix Meira, et al. Síndromes hipertensivas e fatores de risco associados à gestação. Rev enferm UFPE on line., Recife, 11(Supl. 10):4254-62, out., 2017.
ARNALDO, Mariany de Freitas. CARDOZO, Maryanne Neuraide Freire. Assistência de enfermagem às gestantes hipertensas na prevenção da prematuridade: revisão bibliográfica. Revista científica multidisciplinar núcleo do conhecimento. Ano 06, Ed. 02, Vol. 02, pp. 108 – 125 . Fevereiro de 2021 .
CABRAL, Gustavo Pereira. Cuidados de enfermagem a mulheres com doença hipertensiva específica da gestação: uma revisão integrativa. Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso. Uruguaiana, 2019.
ENDRINGER, Deyvid Dantas; CRUZ, Monielle Lima. Representatividade do enfermeiro na assistência a gestantes com pré-eclâmpsia. International Nursing Congress. May 9-12, 2017.
FERNANDES, Amélia Carolina Lopes. Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem na prevenção de infecções em unidade de terapia intensiva. J. res.: fundam. care. online 2015. out./dez. 6(4):1580-1589.
FERREIRA, Sara Santos, et al. Ácido acetilsalicílico na prevenção da pré-eclâmpsia: uma revisão baseada na evidência. Rev Port Med Geral Fam 2017;33:118-32.
FONSECA, J. J. S. Metodologia da pesquisa científica. Fortaleza: UEC, 2002.
GIL, Antônio Carlos. Como elaborar projetos de pesquisa. 4. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2007.
KRAUZER, Ivete Maroso, et al. Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem na atenção básica: o que dizem os enfermeiros? Ciência Y Enfermeria XXI (2), 2015.
LAKATOS, Eva Maria; MARCONI, Marina de Andrade. Fundamentos da metodologia científica. 7. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2010.
MELO, Wyara Ferreira, et al. A hipertensão gestacional e o risco de pré-eclampsia: revisão bibliográfica. REBES – Revista Brasileira de Educação e Saúde (Pombal – PB, Brasil), v. 5, n. 3, p. 07-11, jul-set, 2015.
MONTEIRO, M. M., et al. Emergências obstétricas: características de casos atendidos por serviço móvel de urgência. Rev. Interd. v. 9, n. 2, p. 136-144, abr/mai/jun. 2016 143.
OLIVEIRA, Leilyanne de Araújo Mendes, et al. Cuidados de enfermagem a gestante com síndrome hipertensiva: revisão integrativa. Brazilian Journal of Surgery and Clinical Research – BJSCR. Vol.23,n.2,pp.159-164 (Jun – Ago 2018).
SANTOS, Keilane Carvalho. BRASILEIRO, Marislei Espíndula. Enfermagem e os cuidados Emergenciais na doença hipertensiva específica na gravidez. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento. Ano 03, Ed. 11, Vol. 08, pp. 17-26 Novembro de 2018.
SANTOS, Joelma Oliveira Silva; NETO, Thiago Paulo de Almeida. Atuação do enfermeiro na redução da ocorrência da pré-eclâmpsia: uma revisão integrativa. Revista Científica da FASETE 2016.1.
SARMENTO, Rayani Silva, et al. Pré-eclâmpsia na gestação: ênfase na assistência de enfermagem. Enfermagem Brasil 2020;19(3):261-267.
SILVA, E.L. da; MENEZES, E.M. Metodologia da pesquisa e elaboração de dissertação. Florianópolis: Laboratório de Ensino à Distância da UFSC, 2001.
SOARES, Mirelle Inácio, et al. Sistematização da assistência de enfermagem: facilidades e desafios do enfermeiro na gerência da assistência. Escola Anna Nery Revista de Enfermagem 19(1) Jan-Mar 2015.
TEIXEIRA, Rafaela da Rosa; MINUZZI, Renata Nolibus; TELES, Jéssica Machado. Cuidados de enfermagem à pacientes com hipertensão gestacional: um relato de experiência. XII Semana de Extensão, Pesquisa e Pós-Graduação SEPesq – 24 a 28 de outubro de 2016
[1] Student in Nursing at the University CEUMA.
[2] Master in Tropical Diseases.
Posted: August 2021.
Approved: September 2021.