ORIGINAL ARTICLE
FERREIRA, Thiago Maciel [1], JIMÉNEZ, Luiz Ortiz [2]
FERREIRA, Thiago Maciel. JIMÉNEZ, Luiz Ortiz. The Use of the Active Method, Problem-Based Learning, in Higher Education: An Action Research Proposal. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento. Year 06, Ed. 06, Vol. 16, pp. 23-45. June 2021. ISSN: 2448-0959, Access Link: https://www.nucleodoconhecimento.com.br/education/action-research
ABSTRACT
This scientific article brought the proposal to leave purely theoretical classes and work in higher education, more realistic learning, according to the active method, problem-based learning. To this end, the general objective is presented: to analyze what influence ABP has on the professional training of these students studied. Specifically, we sought to: identify the contribution made by the use of ABP, in the production of knowledge of professional praxis; and describe students’ engagement in active experiences. It can be said that this action research was delineated as follows, as to the approach is qualitative, as the scope: descriptive, as the design: non-experimental. After the treatment of the data collected in this investigation, it was possible to understand the importance of the application of problem-based learning, BPA, in the professional training of these researched students. This action provided gains for higher education students, such as, simulation of the professional routine through problems, production of practical knowledge, the possibility of a collaborative, reflective and autonomous education. Finally, the problem of research, how to bring the student closer to higher education within the classroom, professional practice? So how do you have an efficient, collaborative, reflective and realistic learning? It was properly answered. That is, the problem question was answered, because it was possible to transcend from traditional teaching to practical teaching, with the use of problem-based learning.
Keywords: ABP, PBL, MASP, Action Research, Higher Education.
1. INTRODUCTION
Problem-based learning, ABP, is an active strategic methodology, especially in the teaching and learning process of higher education students. Talking about it is important, due to its ability to simulate the professional reality of the student within the academy, thus preparing them for the future exercise of their activities in the labor market.
It can be said that ABP comes from the medical course, arose with the purpose of fostering in students the ability to solve problems of their professional daily lives. In this context, for Romanowski et al. (2020), it is clear that this active method has the ability to make the student autonomous, creative, reflective and resolutive. The most worrying, however, is to note that this methodological proposal has the difficult mission of replacing traditional methods based on only exposing theoretical content to students.
In this sense, problem-based learning seeks to develop in academics, essential skills that make them more capable to act as a specialized workforce in their respective areas of activity. Therefore, this study was carried out at the Arcoverde Higher Education Center, CESA, in the course of Commercial Management in the discipline of administration in the periods of 2020.1 and 2020.2.
It is worth pointing out that the need to apply a method that brings the students closer to higher education, the reality of their future professional practice, is essential, given that traditional teaching, by itself, is not able to lead the student to the simulation of real life. Therefore, the research question of this research is: how will higher education have practical education? How to provide students with learning: efficient, collaborative, reflective and realistic? The answers to these questions are to leave the traditional method and adopt an active teaching methodology, more specifically: using problem-based learning, ABP, to build knowledge of the professional practice of higher education students.
As verified, the ABP is a methodology that has the proposal to counter theoretical knowledge, and, make available to students, a new proposal of practical experience of their future functions. It is undeniably an active method capable of making students reflective and autonomous. Thus, Nagamini (2016) assures us, the fact that the labour market changes rapidly, thus requiring the same dynamism of education, is of particular importance. It should be noted that the author makes it clear that the ABP also encourages the student to have the initiative to seek and build their own knowledge.
The general objective of this research is to analyze what influence problem-based learning (ABP) has on the professional training of these students studied. To achieve this goal, two specific objectives are proposed: to identify the contribution made by the use of ABP, in the production of practical knowledge and to describe the engagement of students on active experiences.
It is of fundamental importance to emphasize that the labor market requires future graduates of higher education, specific skills to act in this dynamic and increasingly technological environment. This method studied is pretentious to bring the practical reality of their professions into the classroom through the presentation of real problems. Therefore, to give progress to this scientific research, the bibliographic procedures and action research were defined. This action investigation was performed through field research, to understand the correlation of the application of the ABP method within the classroom, in the teaching and learning process of the research participants. In view of the above, then, the objective of the research is exploratory and descriptive, due respectively to have a literary basis of the main authors, as well as to seek to correlate the observations made in this investigation. The purpose is applied, since a practical solution to the problem has been formulated. The approach is qualitative, because it requires the need to understand participating students, which they have in mind about the researched proposal. The first topic refers to the theoretical basis, where it will be discussed on problem-based learning, ABP and the method of analysis and problem solving, MASP. In the second, we will approach the research methodology. In the third topic, it is about the design of the investigation. Then, the fourth topic refers to the results and discussions found in this research. Finally, the Fifth is the conclusion of this investigation. This research was carried out in the city of Arcoverde-PE, at IES: Municipality of Higher Education of Arcoverde, AESA-CESA. In the Course of Commercial Management, in the Discipline of Administration in the two periods of 2020.
2. THEORETICAL FOUNDATION
2.1 PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING, ABP
The acronym ABP, means problem-based learning, in English the acronym is PBL, Problem Based Learning, it can be conceptualized as an active, student-centered method that allows them to simulate the real complications present in their professional journeys. The ABP brings the student closer to higher education, the situations of reality, that is: this method makes it possible to go far beyond the theoretical classes, transcending to a practical class with the application of real problems according to their respective areas of formation.
Problem-based learning (ABP), being an active learning methodology, is an approach in which students deal with problems in small groups under the supervision of a tutor. Learning is focused on the student, learning to learn, the integration of the contents of basic and clinical sciences, as well as interdisciplinary knowledge.(TENÓRIO and SILVA, 2010, p. 221).
This method of active learning, changes the “status quo” of the traditional class, first puts the teacher in the role of mediator of the construction of knowledge, then brings the student to the center of the educational process. This change, which produces several benefits to learning in the classroom. Such as, for example: students learn to interact in groups, to reach a single goal, which is the problem solving of their professional practices; they become autonomous in their learning processes, because the method gives them the ability to learn by themselves. This active proposal, ABP, provides the student with an efficient learning, since they are presented to the experience of the studied craft, as it transforms the theoretical concepts into a practical reality. According to Camargo (2008):
ABP is a method that uses the application of real problems of daily professional life, in order to guarantee the student criticality, as well as in order to enable them to solve problems related to their respective areas of knowledge.
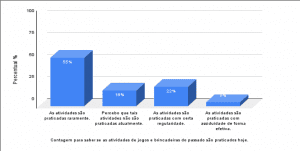
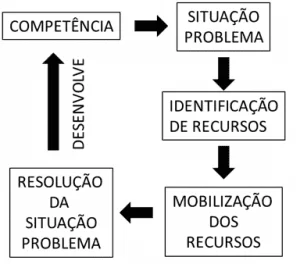
Moreover, problem-based learning should be understood as an active method of teaching and learning, which simulates the experience of the future professional, through the use of problems, within the classroom. Thus, contributing to the acquisition of knowledge, as well as stimulating the development of students at the higher level. In view of the above, the following figure, according to Camargo (2018), emphasizes some gains that the use of ABP produces in the teaching and learning process.
Figure 1: The possibilities of ABP.
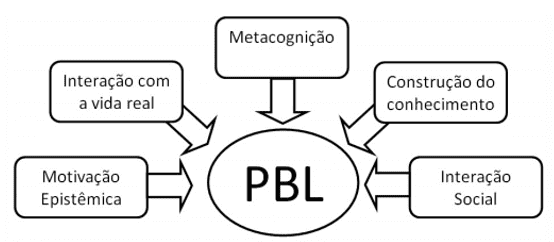
The author makes clear, as explained above, the positive points of this method, such as: the stimulation of logical reasoning in the dynamics of problem solving within the classroom. The possibility of simulating the practical reality of these students also has autonomy in learning and motivates group action, thus fostering in students the need to negotiate, disagree and persuade in this problem-solving dynamic.
Problem-based learning was thought to be a substitute for traditional teaching in higher education, but this did not happen. This is because, the author makes it clear, that it was born in response to the restlessness of medical students who longed for less theoretical and more practical classes. “The original purpose of PBL was to replace traditional teaching with autonomous and guided learning, from the 1st year of the course, through clinical problems. However, its full use did not have great expression […]”. (SILVA, 2010, p. 40). Problem-based learning is an active methodology, created a priori to address the desire for more realistic and less theoretical classes for medical students. The ABP serves to bring into the classroom practices that higher education students would only have contact with in the exercise of their future professions. In the three works mentioned above, it is converging that the problem-based methodology is of great value, its application within the classroom to students, through real problems in their training areas. These authors also claim that the ABP provides the construction of skills in students, such as: autonomy to solve the problems of their professional realities. The author makes it clear in the work of Tenório and Silva that it is evident that this proposed methodology requires supervision by a tutor. In this context, it is clear in Camargo’s work that one of the purposes of the method is to ensure that students are critical about their professional role. The most worrying thing, however, is to note that in Silva’s work, he states that the active method, ABP, did not fulfill the proposal to replace traditional education and, therefore, does not have a great adhesion in higher education. As mentioned by the author, Camargo (2008, p. 10) “PBL is a collaborative, constructivist and contextualized teaching-learning methodology, in which problem situations are used to initiate, direct and motivate the learning of concepts, theories and the Skills development […]”.
It can be said that the ABP method is an indispensable tool for the educational process, especially for higher education, as explained above, it develops and improves interpersonal skills as well as communication skills. It aims to prepare the student to conduct problems of daily work. It also encourages them to understand the problem and its possible causes in depth. The method assists in the synthesis of knowledge, and in the creation of hypotheses. Since, the ABP, is a fantastic active methodology, which is able to offer several didactic possibilities, for example, they have a rich learning process, brings professional practice into the academy. However, it should be pointed out that, despite all these resources offered by this methodology, it is resistance, in its association at the higher level, that is, traditional education is still predominant in these higher education institutions.
It is important to point out that solving problems is a difficult task and, in some cases, they are complex. In this sense, it is essential to use a didactic resource divided into well-structured phases, to support problem solving both within institutions and in the business environment. In order to solve anomalies at once is unlikely, a tool is needed to deal with these irregularities in phase sequences, so that the problem is remedied with the least possible use of resources. (LIMA, 2015). This research is relevant to the scientific community! Since throughout it, the progress achieved in the teaching and learning process in higher education will be evidenced. According to Freitas (2008, p. 160):
Problem-based learning (PBL) is not a didactic procedure, but a curricular proposal, that is, it directs the entire curricular organization, being an option of the entire faculty, administrative and academic. PBL is the main axis of learning the curriculum of some courses. It is based on problems, through which the contents are being studied by students. The problems are carefully elaborated by a committee of experts assigned to this end, and there should be as many problems as the fundamental themes that students must examine and develop in order to be considered able to practice the profession.
The author makes it clear, in the previous reference, that problem-based learning is much more comprehensive than the simple didactic procedure. It is consensual between the author and the researcher that this method is the main axis for the construction of professional practical knowledge in the academic environment. In essence, the author Lima, as well as Freitas, are in line with the point: that it is important to offer students a methodology based on problems. However, it should be pointed out that Lima and Freitas present different views regarding the scope and focus. The first focuses on highlighting the arduous mission of solving managerial problems, and exposes ways of performing in phases, the task of solving real problems from the areas of training. The second author, on the other hand, deals with a more comprehensive purpose for the method, in the conception of the same, the ABP should not only be used in actions within the class, but rather, it should cover many other sectors and authors, in this broad and aggregating way, it is possible to submit the student to the method, and make it fit for the work world.
In view of the above, it should be pointed out that, although higher education institutions do not adopt the majority of the ABP method, it is of relevant importance for the academic environment, because, through this, it is possible to better prepare the student for the job market. This is because, the same provides in higher education, gains such as: the power to stage real problems of the day-to-day of the profession studied, motivate the student to work in groups, and to make the main builder of his search for practical knowledge.
2.2 METHOD OF ANALYSIS AND TROUBLESHOOTING, MASP
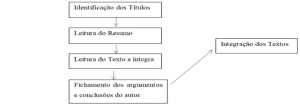
MASP, which stands for: method of analysis and problem solving, is a structured and practical methodology, which, together with quality tools, provides those who use it with an easy and organized way to solve problems! Thus, it helps companies and their professionals to achieve their goals, such as: increasing revenue, reducing costs, innovating, improving the quality of processes, and so on. In the words of Possarle (2014, p. 158), “The method of analysis and problem solving, also known as MASP, is the name that the QC-Story, a problem solving method of Japanese origin […]”. It is important to emphasize that the methodology of analysis and problem solving is a practical model to be applied and managed in higher education. This is because it has the ability to replicate the analysis of real problems within the classroom, as well as being able to solve them. The use of this method in this scientific investigation comes as a complement to the ABP, as the Masp is a structured form in well-defined processes, widely used in the business environment. Where it can be adopted in educational practices, in order to realistically simulate a scenario of managerial problems. “Teaching is too complex a human activity to support a single methodology, and PBL, as far as it is concerned, is not a fixed and finished model, it encompasses many variants and adaptations.” (CAMARGO, 2008, p. 139). Figure two below talks about the eight phases of MASP, in this sense, it is possible to observe that at each level of this methodology, it is rich in guiding details, for those who use it.
Figure 2: Masp phases.
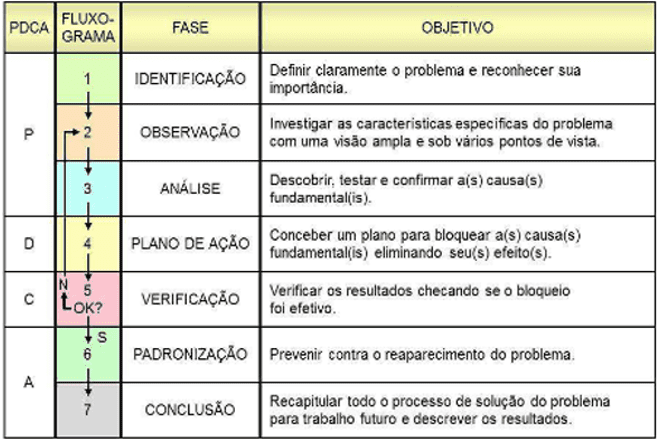
Based on the previous figure, the author shows the structural steps of the MASP, so its structuring and organization is indisputable. It is important to highlight that this problem solving method is also an aggregating instrument of other quality tools, such as PDCA and others.
According to Possarle (2014, p. 158) in his work, he states that:
MASP is an ordered path, composed of predefined steps and sub-steps for choosing a problem, analyzing its causes, determining and planning one of the actions that constitute a solution, checking the result of the solution and feedback of the process for the improvement of learning and the very form of application in later cycles.
It is no exaggeration to say that MASP is a rich tool for problem analysis and resolution. Therefore, it is necessary to assume that when applying it it is possible to foresee the failures, analyze imminent risks, it is also possible to progress with the procedures and, as well as, simulate real cases within the academy. For all these reasons, that the employment of MASP in higher education brings improvement of learning to students.
3. METHODOLOGY
This action research was carried out in the municipality of higher education of Arcoverde, AESA, in the commercial management course, in the discipline of administration.
According to Prodanov and Freitas (2013), they state that research is to plan and execute a study, addressing a research problem. Interrogators, concerns and problems, which present scattered and unsatisfactory answers to science, and therefore, it is necessary to conduct a research to generate new knowledge related to the studied questions.
The subjectivity of the qualitative approach cannot be represented by numbers, but by the interpretation of the subjective nuances of human beings, which are the subjects of the research, in the midst of the world where they live object of investigation. (PRODANOV and FREITAS, 2009).
In this investigation, the bibliographic and action research procedure was explored, in this line, the qualitative approach was used, where data collection came through bibliographic, documentary and field research, through direct observation and interview. Thus collecting, according to the above approach, subjective phenomena about human beings.
According to Andrade (2017), if the goal is to contribute for practical purposes, research is applied. Where it is in the search to solve problems present in the modern world.
According to Gerhardt and Silveira (2009, p. 67), “Descriptive research: they are carried out with the aim of describing the characteristics of the phenomenon”. As well as, descriptive research was used, which aims to report the relationship of the observed phenomena.
To collect the research data, the following instruments were used: information recording, direct observation and participant interview. In the information record, documentary data will be presented in the form of illustrations; on the other hand, direct observation, will print the data according to the perception of the researcher of this research; finally, the interview, which will report the students’ opinions on the theme studied. After data collection through them, the data will be tabulated and presented in the results and discussions of this scientific work.
It was opportune to use the active methodology: ABP, as well as the MASP tool, where it enables students through these methods to acquire essential skills for their academic and professional backgrounds.
In this sense, the purpose or nature is applied, because this study presents a factual problem such as bringing professional practice into the classroom, and having for students, an efficient, collaborative, reflective and realistic learning? As well as this applied purpose, it requires the researcher to develop an effective solution, and applicable in the real world. The approach is qualitative, because it aims to extend to the social world, reporting and explaining it. That is, the purpose of this research is to go far beyond the academic and laboratory walls, but rather, to seek to understand, the subjective human minutiae, of the real world. (FLICK, 2008). In view of the above, to give subsidies and ensure the success of the research, the bibliographic procedures and action research were chosen. By mediating the action research, the methodology of analysis and problem solving was applied to the students, the effectiveness of the application was measured by observation and interviews, and at the end, the result was presented. Through the bibliographic, we sought the foundation of the authors who discuss on topics such as: total quality, analysis and problem solving, quality tools and problem-based learning. The objective of the research is: exploratory and descriptive. Descriptive, the choice was due to the search to correlate the facts observed in this research.
Regarding data collection: bibliographic, documentary and field through unsystematic observation and interview. For the collection of information from the primary data, we used unsystematic observation, with the intention of understanding human actions in a profound way, that is, through it, we sought to describe whether the specific objective, 2nd, enabled or not, the students’ engagement on active experiences. The interview with 43 students in order to verify the achievement of the specific objective 1°, which is to identify the contribution made by the use of ABP, in the production of practical knowledge. As well as the study of the documents, in order to analyze the general objective, which is to examine whether the ABP method influences the professional training of these students studied. For the collection of information from secondary data, through literature: books and scientific studies: articles and monographs. The universe and the sample is a census research, because the entire population was investigated: the 43 students, from the management course, in the commercial management course, of the Municipality of Higher Education of Arcoverde, AESA, in the periods of 2020.1 and 2020.2. Finally, the analysis of the data will also be by frame and figures.
4. RESEARCH DESIGN
It can be said that it is of paramount importance to adopt the ABP method, for more practical classes in higher education. This is because the aim of this article is to analyze what influence ABP has on professional training in students participating in this research. Unfortunately, it worries the fact that this valuable active method is not predominant its application in higher education institutes.
The researchers in the field point out that problem-based learning, ABP, is the ideal method to prepare students in a practical way, to their future jobs. They also point out that there is a great resistance to the adhering to the method, that is, there is still preference for the traditional and theoretical teaching model.It is not only a question of applying the method to the students, but rather assigning specialists for the preparation of a curriculum, so that the use of the method is successful. (FREITAS, 2008).
This investigation was carried out in young students, where most of them already work in the labor market, in the municipality of Arcoverde, where the action research was carried out, as well as in neighboring cities. The meetings took place between the school periods of 2020.1 and 2020.2, at the centro de ensino superiorde arcoverde, CESA, in the commercial management course, in the discipline of Administration. The students who were members of this study were young people over 18 years of age, in two classes of administration in different periods, where all participated in the action investigation, totaling 43 students, plus the research teacher.
Therefore, the proposal is to get out of the traditional method, and adopt an active teaching methodology, the ABP, so that it is possible to make these students able to practice their professions. In the initial approaches, we used the video presentation of case study, where freely the students pointed out the errors perceived in the case reproduced. Gradually the researcher was highlighting important points about the main errors. Throughout the other meetings, they were asking how they could solve such problems listed in each case study. In parallel, it was exposed to the theoretical part necessary for these students to understand tools for problem solving, such as PDCA, and finally, a richer methodology was taught: the methodology of analysis and problem solving, MASP. Culminating before the end of the school semester, in the opportunity to expose a real problem, and all, students and teacher researcher, solve step by step the same.
On the first day of the lesson, the management course, in the management discipline, the lesson plan was exposed and explained, in detail, all the steps and resources that would be used in the experiment. For example, that the Objective ABP (problem-based learning) serves to: clarify facts, generate hypotheses, discussions and be able to unite theory with practice. It was also observed that the students in the first contacts with the case studies, missed many details, stating in general, that the problems always came from financial causes. When the process unfolded, with specific reservations of causes and key consequences of the problems, the students began to have more clinical views, and began to report the key points of the problems studied. It is not an exaggeration to state that the researcher sought the integralization of all in the process, creating an environment conducive to the participation of all without censorship, where the students answered the researcher’s questions orally, as well as were submitted to evaluations.
1st Cycle of action-research
Planning:
- The focus is to replace traditional teaching with problem-based learning, ABP.
- The theme is the adoption of an active methodology in higher education, in this case, the ABP, to migrate from theoretical classes to more practical classes.
- The aim is to have techniques of analysis and problem solving in a practical way.
- It is intended to employ the ABP in higher education, with the purpose of building a practical experience of the daily professional taught.
Share:
- Presentation of real problems of the business environment in the classroom, where the students analyzed the case, listed the probable causes of the problem, and discussed the possible solutions;
- The students had contact with the case study, which was presented in video form, through a projector and sound box;
- The action was performed in the discipline of administration to students of higher education.
Observation:
This dynamic of prospecting practical aspects to students, from their future professions, through problem-based learning, in the present 1st cycle of action research, it was observed that the action did not provide the effect expected by the researcher.
Reflection:
After the application of the 1st cycle of the research, the result was not satisfactory, because the proposal was poorly structured and objective, which resulted in the search to add another tool that proves to be more structured for a better solution of problems.
For the purposes of the use of the ABP, technological resources were applied, such as: tablets, projector, smartphones, Wi-Fi/3G and the Moodle platform. As well, examples of reality problematization were made available mostly in the form of videos. Like, MASP and a number of tools that compose it were used. As for the weather, it was a weekly meeting, on Tuesdays, from 19 to 22 hours. Therefore, the approach chosen was qualitative, therefore, data collection came through interviews and observations. The procedure was the bibliographic, in the form of literatures making available in the virtual library referring to the study and, as well as, the action investigation, Kemmis model, which was carried out spirally and within it, cycles, where the action is performed, in practice, which ends in the evaluation if the supposed proposal of improvements, was satisfactory, and if not , resubmit to the cycle as many times as necessary until an appropriate result is reached. “Action research enables the researcher to intervene within a social problem, analyzing it and announcing its objective in order to mobilize participants, building new knowledge.” (FIGUEIRA, 2019, p. 252).
2nd Cycle
Plan review:
In accordance with the need for a new format, it is proposed:
- Apply another more timely solution;
- Look for another form of education, by the use of problems in the classroom
- May this new model be more structured and resolute.
Share:
- Take ownership of the MASP, so that students actually analyze and solve problems;
- Present a problem present in a real case study, and together, solve in detail and step by step, the problem studied.
- This action was also carried out in the discipline of administration in the heis already mentioned.
Observation:
It was found that the review of the action plan of the 2nd cycle of action research, according to kemmis’ model, was successful. This proposal for improvement was successful, since, through MASP, students have obtained a learning: realistic, collaborative and reflective.
This exdisplay of the real problems of the work routine of these trainees, allowed prospecting situations “unusual and in other cases, thoughtless”, according to reports of the students themselves. This action research is not only about ensuring practical experience for students, it is important to emphasize that this investigation also sought to give autonomy to students in solving managerial problems.
Reflection
Therefore, the review of the action plan of the, 2nd Cycle was successful! In this scientific research, several achievements related to learning through the application of problems were obtained, such as: exercise of professional practice and simulation of reality. It was also noticed that the referring active methods, ABP and MASP, positively influenced all participants, as well as engaging them in collaborative actions. For all these reasons, it can be inferred that the research was successful.
5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
This research aimed to apply the method, learning based on problems in the discipline of administration, and at the end of the process, to analyze whether the ABP positively influenced the training of these students studied.For this, this article sought to replace the purely theoretical classes, with classes according to this proposed active method, in accordance with the purpose of making these students of higher education fit for the labor market.
This article was intended to understand the impact on student education, after the application of the active methodology, the ABP, as well as specifically proposed to identify the contribution of the method and describe the engagement of the students. According to Camargo (2008), the author makes it clear that research in the area of problem-based learning focuses mainly on providing effects in the educational process, such as ensuring a higher performance for students.
Thus, it is of particular importance to note that the plan of the specific objective 1°, of: identifying the contribution made by the use of ABP, in the production of practical knowledge, was successful. This statement comes from the data derived from the observation of the researcher, such as the interviews answered by the students, according to table 1, (General Objective Deceit in The Consequences of the Action on ABP and MASP), below, where in the opinion, yes, there was production of practical knowledge within the classroom.
It is important to highlight that, for example, that students were able to practice, simulate their professional practices and, build their own knowledge in class.
For Tenório e Silva (2010), as explained above, the method provides students with contact with real problems, bringing them to the center of the study and giving them autonomy in the construction of their own knowledge.
Thus, it is particularly important to note that the level of the specific objective, 2nd, of: describing the students’ engagement in active experiences, was successful. The fact is that the report of this engagement was pointed out in the field diary, where the researcher pointed out the increased interest in the method, while it was shown to be effective and replicable in their professional realities. As also reported by these students, in the interviews answered in this study.
Thus, the students, in most cases, understood and embraced the proposal of action-research, for example, they began not only to participate, but also to bring their own dilemmas of their work routines and exchange experiences of the actions performed in the reality of the labor market.
The PBL was born with the proposal to counter theoretical teaching, by practical learning, thus, as explained above, instigating engagement and a greater interest in them, as well as ensuring a oriented and autonomous learning. (SILVA, 2010).
Therefore, it is indisputable that it was possible to succeed in the general objective of analyzing the influence that ABP has on the professional training of students. Because, in this sense, it was observed that the students became aware of the need for a structured method, to use as a tool, to understand and solve, definitively, the managerial problems studied, which arise in the professional environment. Since, for example, according to the report of these students surveyed, they only saw the consequences of a problem, they thought they solved it and soon returned it. That is, they did not understand the differences between problem, cause and consequence, so they did not really solve the problems present in their work routines. Moreover, the chosen methodology was also a basis for achieving this objective, especially action research, which through incessant cycles, until reaching the improvement of educational processes, as well as changing the “status quo” of how, management problems were seen and solved. That is, through AI, and its procedures of: planning, acting, observing and reflecting; the researcher is able to evolve with the educational process, as well as to delve deeper into the real problems that come from the labor market. With this, producing self-reflection and mobilization for the participants, and finally, generating new knowledge about the field studied.
In view of the above, it is important to highlight that this research provided gains for both students and the research professor. This was possible by the effect of triangulation of the method, procedure and with the application of problem-based learning, ABP. Qualitative research, through participant observation and structured qualitative interviews, it was possible to verify that ABP positively influenced: the acquisition of skills necessary for the labor market and the engagement of students to understand and deal with the proposed problems. On the other hand, bibliographic research is based on the study of art, the main and most current authors of the subject addressed. The documentary research provided the registration of photos and the researcher’s field diary, necessary to understand the degree of influence and engagement of the researchers. Action research, which evolved with the teaching and learning process of these higher education students. Finally, the application of the ABP, together with the MASP tool, promotes professional practical experience within the academy, so that it makes these students more prepared for the future exercise of their professions.
Therefore, after the promotion of action research, important results were obtained, based on them, it was quite possible to answer the following problem of the research: how to approach the student of higher education within the classroom, professional practice? So how do you have an efficient, collaborative, reflective and realistic learning? According to the following information.
5.1 ABP
Thus, Figure 3, just below, refers to the application of the active ABP method.
Based on the specific objective 1°: to identify the contribution made by the use of ABP, in the production of practical knowledge; and then the corresponding question: how to qualify the contribution of the ABP, in the consolidation of practical knowledge?
In response to this question, shortly after the execution of the action research, carried out in the classroom, a video was presented about the case study of the CCE company, after this, the mediator, asked the class to enumerate facts, indicate deficiencies and generate hypotheses, according to the case presented. Finally, with the collaboration and participation of all, the students discussed and argued about which data would best represent the purpose of understanding and solving the proposed problem, and, they themselves reached the consensus, listed the information required by the mediator of the activity, and the following results were achieved:
Figure 3: Application in class of the ABP.
Figure 3 above is a clipping of the initial action of presenting problems, and through the ABP, seek to solve them. At this moment it portrays the act of the investigated to listen to the students’ debates, regarding the questions previously received from them, and project the answers, for all, thus evidencing the result of the whole process performed, as it is practiced in the reality of the companies.
5.2 MASP
So, Figure 4 pictured below is a response to action involving the application of MASP in practice. In accordance with the specific objective, 2nd: to describe the engagement of students on active experiences; there is the following question: how to report the students’ involvement with the proposed action? Thus, the second part of the research was carried out in the same class, however, in the distance education modality, distance education, due to the need for social distancing in these times of crisis in world health. It is noteworthy that there was no loss regarding the number of participants and the contributions of these students, on the proposal to analyze and solve problems. The method of analysis and problem solving came as a complementary tool to the ABP method, however, with much more resources and richness of details, simulating the step-by-step analysis and resolution of a real problem, present in the professional routine of these students surveyed.
Figure 4: MASP development.
Chart 1 represents the achievements achieved after the kemmis model practical action research, according to the theme researched.
Table 1: General Objective Deceit in The Consequences of the Action on ABP and MASP
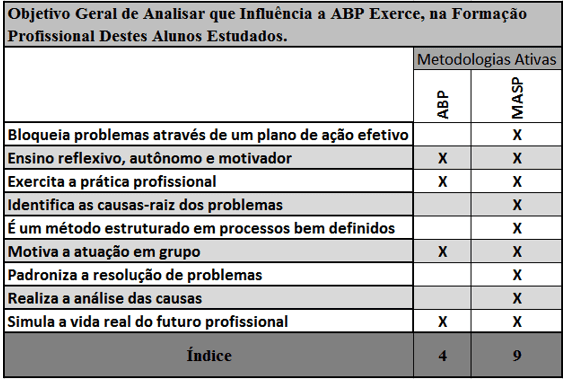
Table 1 demonstrates the gains by adopting an active method to educate one another through the practical application of problems. The importance of the ABP method is visible, but it is also evident that it requires a methodological complement. In other words, the MASP continued the purpose of problem-based learning, in a structured and rich in detail, and went beyond, therefore, it provides for going deep, not only in the resolution, but, to understand the causes and block it definitively.
6. FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
Then, the present study allowed us to analyze the influence exerted on the professionalization of the participating students, in addition, through several other resources, it was possible to observe that all contributed to the achievement of the proposed goal.
It is not an exaggeration to state that the research contributed to the production of practical knowledge, as well as to the engagement of these same students, except for a small number of students who, indifferent to the proposal, focusing only on obtaining the grade of the subject. The researchers also reported that the whole process that culminates in the resolution of a problem, is laborious and often takes a long time, however, they confessed that it is a thorough and necessary procedure, so that in fact, management problems are eliminated. Given the data students themselves through the analysis of the research data collection, all the objectives of each didactic proposal presented were successfully achieved.
The first action was the presentation of a video, about the case study of the “CCE company”, the researcher, measured the action as a tutor, responsible for only organizing the students’ debate, as to the most critical points, of the case study of business failure. As well as, it encouraged the participation of the students, and took note of the answers of all the points raised. This activity led the students to observe in detail nuances, never observed before by them, due to factors, such as: judging that they already know how to treat problems, lack of time and method. The second action, on the other hand, was due to the need for a more structured tool to face problems of greater complexibility, which was the use of the “methodology of analysis and problem solving, MASP”, in the distance modality, due to the need for social distancing.This tool proved to be effective in solving management problems, due to the same requiring those who use it, to follow a detailed step by step about each phase of the process, to understand and solve problems autonomously. It is worth pointing out that this theme, problem-based learning is of paramount importance, and therefore, for future studies, it is suggested to seek a case study of the practical application of the same in the work environment, of people who were presented to the ABP method, and who use their precepts to solve their daily problems.
Finally, this research was successful in achieving the general objective, since it was possible to contribute to the construction of practical knowledge in higher education. In other words, the active ABP method, as well as the MASP, together, produced several educational gains, such as: reflection, autonomy, collaboration and knowledge of cause, thus positively influenced the professional education of these students participating in this action research.
REFERENCES
ANDRADE, M. M. de. Introdução à Metodologia do Trabalho Científico. 10. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2017.
ARNAL, J. J. Investigación educativa: Fundamentos y metodologías. Barcelona: Labor, 1994.
CAMARGO, C. L. R. de. Aprendizagem Baseada Em problemas (PBL) uma experiência no ensino superior. São Carlos: Edufscar, 2008.
CAMPOS, V. F. Qualidade total: padronização de empresas. Rio de Janeiro: Record. 1992.
FIGUEIRA, E. Introdução geral à educação inclusiva. Clube de Autores, 2019.
FLICK, U. Managing Quality in Qualitative Research. London: Sage, 2008. ISBN 1446238733, 9781446238738.
GERHARDT, T. E.; SILVEIRA, D. T. Métodos de pesquisa. Porto Alegre: UFRGS, 120 p. 2009.
LIMA, V. M. do R. A gestão da aula universitária na PUCRS. Porto Alegre: EDIPUCRS, 170p. 2008.
KEMMIS, S.; McTAGGART, R. Cómo Planificar la investigación-acción. Barcelona: Laertes, 1988.
LIMA, S. P. C. Importância da Masp – metodologia de Análise e solução de problemas – na Melhoria dos índices de serviços Empresariais. MBA em Gestão da Logística Integrada, Aparecida de Goiânia, 34 p. 2015.
MINASI, L. F.; et al. Leituras De Paulo Freire. Rio Grande: Clube de Autores, 2011. ISBN 978-85-912855-0-1.
NAGAMINI, E. Questões teóricas e formação profissional em comunicação e educação. Ilhéus-BA: Editus, 287 p. v. 1. 2016. ISBN 978-85-7455-411-2.
POSSARLE, R. Ferramentas da qualidade. São Paulo: SENAI-SP Editora, 2014.
PRODANOV, C. C.; FREITAS, E. C. de. Metodologia do trabalho científico [recurso eletrônico]: métodos e técnicas da pesquisa e do trabalho acadêmico. 2. ed. Novo Hamburgo: Feevale, 2013. ISBN 978-85-7717-158-3.
PRODANOV, C. C.; et al. Educação e Tecnologias: Desafios dos Cenários de Aprendizagem. Curitiba – PR: Bagai, 2020. ISBN 978-65-87204-67:3.
MARTINS, J. A.; SALDANHA, C. Bioquímica em Medicina. Lisboa: Edições Colibri, 2010. ISBN 978-972-772-997-7.
TENÓRIO, R. M.; SILVA, R. de S. Capacitação docente e responsabilidade social: aportes pluridisciplinares. Salvador: Edufba, 2010.
[1] PhD in progress in Ciencias de la Educación, Master in education science and multidisciplinarity, Specialization in Teaching of Higher Education, Specialization in MBA in Strategic Business Management, Graduation in Systems for Internet and Graduation in logistics.
[2] Advisor.
Submitted: March, 2021.
Approved: June, 2021.