SANTOS, José Ribeiro dos [1]
SANTOS, José Ribeiro dos. Social and Environmental Awareness measures on exploitation and conservation of biodiversity in Brazilian biomes, actually restricting so biopiracy. Multidisciplinary Core scientific journal of knowledge. 02 year, Ed. 01, vol. 13, pp. 225-241 January 2017. ISSN: 2448-0959
SUMMARY
The Atlantic forest is one of the Brazilian ecosystems of greater importance and representativeness, and is considered the second largest rainforest in the country. Despite the recognized importance of forests and the strong pressure of national and international environmental movements, in Brazil the remnants were and continue being devastated. Therefore, this is not a purely environmental issue, but economic and political, geostrategic, insofar as the wealth that could be used to combat social problems and infrastructure of these traditional communities, or in your registry cultural heritage. It is necessary to intensify the policies to combat the black market of international exploitation of biodiversity. The aim of this work is to check what are the key measures to curb the practice of biopiracy in Brazilian biomes. Methodology adopted was the literature review, the research was developed between the months of September and December 2016. The results show that both the international scientific community as Governments and non-governmental entities environmentalists come warning of the loss of biological diversity worldwide, particularly in tropical regions. Biotic degradation which is affecting the planet finds roots in the contemporary human condition, exacerbated by the explosive growth of human population and the uneven distribution of wealth. Conclusion: the Federal Constitution of 1988, the caput of the art. 225, alludes to the high dependence of the ecologically balanced environment for the present and future generations. In this context, in contemporary times one of the leading paradigms appears on environmental issues, more precisely, the possibility of survival of man without degrading the natural environment. It is necessary to step up the fight and the debate of the operating practices of biodiversity in the country. The exploitation of plant resources of forests and woods of consciously and controlled to ensure an increase in the quality of life of the human population, both in present and in future generations.
Keywords: Environment, Biomes, Biodiversity, Biopiracy.
INTRODUCTION
The Atlantic forest is one of the Brazilian ecosystems of greater importance and representativeness, and is considered the second largest rainforest in the country. Despite the recognized importance of forests and the strong pressure of national and international environmental movements, in Brazil the remnants were and continue being devastated. PATIL, (2011).
Initially, in the Northeast, this biome covered an area of 255,245 km ² and, currently, due to deforestation, only 8% of the Recife metropolitan region has a vegetal cover of Atlantic forest remnant, represented by fragmented areas. RAMALHO (2014)[2].
Environmental protection is the responsibility of all humanity. The adoption of actions to ensure sustainability in the medium and long term a planet in good conditions for the development of the various forms of life, including the human.
Therefore, this is not a purely environmental issue, but economic and political, geostrategic, insofar as the wealth that could be used to combat social problems and infrastructure of these traditional communities, or in your registry cultural heritage. It is necessary to intensify the policies to combat the black market of international exploitation of biodiversity.
As is well known, the human being since long has been concerned about the study, description and classification of plant and animal species, with information already in the Antiquity naturalists and Greek philosophers have to list and classify the species of organisms that were known in your time.
Among the main measures that can be adopted for the preservation of natural resources awareness is one of the most important. More than ever, the preservation of ecosystems and natural resources is a subject that requires the full attention of the society. To ensure the natural resources needed for future generations, enabling the maintenance of natural resources (forests, Woods, rivers, lakes, oceans) and ensuring a good quality of life for future generations. FERREIRA, et al. (2014).
According to t[3]he IBGE, Brazil is formed by six distinct characteristics biomes: Amazon, Caatinga, Atlantic forest, Cerrado and Pantanal Pampa. Each of these environments is home to different types of vegetation and fauna. As the vegetation is one of the most important components of biota, your state of preservation and continuity define the existence or not of habitats for the species, the maintenance of environmental services and the supply of goods essential to the survival of human populations.
Biopiracy covers for centuries, the extraction of red pigment of Redwood by the Portuguese at the time of the discovery, following Act of piracy occurs in the Amazon with sending seeds of syringe for England (PANCHERI, 2013 p. 443).
The Brazil is considered a megadiverse country, with about 22% of the world's native species, in fact, the country with the highest biological diversity (biodiversity) of the planet. The vast plant and animal wealth, Brazil is constant target of biopiratas. (GOMES, 2007 p. 183).
Biopiracy can be conceptualized as exploration, manipulation and export of biological resources for commercial purposes. Biopiracy is the name given to the exploitation and use of natural resources or traditional knowledge about these resources illegally. The animal trafficking the extraction of active principles and the use of the knowledge of indigenous people without authorization are examples of biopiracy.
According to data from the Ministry of the environment, Brazil is a country of continental proportions: its 8.5 million km ² occupy nearly half of South America and spans several climatic zones – as the humid tropics in the North, the semi-arid temperate areas in the Northeast and in the South.
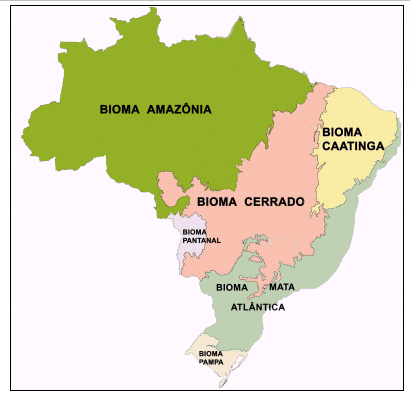
Of course, these climatic differences lead to major ecological variations, forming distinct biogeographical zones or biomes: Amazon rainforest, the largest rainforest in the world; the Pantanal, the largest floodplain; the Cerrado savanna and woodlands; the Caatinga semi-arid forest; the fields of the Pampas; and the rain forest.
Rain from the Atlantic forest. In addition, Brazil has a marine coast of 3.5 million km ², which includes ecosystems such as coral reefs, dunes, mangroves, lagoons, estuaries and marshes. A biome is characterized by a main type of vegetation (in the same biome can exist different types of vegetation).
Living beings of a biome living so adapted the conditions of nature (rain, humidity, heat, etc.). The Brazilian biomes are characterized, in General, by a great diversity of animals and plant species (biodiversity).
Biopiracy also causes damage to the environment, because it puts at risk the biodiversity of an area. To explore heavily a species, your population decreases and, consequently, raise the risks of extinction. From the beginning of the years 70, the environmental problem has become questioned reframing and rethinking a new reality (Lirio, et al. 2011, p. 48). In search of profitability occurs to unbridled destruction of natural resources, this destruction unconscious causes destruction of ecosystems.
The variety of biomes reflects the enormous wealth of flora and fauna in Brazil: the Brazil hosts the largest biodiversity on the planet. This abundance and variety of life – which translates to more than 20% of the total number of species on Earth – raises the Brazil to the rank of principal nation among the 17 mega diverse countries (or biodiversity).
The environmental problems of today has taken on more and more importance. Thoughtless attitudes of man as the deforestation of forests. Along with the public authorities and the society, directs itself to protect the relationship between man and the environment, not only with regard to the application of sanctions, but also in trying to trace paths that provide sustainable development. RAMALHO, (2014)
The model of a sustainable society requires the ability to satisfy your needs, without compromising the chances of survival of future generations so that they meet your own needs. For years discusses the issue of Biopiracy lato sensu, which encompasses the exploitation and illegal trade of wood, the trafficking of animals and wild plants (PANCHERI, 2013).
Biodiversity is one of the elements that make up the balance of the environment and might serve as a differential factor in the realization of own development. The plants have great importance for the entire planet, renewal of the atmosphere and release oxygen (CRC p. 7)[4]. Our dependencies in relation to plants are huge, just observe around us the production and construction of several segments.
In this context, as the more exuberant biodiversity on the planet, the Brazil meets privileges and huge responsibility. Features the Atlantic rainforest is a biome (set of different ecosystems interacting with the physical environment and each other) present on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean from Brazil expanded until the middle of the country, reaching even part of Paraguay's territory and Argentina.
Followed the whole line of the Brazilian coast of Rio Grande do Sul Rio Grande do Norte. For being a biome which occupied almost the entire brazilian coast, crossed by several soils and climates, thus creating local and a quirks not homogeneous formation. PERES, (2010).
One of the definitions of biodiversity is the exuberance of life on Earth – in a seemingly endless cycle of life, death, and transformation. The term biodiversity relates to the number of different biological categories (wealth) of the Earth and the relative abundance of these categories (equitability), including local variability (alpha diversity), biological complementarity between habitats (beta diversity) and variability between landscapes (gamma diversity).
Increasingly the society consumes natural resources than the planet offers, without worrying about how this exploration can impact on nature as a whole and on the survival of the species. In this sense, the conservation and exploitation of natural resources is an account that needs to always close in blue, that is, with a conscious consumption that does not cause environmental imbalance and not exhaust what the planet has to offer.
By having a great biodiversity, even today there is a great exploitation of natural resources without authorization in our country. With the advances in the area of biotechnology, the operation became even greater, since they carry genetic material is more "simple" than transporting an animal or a plant, for example.
Some important cases of biopiracy in Brazil. In 1746, cocoa was taken from Bahia to Africa and Asia, where the product began to be used and a number of derivatives were produced. Before the success of plantations, cocoa production became one of the main economic activities in these locations. In addition, another contributing factor to the biopiracy in Brazil is the lack of specific legislation.
Some of the Brazilian industries of pirated resources other countries are as follows: the most classic is The acai berry that was patented by Japanese firm k. k. Eyela Corporation, but that due to pressure from various Ngos and the media, had your patent Hunt by Japanese Government (this after more than a year); the second is the famous case of the Bothrops venom that had the active ingredient discovered by a Brazilian. But the record ended up being done by an American company (Squibb) who used the work and patented the production of a drug against hypertension (Captopril) in 70 years. Cold, (2016).
In the first case there was success (even if time-consuming) because the patent had been made recently, after the Convention on biological diversity. But, in cases like the second, in which patents are old the chances of this happening are virtually nil and, like most resources go to biopirateados large and still no multibillion-dollar companies and legislation in Brazil that set the biopiracy as a crime, ends up being a costly action and almost always unsuccessful.
The action of "biopiratas" is facilitated by the absence of legislation that set the rules of use of natural resources. For the perpetuation of life in biomes, is necessary the establishment of environmental public policies, the identification of opportunities for the conservation, sustainable use and sharing of benefits from biodiversity.
The Atlantic forest comprises one of the largest ecosystems on the planet, formed by an immense biological diversity. Although your importance is notorious, this biome has large number of species that are threatened with extinction, in addition to being one of the most threatened ecosystems of Brazil.
The Atlantic forest biodiversity is similar to that of Amazon. There's section of the biome because of variations in latitude and altitude. The interface to this diversity of biomes creates unique conditions of fauna and flora.
Another element fundamental to the existence of biodiversity is the water. Water is fundamental to a biome as the Atlantic forest that is permanently damp. Therefore, this biome has great relevance for support of the hydrological basins processes involved in these forests. PERES, (2010).
The Atlantic forest comprises one of the largest ecosystems on the planet, formed by an immense biological diversity. Although your importance is notorious, this biome has large number of species that are threatened with extinction, in addition to being one of the most threatened ecosystems of Brazil. RAMALHO, (2014).
The contemporary brazilian society history is witness to an intense debate in the face of the imposition of the normative content of the Brazilian forest code (Law n° 4,771, 15-09-1965), which makes the exercise of the powers inherent in the area about the agrarian property to public and social interests. Essentially, the debate occurs around two legal figures: the Legal reserve and the forests; the native vegetation and the Permanent preservation areas. PRIOSTE, (2009)
Along the biome, are still exploited forest timber species, medicinal plants and ornamentals, among others. If on the one hand this activity generates jobs and foreign exchange for the economy, much of the exploration of the Atlantic flora happens so predatory and illegal and is often associated with the international trafficking of species. Faced with the challenge of keeping alive the awareness of the individuals on the subject, this work aims to deepen the debate on socio-environmental awareness measures on exploitation and conservation of biodiversity in Brazilian biomes, so actually restricting the biopiracy.
For analysis of this context was drafted the following questions: what additional instruments would have greater effectiveness to curb biopiracy in Brazilian biomes? What additional measures should be taken to ensure that the Atlantic forest biome is actually preserved for future generations? Why environmental legislation in General can not inhibit the unbridled destruction of the Brazilian biomes?
2. METHODOLOGY
This is a literature review, the study is a systematic review which consists of a scientific objective, technical efficient and reproducible, that represents a reflection on the importance of the actions of man on the environment in specifically the Brazilian biomes in particular the Atlantic forest. The review consists of a meticulous and extensive critical analysis of current publications in a particular area of knowledge. A survey of the features or components of the fact, phenomenon or problem, the review is carried out as part of an initial scientific study, either undergraduate or graduate level, being part in a master's thesis or a doctoral dissertation PhD. Drawn from material already published in books, newspapers and periodicals available on the internet. The research was developed between the months of September and December 2016.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Population growth, coupled with new technologies, makes the man use in various forms of use, increasingly complex areas. In recent decades, humanity has undergone a series of technological changes, affecting human relations and with the natural environment (Sa; Milk, 1999).
Amazon: brazilian Equatorial Forest occupies about half of Brazil's territory and is concentrated in the North and in part from the Midwest. This biome is greatly influenced by the equatorial climate, which is characterized by low temperature range and great moisture from evapotranspiration of rivers and trees.
The Cerrado, or Savanna, brazilian stretches over much of the Midwest, Northeast and Southeast of the country. Is a biome typical of continental tropical climate, which, by reason of the occurrence of two well-defined seasons – a humid (summer) and other dry (winter)-, has a vegetation with trees and small shrubs, twisted trunks, thick shell and generally, deciduous (the leaves fall in autumn). The fauna of the region is very rich, composed of Capybaras, wolves-guarás, Anteaters, tapirs, seriemas etc.
Caatinga: extends throughout the sertão, occupying approximately of 11% of the national territory. This is the driest region of the country, located in the semi-arid tropical climate. The vegetation of this region is composed mainly by arborescent plants (used with the aridity, as the Cactaceae) and deciduous (lose foliage during the dry period), plus some trees with very large roots that can capture water from water table in great depths and therefore do not lose their leaves, like the juazeiro. The fauna of this biome is made up of a wide variety of reptiles, sapo cururu, asa branca, agouti, opossum, PREA, catingueiro deer, six-banded Armadillo etc.
Pampas: Located at the southern end of Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul, this biome is quite influenced by the subtropical climate and the formation of the relief, which mainly consists of Plains. Because of the cold and dry climate, the vegetation can't grow, being composed primarily of grasses, such as grass-goat's beard, fat grass, capim-mimoso etc. Are examples of animals that live in this biome the deer, Heron, otters, Capybaras and others.
Pantanal: rata-if the greater floodplain of the country and is located in the States of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do sul. This biome is greatly influenced by the regimes of the rivers present in these places, because, during the rainy season (October to April), the pantanal water flooding much of the plains in the region. When the rainy season ends, the rivers decrease your volume of water and return to their beds. For this reason, the vegetation and the animals need to adapt to this movement of water. All these factors make the very diverse wetland vegetation.
Atlantic forest: consists of a set of forest types (forests: Rain, Rain, Tropical Deciduous and Semi-deciduous, Open Rain) and associated ecosystems such as reefs, mangrove swamps and grassland, which extended by approximately 1.3 million km2 in 17 States of the Brazilian territory.
In other words, a biome is made up of all living beings in a certain region, whose vegetation has enough similarity and continuity, with a more or less uniform climate, having a common history in your training. So all your biological diversity is also very similar.
The Federative Republic of Brazil and the other countries of the Amazonian hileia are holders of a wide biodiversity and rational use of such wealth can be an alternative for the sustainable development of those countries in the context of globalisation and the subregional integration. (BIRTH, 2007 PG11).
The Brazil has enormous territorial extension and features very varied soils and climates. In light of these characteristics, there is an obvious diversity of bioregions, defined, particularly by the vegetation cover.
| Continental Brazilian Biomes | Area (km ²) | Area/Total Brazil |
| AMAZON Biome | 4,196,943 | 49.29% |
| The CERRADO Biome | 2,036,448 | 23.92% |
| The Atlantic Rainforest Biome | 1,110,182 | 13.04% |
| The CAATINGA | 844,453 | 9.92% |
| The PAMPA Biome | 176,496 | 2.07% |
| PANTANAL Biome | 150,355 | 1.76% |
| Total Area Brazil | 8,514,877 | 100% |
Source: http://www.ibge.com.br/home/presidencia
The loss of diversity carries numerous consequences to humanity, can quote as an example: climate change, introduction of alien species, loss of the beauty and exuberance of the biomes, and destruction of natural habitats, the fall quality of life of the population, reduce supply and irregular distribution of drinking water, increase of diseases and epidemics, social, political and economic instability, among others. With this, it is necessary to conserve the biodiversity of our planet and reflect on ways of rational consumption of natural resources.
The diversity of forest typologies must also be considered, allowing the creation of policies, adapted to local situations and differentiated characteristics of each biome. In this sense, the land use planning and natural resource management assume a high degree of importance to the quality of future lives here on Earth. LOBLER, (2015).
Both the international scientific community as Governments and non-governmental entities environmentalists come warning of the loss of biological diversity worldwide, particularly in tropical regions. Biotic degradation which is affecting the planet finds roots in the contemporary human condition, exacerbated by the explosive growth of human population and the uneven distribution of wealth.
According to IBAMA, only in the year 2006 it is estimated that there was a daily loss of $ $16 million in the light of the Brazilian products patented by foreign companies that prevent the country has marketed their own products and still require royalties for import them.
This type of practice is considered a crime according to the Convention of biological diversity created by the United Nations during the ECO92, held in Rio de Janeiro, in which several countries participated in the debate.
The origins of the legislation: the forest code of 1934 and the restrictions on the right of property in Brazil wants to be like colony, Empire or Republic, there has always been the prevalence of an interventionist Government perception about the ownership of forests. In your recent history, Brazil had two codes: the Forest of 1934, and in force at the present time, established in 1965. The forest code of 1934, for the first time in the country, regulates the legal guardianship of the "existing forests in national territory". Establishes a specific legal concept of which are forests rising to the "well of common interest of the inhabitants of the country", thus permitting State intervention to impose restrictions on property rights of each one, in the name of good legal forests are designed by the company. The next regular Code some practices and establish institutes in order to surround and maintain mineral resources and genetic under the sovereignty of the State. PRIOSTE, (2009).
Pichot and Shaved (1994) state that, since the late 80, environmental policies occupy a foreground position on economic and political concerns, as the European Union countries face a growing number of problems, such as the scarcity of resources for the maintenance of the protected areas. In Germany and in Belgium, various initiatives have been taken aiming at the protection of natural resources. The European Union has taxed heavily fossil fuel consumption. Countries such as Denmark, Finland, Norway, Netherlands and Sweden have applied tax on carbon production, with the main objective to generate funds for promoting environmental projects. PIRES, et al. Apud, PICHOT; SHAVED, (1994). The extraction of vines is an activity economically and culturally important to indigenous communities Kaingang. However, this practice has generated conflicts with the management of protected areas, environmental legislation in the area of Atlantic forest and owners of areas with forest fragments.
The main processes are responsible for the loss of biodiversity are: loss and fragmentation of habitats; introduction of exotic species and diseases; overexploitation of species of plants and animals; use of hybrids and monocultures in agribusiness and reforestation programmes; contamination of soil, water, and atmosphere by pollutants; and climate change. FRAMES, (2008).
Biodiversity is one of the elements that make up the balance of the environment and might serve as a differential factor in the realization of own development. The model of a sustainable society requires the ability to satisfy your needs, without compromising the chances of survival of future generations so that they meet your own needs. For years discusses the issue of Biopiracy lato sensu, which encompasses the exploitation and illegal trade of wood, the trafficking of animals and wild plants (PANCHERI, 2013).
The plants reach an extraordinary biodiversity in the Amazon. It is estimated that the region houses about 40000 vascular species of plants, of which 30000 are endemic to the region. (Vieira, 2005)
Biopiracy refers to knowledge pertaining to local populations and indigenous people of the Brazilian Amazon occurs due to the unauthorized use of these knowledge by third parties-most of the time represented by the rich countries in technology and poor in biodiversity, which make use of them to save time and money for research to manufacture of a given product or medicine, causing losses of various forms to Brazil. (Alencar, 2006).
The forest code of 1934, for the first time in the country, regulates the legal guardianship of the "existing forests in national territory". Establishes a specific legal concept of which are forests rising to the "well of common interest of the inhabitants of the country", thus permitting State intervention to impose restrictions on property rights of each one, in the name of good legal forests are designed by the company.
The Federal Constitution of 1988 comes to reaffirm this insight, in particular articles 170 (subordinate to economic activity to the rational use of environmental resources), 186 (reports on the Social Function of rural property) and 225 (on the environment and on the current rights, of future generations). PRIOSTE, (2009).
One of the promising alternatives to encourage the rational use of resources is the implementation of tax incentive programs for the conservation and sustainable use of forests. PIRES, et al (2011).
CONCLUSION
The Federal Constitution of 1988, the caput of the art. 225, alludes to the high dependence of the ecologically balanced environment for the present and future generations. In this context, in contemporary times one of the leading paradigms appears on environmental issues, more precisely, the possibility of survival of man without degrading the natural environment.
It is necessary to step up the fight and the debate of the operating practices of biodiversity in the country. The exploitation of plant resources of forests and woods of consciously and controlled to ensure an increase in the quality of life of the human population, both in present and in future generations.
Discussing on new laws until the emergence of what is now the legal framework of the protection of the Atlantic forest from the 1988 Federal Constitution which recepcionava the forestry code and the law of National Environmental Policy. The Atlantic forest is the specific legal guardianship with the entry into force of the law/2006 which 11,428 discipline on the use and protection of native biodiversity of this biome.
The awareness of people and the opportunity to broaden the debate on the subject will bring important changes in posture and in rates of illegal exploitation of natural resources.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES.
ALENCAR, Aline Ferreira. Legal analysis on biopiracy associated traditional knowledge related to genetic patrimony of the Brazilian Amazon. XV National Congress (CONPEDI), 2006.
BRAZIL, Brazilian Institute of environment and renewable natural resources (IBAMA): available in: www.ibama.gov.br. [acesso 18/10/2016].
BRAZIL, the Atlantic forest biosphere reserve (RBMA): DISPONÍL in: www.rbma.org.br. [acesso 16/10/2016]. São Paulo, 2016.
BRAZIL, Brazil's Biomes. Available in: <http: www.biomasdobrasil.com="">.</http:> Access in 11/12/2016 the Brazilian Institute of geography and statistics (IBGE) available at: <http: www.ibge.gov.br="">.</http:>
BRAZIL, Biomes-Ministry of the environment. Available at: www.mma.gov.br/biomas[acesso 30/11/2016]. São Paulo, 2016.
CRC, notebook of reference content. Foundations and methods of plant biology teaching i. Claretiano School-education network, Batatais 2015.
FERREIRA, Hugo Fernandes. Alves, Romulus Romeo da Nóbrega. Media and law involving the hunting of wild animals in Brazil: a historical and socio-environmental perspective. Gaia magazine Scientia (2014) Volume 8 (1): on-line Version ISSN 01-07 1981-1268 http://periodicos.ufpb.br/ojs2/index.php/gaia/index
FREITAS, Vladimir Steps. The Federal Constitution and the effectiveness of environmental standards. São Paulo: Editora RT, 2002.
GARCIA, Rodrigo Castro. The control and the Suppression of piracy in Brazil. Magazine. Jurisprudence, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. 58, n° 183, p. 27,/dez.. 2007.
Löbler, Carlos Alberto. Sccoti, Anderson Augusto Volpato. Werlang, Mauro Kumpfer. Contribution to the delimitation of the Pampa and Atlantic forest biomes in the municipality of Santa Maria, Rio g. do Sul. Electronic magazine in management, education and Environmental Technology Santa Maria, v. 19, no. 2, may-Aug. 2015, 1250-1257 p. Journal of Natural and exact Sciences Center-UFSM ISSN: 2236117.
BIRTH, Danilo Lovisaro. Biopiracy in the Amazon: a proposal of transnational protection of biodiversity and associated traditional knowledge. Dissertation submitted to the graduate program in law at the Federal University of Santa Catarina-UFSC, for a master's degree. Santa Catarina, 2007.
PANCHERI, Kathleen. Biopiracy: reflections on a criminal type. Journal Faculty of law University of São Paulo. Vol. 108, p. 447. Jan/Dec of 2013.
Pires, Paulo de Tarso de Lara. Peters, Narasimhan. Zeni, Douglas. Gaulke. The Araucaria forest biome and the brazilian tax laws. Forest Magazine – Vol. 41 n. 3, 2011.
PRIOSTE,: Fernando G. Vieira. Afanc, Juliana. Pacher, Larissa. Vieira, Judith. Changes in environmental legislation and the reflections on peasant and family agriculture people and traditional communities: political and technical allowances for the debate. Earth Magazine rights human rights organization. Curitiba-August 2009.
Frames, Bruna. Conservation and exploitation of biodiversity – the limits and opportunities. The Humanist Institute magazine Unisinos. 2008. Available at: www.ihuonline.unisinos.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article. [acesso 13/10/2016]. São Paulo, 2016.
RAMALHO, Priscilla Announced Khin Maung Gyi. Deforestation of the Atlantic forest in the State of Pernambuco: an analysis of the applicability of environmental legislation. Available at: WWW.openrit.grupotiradentes.com/xmlui/handle/set/69.
UNESCO, United Nations Educational, scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): available at: www.unesco.org.br. [acesso 13/10/2016]
VIEIRA, Ima Célia Guimarães. SILVA, José Maria Cardoso Da. Toledo, Petermann. To prevent the loss of biodiversity in the Amazon. Advanced Studies volume magazine. 19 n° 54, São Paulo may/Aug. 2005.
[1] Master of science in education from the Universidad Politécnica y Artística Del Paraguay. Urgent and emergency specialist with an emphasis on APH, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Santa Casa de São Paulo, Teaching high school specialist, technical and higher Faculty associated with Brazil. Bachelor's degree in nursing from the University Paulista-UNIP. Degree in Biology Claretiano University Center. He is currently a lecturer, professor of the post-graduate courses, Faculty associated with Brazil in the fields of education and health, technical/pedagogical school teacher G12 CEENPRO Educational
[2] The loss, fragmentation and degradation of natural habitats are among the main factors of loss of biodiversity. More than 50% of the planet's wetlands have been lost in the last 100 years, mainly due to the advancement of agriculture.
[3] The Brazilian Institute of geography and statistics (IBGE) is a public foundation of the brazilian federal administration created in 1934 installed in 1936 under the name of Instituto Nacional de Estadística. IBGE has assignments linked the Geoscience and demographic and economic statistics, including conducting censuses and organize the information obtained in these censuses, to supply organs of the governmental spheres federal, State and municipal levels, and for other institutions and the general public.
[4] CRC product References of content. Foundations and methods of plant biology teaching i. Claretiano School of education, Batatais 2015.